
Nature versus nurture. The complex interactions between nature and nurture that influence phenotypes are just as important to plants as they are to animals. Consider a simple experiment with the arrowleaf plant (Sagittaria sagittifolia) as an example. First, from a single plant, take three cuttings. These are sections of the plant containing a part of the stem that includes a meristem. Cuttings can be used to produce a new plant, genetically identical to the original. Plant each cutting in a different habitat: one in deep water, the second in shallow water, and the third on land.
771
Each new plant has the exact same set of genes; they are like identical triplets. But in the deep water, the plant will grow long, ribbon-
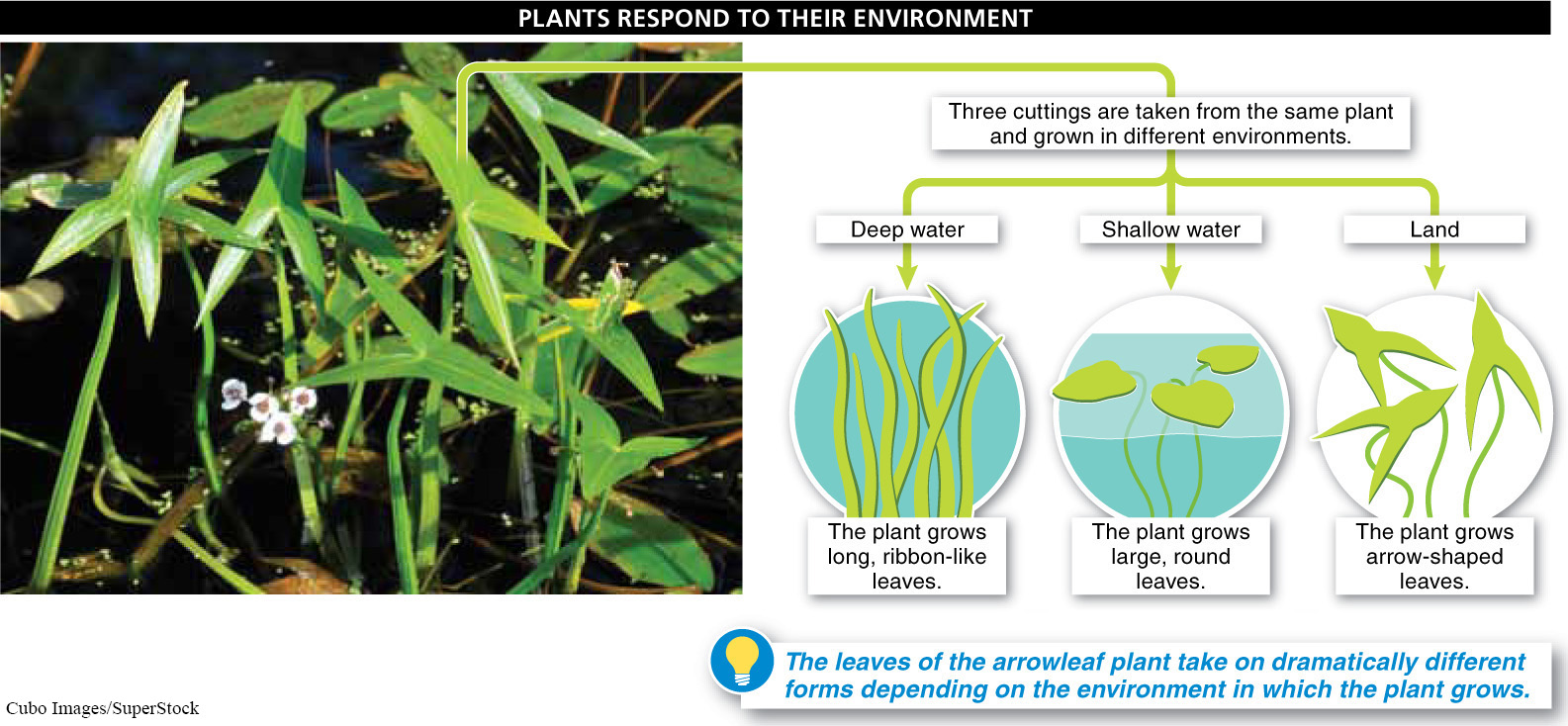
The arrowleaf plant is not “hard-
Plant hormones are chemical signals that enable plants to respond quickly and appropriately to changing environmental variables (such as amount of moisture, amount and direction of sunlight, and temperature). These chemicals convey information about the physiological state of the plant’s tissues or the environment in which the plant finds itself and then regulate some aspect of the metabolism of the plant’s cells. Sometimes, a hormone may stimulate a certain response—
The hormones in humans and other animals are generally produced in specific glands or tissues and then transported (commonly in the bloodstream) to different locations to exert their influence. In contrast, many plant hormones are produced in numerous places throughout the plant body and may have their effects in those same places or may be transported to another part of the plant before taking effect. As we will see, the effects of plant hormones are usually predictable and easily observed.
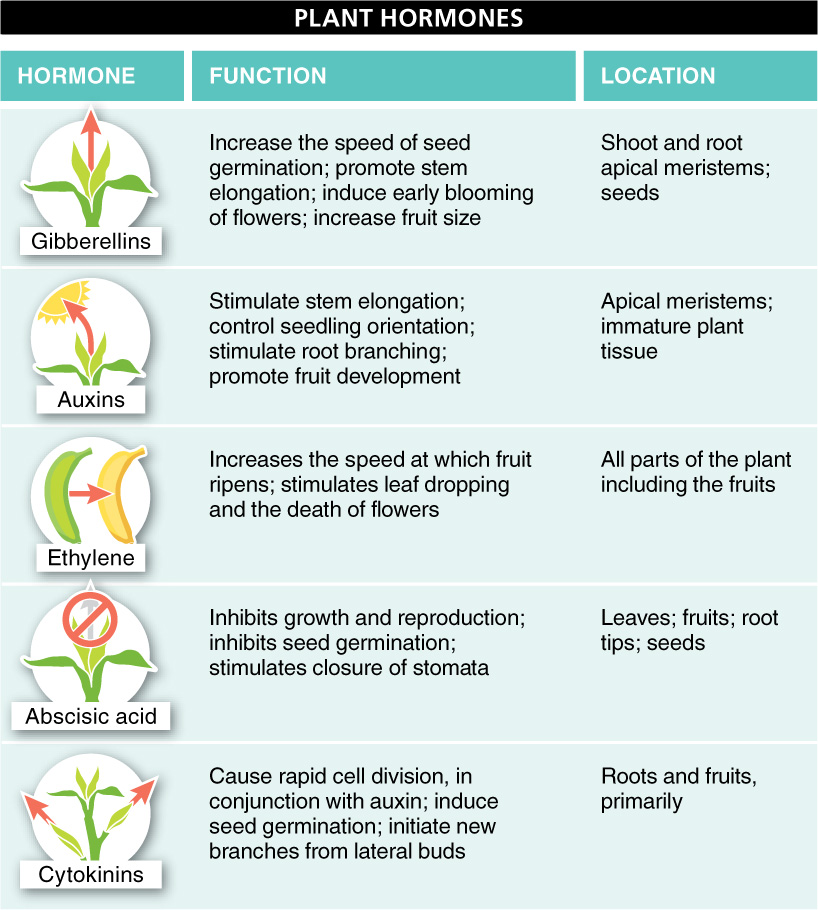
There are many plant hormones, many of which fall into one of five major groups: gibberellins, auxins, ethylene, abscisic acid, and cytokinins. FIGURE 19-9 provides a brief summary of the functions of these hormones. We explore them in greater detail in the next three sections.
TAKE-HOME MESSAGE 19.4
Plant hormones are chemical signals produced by plant cells that enable the plant to respond to environmental variables (such as amount of moisture, amount and direction of sunlight, and temperature) and that influence its growth and development.
What are plant hormones, and what are the five major types of plant hormones?
Hormones are chemical signals produced within a plant that influence the growth and development of the plant. The five major types of plant hormones are gibberellins, auxins, ethylene, abscisic acid, and cytokinins.