20.1–20.6
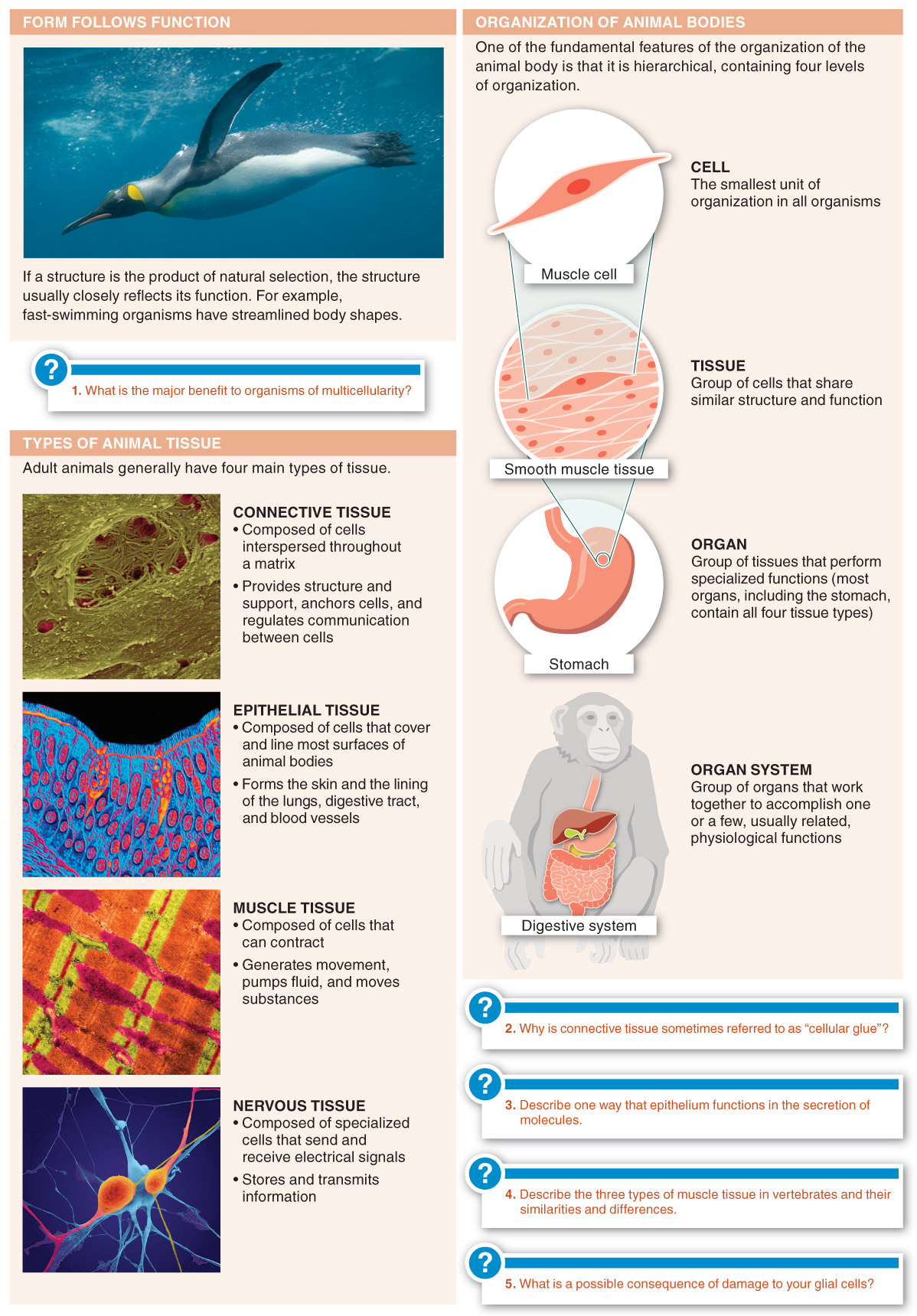
20.1–Animal body structures reflect their functions.
At all levels of animal organization, from molecules to whole organisms, the physical features of a structure are closely related to its function.
823

Q
Which of the following is not one of the major categories of vertebrate muscle cells?
- a) smooth muscle
- b) cardiac muscle
- c) respiratory muscle
- d) skeletal muscle
- e) All of the above are major categories of vertebrate muscle cells.

Neurons generally have all of the following components except:
- a) dendrites.
- b) a cell body.
- c) an axon.
- d) glial processes.
- e) a nucleus.

With the exception of _______, all animals have some tissues organized into organs.
- a) sponges and some cnidarians
- b) insects
- c) roundworms and flatworms
- d) sponges and insects
- e) amphibians

Which of the following explains why complex multicellular organisms face a major challenge in maintaining homeostasis?
- a) Most of the body cells are not in direct contact with the external environment.
- b) Most of the body cells are protected from harsh or changing environmental conditions.
- c) There is less extracellular fluid from which to gather nutrients.
- d) There are more chemical reactions per cell that require energy and nutrients.
- e) Nutrients and waste materials enter or leave the cells too quickly.

824