21
Circulation and Respiration
TRANSPORTING FUEL, RAW MATERIALS, AND GASES INTO, OUT OF, AND AROUND THE BODY
826
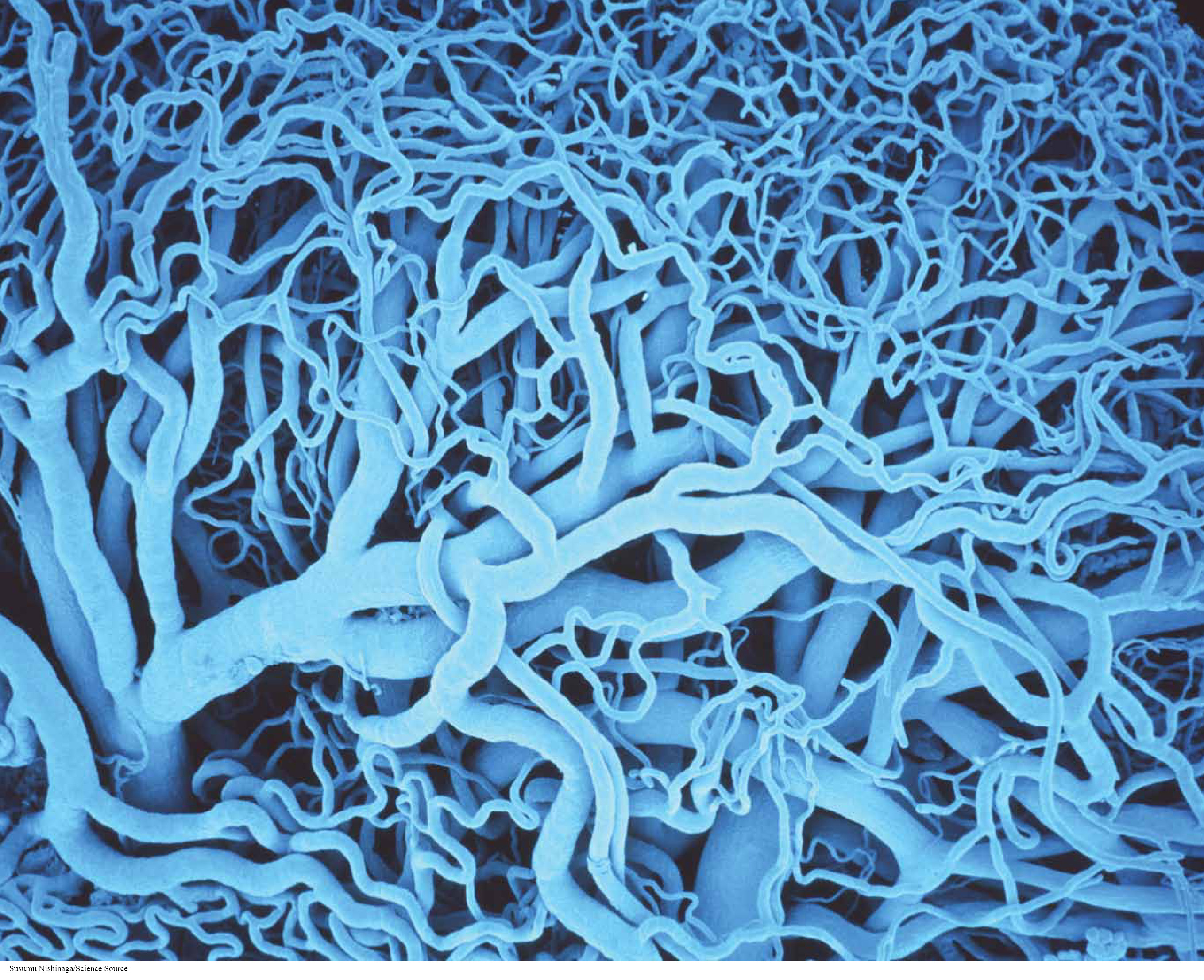
827
The circulatory system is the chief route of distribution in animals.
- 21.1 What is a circulatory system, and why is one needed?
- 21.2 Circulatory systems can be open or closed.
- 21.3 Vertebrates have several different types of closed circulatory systems.
The human circulatory system consists of a heart, blood vessels, and blood.
- 21.4 Blood flows through the four chambers of the human heart.
- 21.5 Electrical activity in the heart generates the heartbeat.
- 21.6 Blood flows out of and back to the heart in blood vessels.
- 21.7 This is how we do it: Does thinking make your head heavier?
- 21.8 Blood is a mixture of cells and fluid.
- 21.9 Blood pressure is a key measure of heart health.
- 21.10 Cardiovascular disease is a leading cause of death in the United States.
- 21.11 The lymphatic system plays a supporting role in circulation.
The respiratory system enables gas exchange in animals.
- 21.12 Oxygen and carbon dioxide must get into and out of the circulatory system.
- 21.13 Oxygen is transported while bound to hemoglobin.
- 21.14 Gas exchange takes place in the gills of aquatic vertebrates.
- 21.15 Respiratory systems of terrestrial vertebrates move oxygen-
rich air into and carbon- dioxide- rich air out of the lungs. - 21.16 Birds have unusually efficient respiratory systems.
- 21.17 Muscles control the flow of air into and out of the lungs.
Evolutionary adaptations maximize oxygen delivery.
- 21.18 Animals living at high elevations have special adaptations to the low-
oxygen conditions. - 21.19 Humans become acclimated to low-
oxygen conditions.
828