21.1–21.3
21.1–The circulatory system is the chief route of distribution in animals.
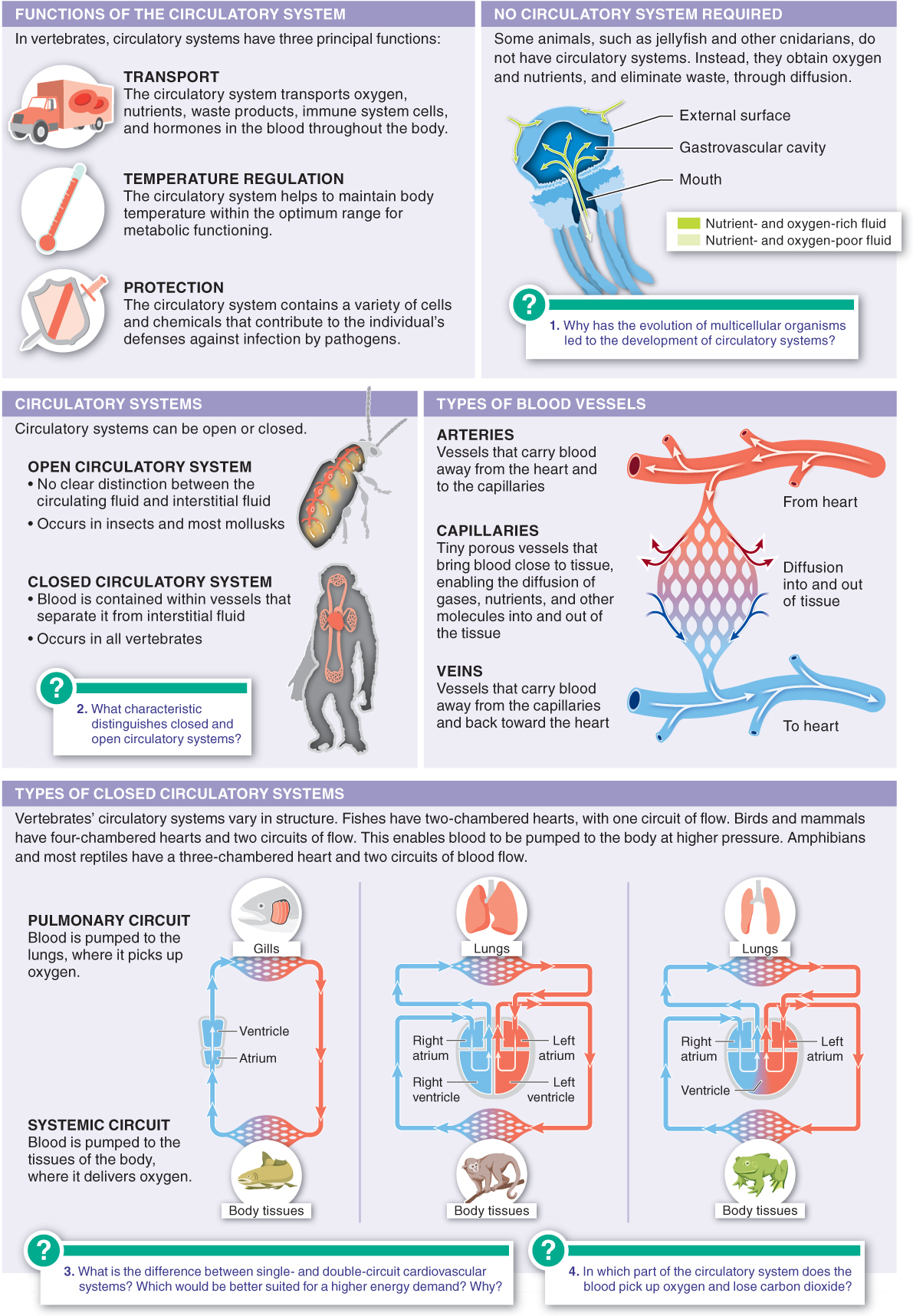
The circulatory system transports gases, nutrients, waste products, immune system cells, and hormones. It also helps animals maintain homeostasis.
869
Q
The heartbeat in a vertebrate:
- a) is initiated by modified muscle tissue, the sinoatrial (SA) node, that contracts without nerve stimulation.
- b) is triggered by rhythmic stimulation from the cardiac nerve.
- c) begins at the bottom of the ventricles and moves upward through the heart.
- d) cannot be recorded by an EKG, but the neurons that control it can be.
- e) is initiated by the atrioventricular (AV) node.

Both red blood cells and white blood cells are derived from cells in the:
- a) heart.
- b) liver.
- c) spleen.
- d) lungs.
- e) bone marrow.

In a person at rest, most of his or her blood is likely to be in the:
- a) heart.
- b) capillaries.
- c) veins.
- d) arteries.
- e) interstitial fluid.

Which of the following components of human blood is a cell fragment?
- a) spiracle
- b) red blood cell
- c) white blood cell
- d) plasma
- e) platelet

How are the blood-
- a) Blood carries nutrients to cells. The lymphatic system removes waste from cells.
- b) Blood carries nutrients and oxygen to cells and removes their waste. The lymphatic system removes bacteria and debris from the blood.
- c) Blood carries nutrients and oxygen to cells and removes their waste. The lymphatic system takes the cellular waste to the kidneys.
- d) Blood carries oxygen to the cells. The lymphatic system removes carbon dioxide from the blood and carries it to the lungs.
- e) Blood carries carbon dioxide from tissues to the lungs. The lymphatic system carries oxygen from the lungs to the body tissues.
