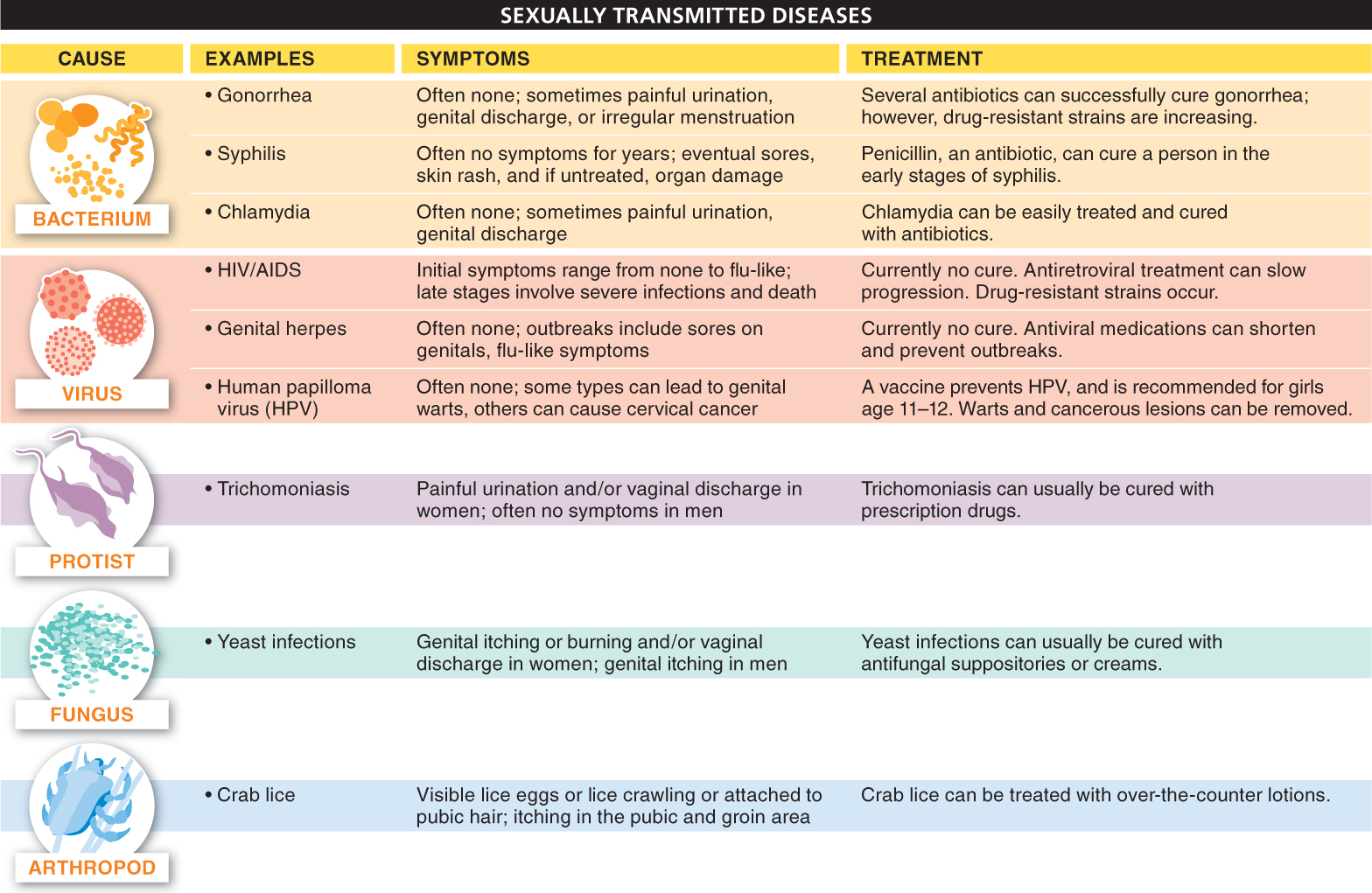
To many microbes, the human genitals and reproductive tract are desirable places to find shelter, nourishment, and opportunities for reproducing and dispersing. Unfortunately, these microbes can cause problems for humans in the form of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). STDs produce symptoms of varying severity, from mild to extreme discomfort, to sterility, or even death. It is estimated that more than 300 million new cases of STDs occur each year worldwide.
STDs are caused by all types of microbes—
547
Although most STDs are curable with drugs, two characteristics of STDs make them nearly impossible to completely eradicate from a population: (1) their symptoms may be mild or absent, causing many people to unwittingly pass an infection to their partners, and (2) to prevent reinfection, both partners must be treated simultaneously. Furthermore, because most microbes have such high reproductive rates, populations of a microbe can evolve quickly and become resistant to existing drugs. The treatment of STDs is one of the most pressing public health issues in the world today.
TAKE-HOME MESSAGE 13.9
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are caused by a variety of organisms, including bacteria, viruses, protists, fungi, and arthropods. Worldwide, more than 300 million people are newly infected each year.
Why is it nearly impossible to eradicate STDs from the population?
The symptoms of STDs may be mild or completely absent at times, causing many people to unwittingly pass infections along. Also, to prevent reinfection, both partners must be treated simultaneously. Microbes have high reproductive rates and, due to rapid evolution, can become resistant to existing drugs.
548