When it functions properly, the human body can resemble a finely tuned, responsive machine. Nowhere is this more evident than in the processing of food. After you digest and absorb food, there’s an increase in the amount of glucose circulating in your bloodstream. This triggers the release of insulin by your pancreas. Insulin is a storage-
Foods differ in the extent to which they cause a surge in blood sugar and subsequent release of insulin. Foods that cause a rapid and large surge—
Even finely tuned machines can malfunction. More than 10 million Americans (and 100 million people worldwide) have problems with their insulin-
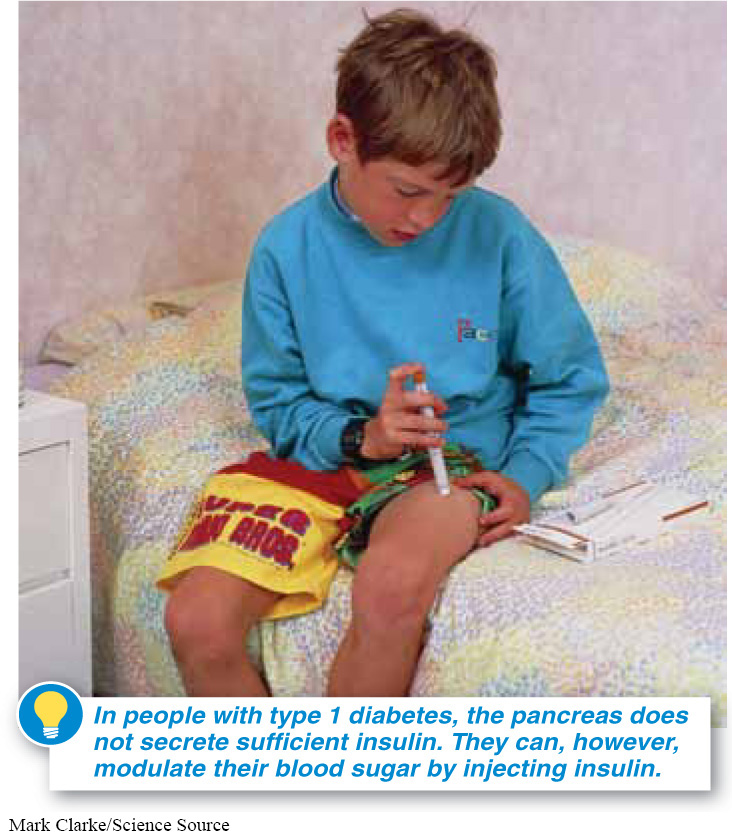
Why must people who have diabetes inject insulin rather than taking it in pill form?
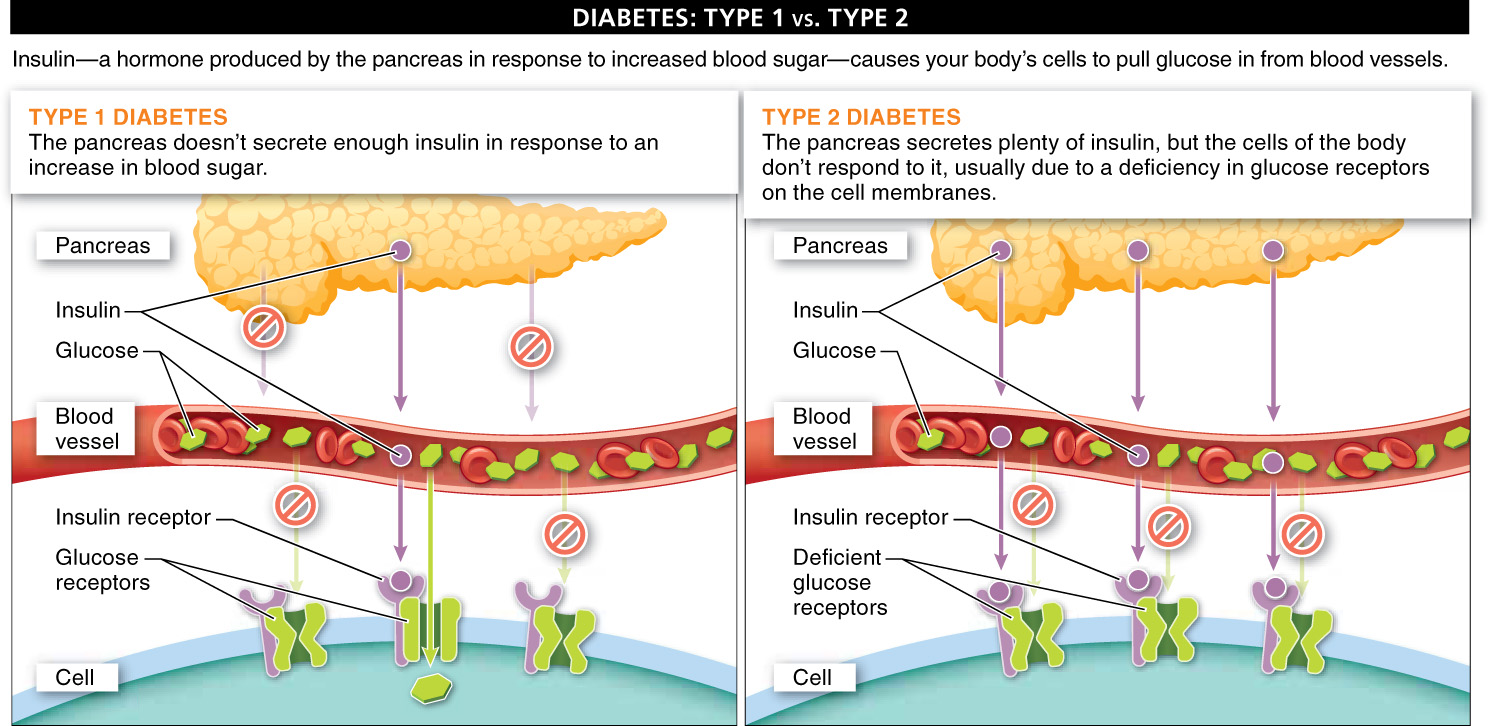
The first type of diabetes (called type 1) is believed to be an autoimmune disease and is most often diagnosed in children or young adults. Generally, people with type 1 diabetes have a pancreas that doesn’t secrete enough insulin, and thus they can be treated by insulin injections (FIGURE 22-37). (Unfortunately, because insulin is a protein, it is digested by stomach acids and the enzymes of the small intestine, so insulin must be injected in order to get it into the bloodstream intact.) The second type of diabetes (type 2) is about 10 times more common. It generally develops after the age of 40, and in about 90% of cases it is a consequence of obesity. It appears that chronic and excessive amounts of sugar in the diet (and, later, in the bloodstream) reduce the sensitivity and/or number of cellular insulin receptors that help control blood sugar. This causes even greater releases of insulin, which can, ultimately, wear out the insulin-
907
Because chronically high levels of blood sugar affect nearly all the cells of the body, the health effects can be far-
TAKE-HOME MESSAGE 22.18
Digesting and absorbing food leads to an increase in the amount of glucose circulating in the bloodstream, which triggers the release of insulin by the pancreas; insulin causes the body’s cells, especially muscle cells and fat cells, to pull the glucose in for energy or storage. Problems with regulation of blood sugar, called diabetes, affect millions of people and are caused by heredity or by poor diet.
How does type 1 diabetes differ from type 2 diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes results from insufficient insulin production or release from the pancreas, whereas type 2 diabetes results from an insufficient response of cells to the insulin released by the pancreas.
908