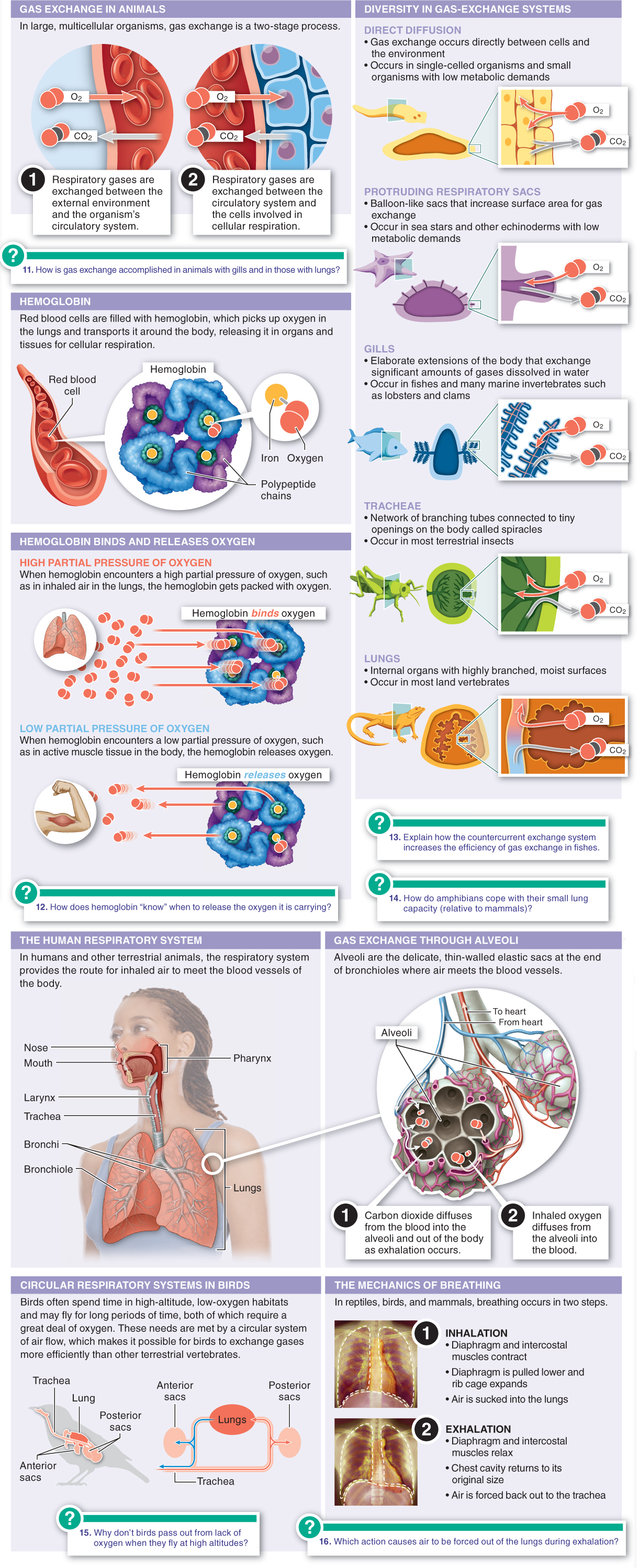
21.12–21.17
21.12–The respiratory system enables gas exchange in animals.
Aerobic respiration requires cells to take up oxygen and release carbon dioxide.
871
Q
Why is carbon monoxide (CO) so dangerous?
- a) CO prevents hemoglobin from binding to and transporting O2 to the body tissues, resulting in oxygen starvation and death.
- b) CO prevents CO2 from dissolving in the blood, and CO2 builds up to toxic levels.
- c) CO modifies the structure of hemoglobin, making it more difficult for O2 to be transported and released in the body.
- d) CO coats the inside of the alveoli, preventing diffusion of O2 from the lungs into the blood.
- e) CO binds to hemolymph, so tissues cannot remove O2 from the red blood cells and the tissue dies.

Which of the following has the highest binding affinity for oxygen?
- a) hemolymph
- b) human hemoglobin
- c) llama hemoglobin
- d) plasma
- e) All have equal binding affinity for oxygen.

Why does llama hemoglobin have a higher oxygen-
- a) Like humans, llama fetuses use a form of hemoglobin with a higher binding affinity than the mother’s hemoglobin, but unlike humans, llamas continue to use this form of hemoglobin after birth.
- b) Because llamas are more active than humans, they require hemoglobin with a greater maximum oxygen saturation.
- c) Llama blood has a higher CO2 concentration than human blood, resulting in a need for hemoglobin with a higher binding affinity.
- d) Llamas live at higher elevations than most humans and require a means to bind O2 when oxygen is at a lower concentration in the air.
- e) Llamas produce hemoglobin molecules that carry six oxygen molecules rather than the four carried by human hemoglobin.

Diphosphoglyceric acid (DPG):
- a) causes the release of more O2 to body tissues.
- b) makes it possible for blood to carry more CO2.
- c) is the main reason that breathing is difficult at high elevations.
- d) increases the binding affinity of adult hemoglobin for O2.
- e) encourages the production of more hemoglobin.
