19.8–19.10
19.8–External cues trigger internal responses.
788
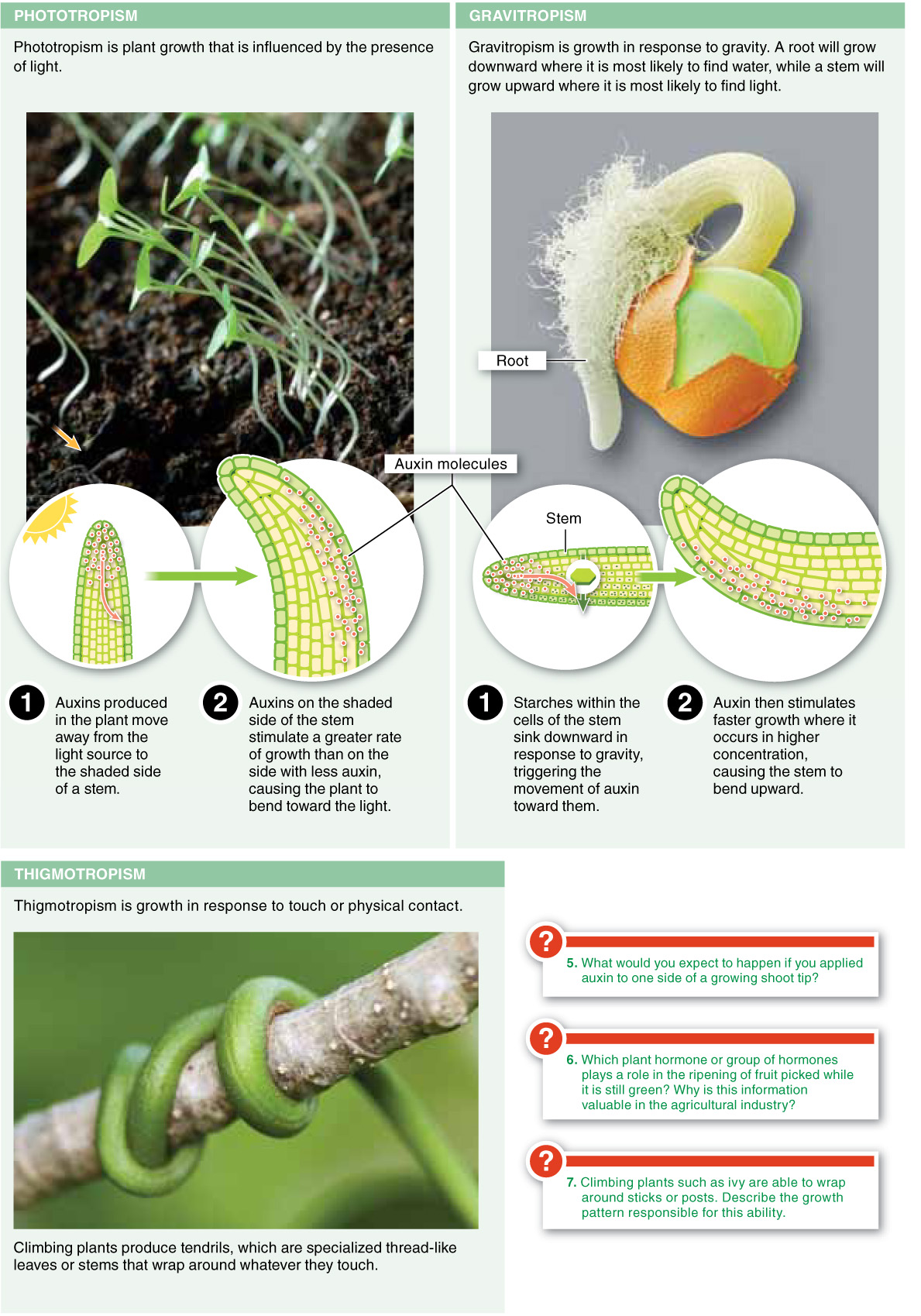
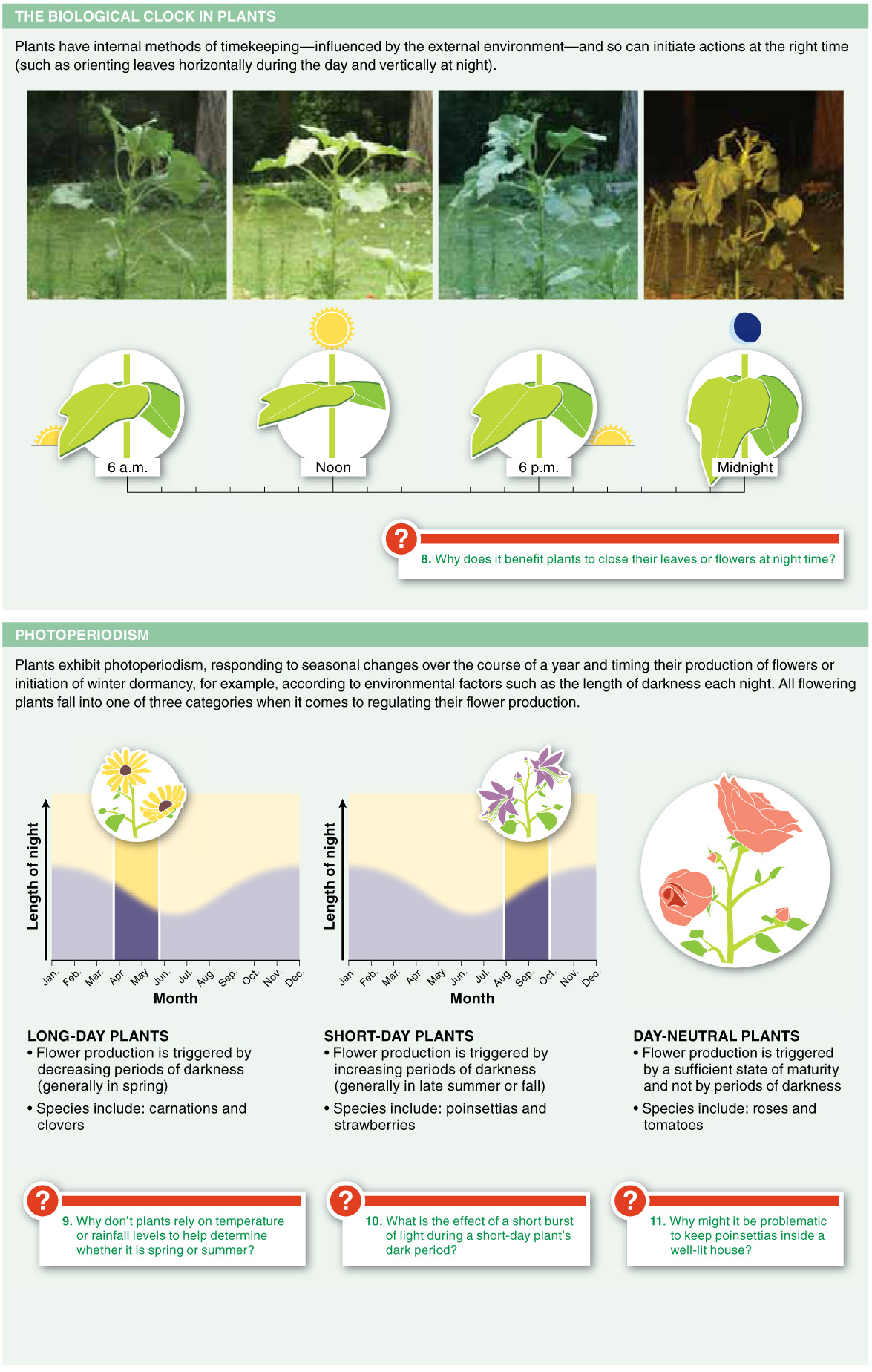
Plants have a variety of growth patterns known as tropisms by which they grow toward or away from various environmental stimuli.
Q
Which hormone or group of hormones stimulates the ripening of fruit?
- a) auxins
- b) ethylene
- c) cytokinins
- d) gibberellins
- e) abscisic acid

Which plant hormone or group of hormones is responsible for bud and seed dormancy?
- a) auxins
- b) ethylene
- c) cytokinins
- d) gibberellins
- e) abscisic acid

Which hormone or group of hormones is primarily synthesized in the roots and travels to other regions of the plant?
- a) cytokinins
- b) gibberellins
- c) 2,4-
D - d) auxins
- e) cytochromes

Which of the following reverses the inhibitory effects of auxin on lateral buds?
- a) abscisic acid
- b) cambium
- c) ethylene
- d) gibberellin
- e) cytokinin

789
Q
Phototropism in plants is:
- a) a process that produces glucose.
- b) caused by ethylene.
- c) mediated by cytokinins.
- d) the bending of roots away from the light.
- e) the bending of the shoot tip toward a light source.

Which hormone or group of hormones is involved in phototropism?
- a) ethylene
- b) gibberellins
- c) cytokinins
- d) auxins
- e) abscisic acid

What is the effect of a short burst of light during a short-
- a) The plant will not flower if the burst of light makes the longest period of continuous darkness shorter than the critical dark period.
- b) The plant will flower, because the length of day remains unchanged.
- c) The plant’s flowering does not depend on light, so the burst of light will have no effect.
- d) The plant will not flower, because the burst of light restarts its biological clock.
- e) The plant will flower perpetually, because the burst of light makes the longest period of continuous darkness shorter than the critical dark period.
