Chapter 7. Chapter 7 Graphic Content
Introduction
Graphic Content
true
true
You must read each slide, and complete the question on the slide, before proceeding to the next one.

Instructions
Review the information provided in the graph to answer each question below.
After submitting your answer, you will be provided feedback to check if your response is correct.
(This activity contains 6 questions.)
Question 7.1
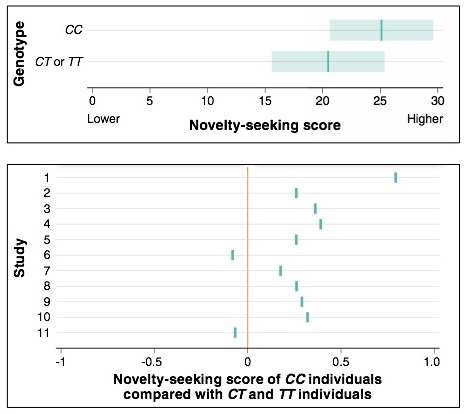
A novelty-seeking score was measured for individuals with different genotypes. Measurement was based on the individuals’ responses on a questionnaire. While this might be a fast and easy way to estimate one person’s propensity for novelty-seeking relative to another person’s propensity, it would have been better to observe individuals’ actual behavior. If you are interested in behavior, it is always better to see how someone behaves than to ask them how they think they would behave.
Question 7.2

CC refers to the genotype for the promoter polymorphism--521C/T, which alters the transcription rate of the dopamine receptor gene. The gene influences the activity of the brain's pleasure centers. There are two different alleles, C and T, and a person can have one of each or two copies of C or two copies of T. Having one or two copies of the T allele (that is, CT or TT) seems to lead to reduced transcription of the dopamine receptor gene, while having the CC genotype is associated with greater gene activity and, hence, greater novelty-seeking behavior.
Question 7.3

The data reported for the initial study provide information on how much individuals with genotypes in the two groups (first group: CC, second group: CT or TT) varied in their score on the novelty-seeking questionnaire (since everyone would not be expected to score exactly the same). This information is useful because it helps us see that not only was the average novelty-seeking score higher among those with the CC genotype, but those with the lowest novelty-seeking scores in the CC genotypes group had higher scores that those with the highest novelty-seeking scores in the CT/TT group. The smaller the variation observed in each group, the more likely it is that differences between the two groups reflect true differences in the measure between the groups.
Question 7.4

A meta-study combines the results of several or many studies that address a related research hypothesis. This is commonly done because the results from a group of studies can allow more accurate data analysis, whereas a single study doesn’t necessarily have enough power to reveal a true effect.
Question 7.5

The 11 different studies did not include exactly the same subjects. In fact, they may have used groups of subjects that differed in signifcant ways, such as age, sex, profession, or ancestry. They may also have measured different numbers of subjects, or they may have used slighly different versions of novelty-seeking questionnaires.
Question 7.6

The results of any one study showing that individuals with the CC genotype score higher on a novelty-seeking questionnaire than individuals with the CT or TT genotype might be interesting, but unconvincing. Questions might remain about the population from which the subjects were chosen, the number of subjects used, the laboratory methods used in determining genotypes, the conditions under which the questionnaire was administered, and a whole range of unconscious, inadvertent, or otherwise hidden biases that the researchers may have had. But it is powerful when the results of all 11 studies that tested this hypothesis are reported and most of the studies seem to show similar results. This means that you can be more certain about the conclusions drawn in any one of the studies. It's important that all of the studies conducted on this hypothesis were collected and analyzed, rather than the meta-study simply selecting studies that supported or rejected the hypothesis. We can have more confidence in concluding that an individual's genotype for this gene influences novelty-seeking behavior. (In fact, though, without information about how well a peron's score on this questionnaire predicts actual behavior, it might be safer to simply conclude that individual's genotype influences his or her score on a novelty-seeking questionnaire. This conclusion gives rise to numerous new hypotheses that could be tested.)
Activity results are being submitted...