Chapter 12. Chapter 12: Plant and Fungi Diversification
Review & Rehearse
Review & Rehearse
true
true
You must read each slide, and complete any questions on the slide, in sequence.

Instructions
Review the visual summaries and answer the essay questions below.
Make sure to enter a brief response that completely answers each question and explains your reasoning. When you click "Submit," you will be provided instant feedback, allowing you to check if your response is correct.
(This activity contains 16 total essay questions. Each new question will be revealed once you complete the preceding question.)
Question 12.1


Sexual reproduction: Getting sperm to eggs for fertilization can be a challenge for many plants living on land, especially if the plants are large or live in dry locations. Resisting predators: As a result of their inability to move, plants cannot run or otherwise escape from predators, and they have had to develop other means of defense, including thorns and poisonous chemicals.
Question 12.2
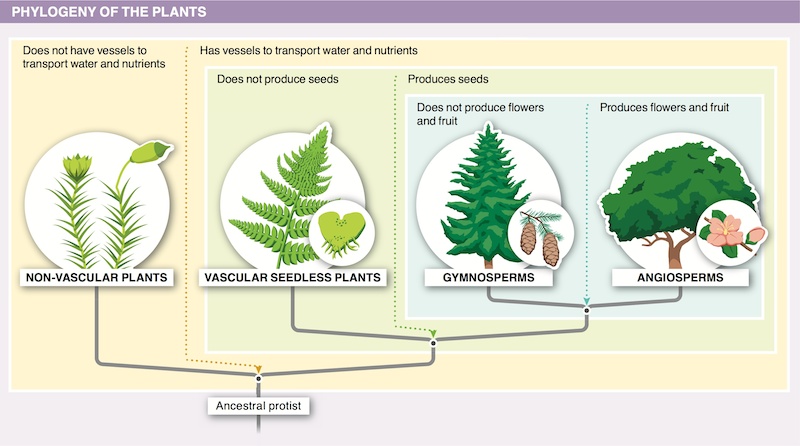


The earliest plants grew close to the ground to minimize the effects of gravity on the plant body—a major adaptation necessary for life on land. Buoyancy provided by water enables aquatic organisms to resist gravity; in organisms living on land, including the plants, traits to resist gravity had to evolve.
Question 12.3
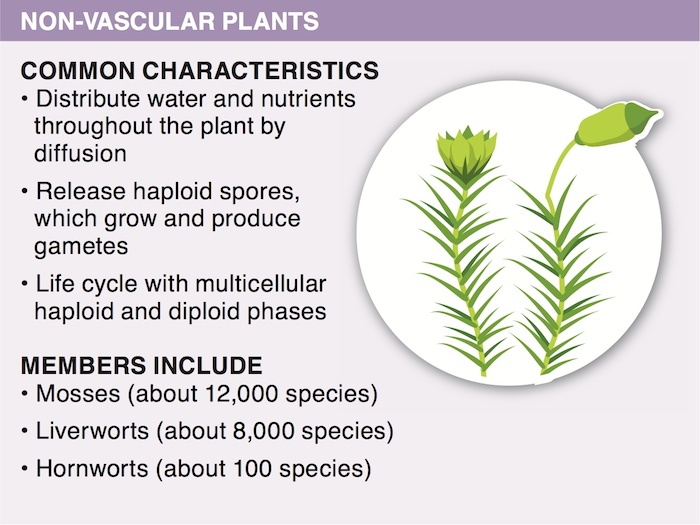
Mosses produce motile sperm with flagella, which require water so they can swim to the eggs and fertilize them. Since mosses grow low to the ground, areas they inhabit become temporarily flooded as rain falls or snow melts, providing the needed environment for sperm to reach eggs.
Question 12.4
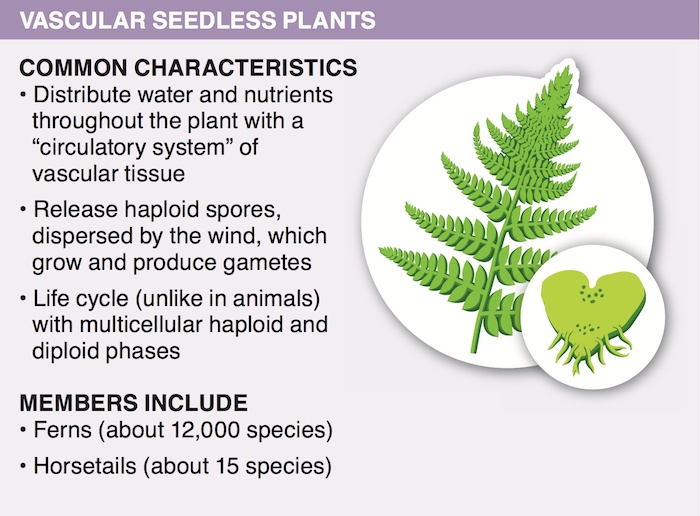
Non-vascular plants do not have vascular tissue, which limits their height to only a few centimeters; their gametophyte is the dominant generation. Vascular plants have vascular tissue that transports water and nutrients over great distances within the plant body, enabling them to grow very tall; the sporophyte is the dominant generation. Vascular plants are more successful in areas where the surface of the ground dries out between rains. Non-vascular plants and mosses can grow in deserts.
Question 12.5

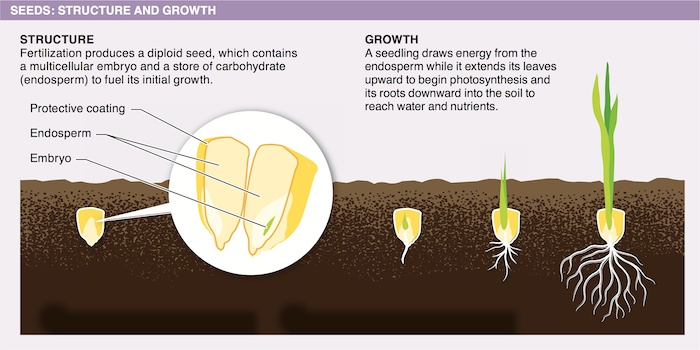
The growing embryo and young seedling derive nutrients from the endosperm, a specialized nutritive tissue contained in the seed. The endosperm provides the nutrients and energy required for the embryo to grow before the seedling establishes roots and leaves and the ability to photosynthesize.
Question 12.6
nTr4TeUU0QefLoNCk5J1cciMtGV4KOFoUjo4qccsoI+fkCa2QNN4uIxV5kpxU7uqHE9vVF/N8Cd3GMn3/+W/yL6U2H+bjPtC11UxiZ2B+1ZOJax1WQK1nObMrwA=Seeds contain nutrients and an embryonic plant within the protective seed coat. Spores contain only a cell with DNA, RNA, and a small amount of nutrients. For seed plants, growing from an embryo provides a head start and can improve chances for success.
Question 12.7

There are more species of conifers, which number about 600, than any other group of gymnosperms, and they inhabit more regions of the world, including every continent except Antarctica. They grow larger and live longer than other gymnosperms.
Question 12.8

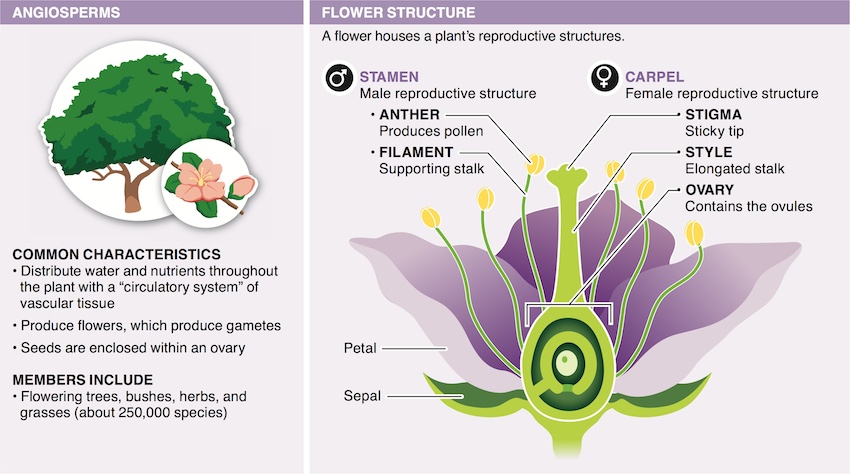

A flower contains: (a) petals, the colorful part of the flower; (b) sepals, which form the structure that covers the flower while in bud; (c) male reproductive structures: stamens, with the anther, which produces pollen and is supported by the stalk; and (d) female reproductive structures: the carpel, which encloses the ovary, where eggs develop, and the style, which extends from the ovary and has a sticky tip, called the stigma.
Question 12.9
uKzwfqY9ayavyv01/rul5KrvuYhdVm9F/ftzcdwq/nD5opQs22UO1YZMFoHoNvAtB2ISu8MrB9y4rwmqKppVdpNCoTd1U8Yro7MwCvdW7txVztdiJiyRMYhIhLU=Plants and animals have evolved together, depending on each other for survival. If animals became extinct, there would be no bees or other pollinators, and many plant species would no longer be able to reproduce. And for many plants, there would be no way for seeds to be dispersed away from the parent plant. Altogether, this would result in many plant species becoming less common, if not extinct. Plants that do not depend on animals for pollination and seed distribution would dominate.
Question 12.10
FO8FU1GKXWynpBUupHx7ApJYmT9dmoCFIgYnAG/Hp7bJ6A01bFfLOeX1FdTeOqvdQ6hU/bnLg9SwyBHbhbmcJZb9eSSbCrvGXFbvgFOA17HnfLBxTtPQo5XrjMLN3Q20pijTJiUq9Cm5zDH+YKSjRiVP9FTzNGgCA pollen grain lands on the stigma, a pollen tube grows down the style into the ovary, and two sperm travel down the pollen tube. One sperm fertilizes the egg to form a zygote, and the other fuses with the two central nuclei in the embryo sac to form endosperm. The endosperm grows into a food source for the developing embryo after germination. Thus, double fertilization forms not only a zygote but also a significant food source. Gymnosperms do not produce endosperm, so angiosperms have the advantage when it comes to nourishing the embryo.
Question 12.11


The fleshy fruit provides a bribe to entice an animal into eating the fruit and transporting the fruit along with its seeds to another location, away from the parent plant. After the seeds have passed through the digestive system, they are deposited with some nutrient-rich manure to help nourish the seedling.
Question 12.12

There are two categories of plant defenses: anatomical structures and chemical compounds. Plant structures that provide protection include thorns on rose bushes, spines on acacia trees and palm fronds, and the microscopic hairs of the stinging nettle, which cause pain when bare skin rubs against them.
Question 12.13

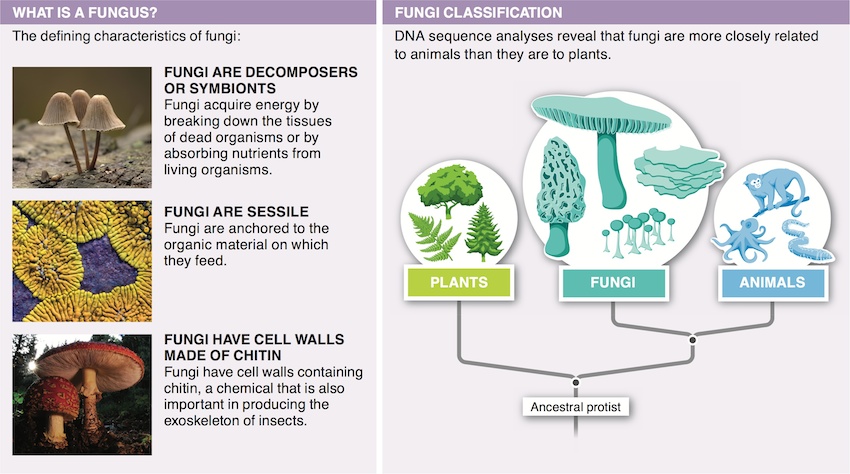
Unlike other eukarya, fungi have cell walls containing chitin and are decomposers, digesting food externally prior to absorption of nutrients.
Question 12.14
Y0N0Zdb0vqybUmXi5Smki4PFXpDS+3XkKBI/SF2PynPZI/j6XXqiX/+iqBn5BlsLTBJsKSDS+l3S0uzIYc6oMJ61qys=Answers could include: (a) fungi are a source of antibiotics, (b) they are a food source, and (c) they make possible the production of alcoholic beverages and bread.
Question 12.15
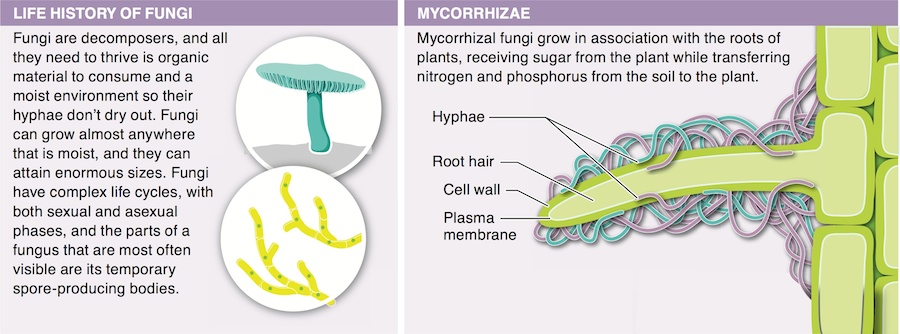
Fungi are associated with the roots of many plants, forming mycorrhizae, in which fungal hyphae wrap around the plant’s root hairs. The plant benefits by getting minerals such as phosphorus and nitrogen from the fungus. The fungus benefit by getting small amounts of sugar from the plant.
Question 12.16
2z+q6Jp21aCe6BdP8IbdHEiNU4gC2iizMFgqCCygg6GEypkBnZ+f+yNr37O9fmDtksj/bZI61AAl+1NfGpTQtUk4toWFcI/vhdvMRvGCJuhxx526hALGBHQEkZ0=Because fungi are not capable of photosynthesis, they depend on outside food sources for nutrients. An association with plant roots enables them to obtain food easily (without having to externally digest and absorb food), since the plant supplies them with sugar.
Activity results are being submitted...