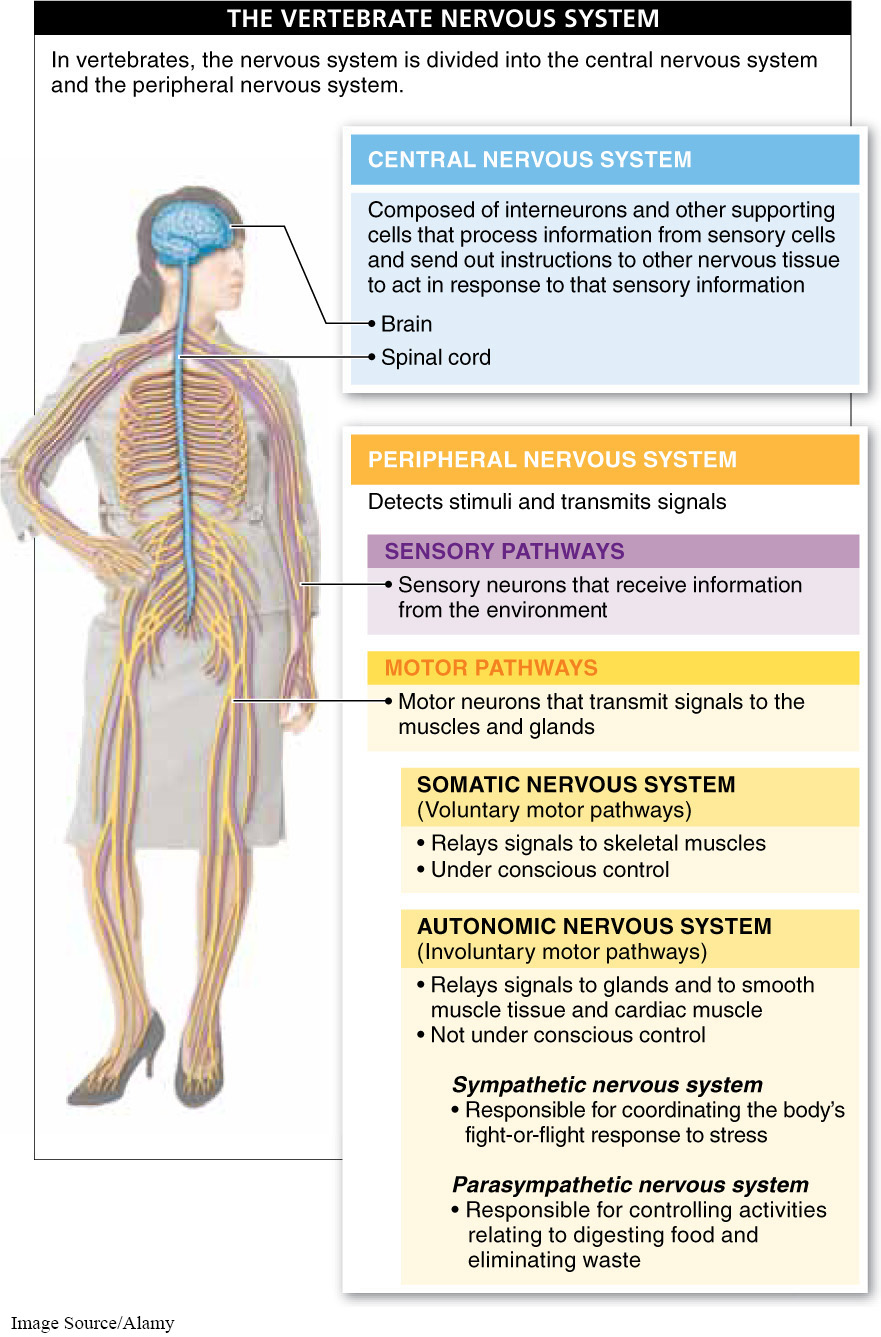
In most animals, including all vertebrates, the nervous system is divided into two components: the peripheral nervous system and the central nervous system (FIGURE 23-5). The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is the network of (1) sensory cells modified to receive information from the environment and (2) motor pathways that transmit signals to effectors, the muscles and glands that are capable of responding to that stimulus. But the information received by the body’s sensory cells does not generally go straight to the cells that control the muscles and glands. First it passes through the central nervous system (CNS), which is made up of the spinal cord and brain. Not directly connected to sensory organs or to muscles, the central nervous system processes information that it receives from sensory cells about the organism’s surroundings and sends out instructions to other nervous tissue to act in response to that sensory information. Later in this chapter, we discuss the elaborate specializations—
922
The motor pathways of the peripheral nervous system have two major divisions: the somatic and the autonomic nervous systems. The somatic nervous system relays signals to your skeletal muscles and enables you to contract those muscles and move your limbs consciously, such as when you pick up a fork. The autonomic nervous system relays signals to your glands and your smooth muscle tissue and cardiac muscle. These signals, which are not under conscious control, cause the muscles surrounding your stomach and intestine, for example, to contract and to move food through the digestive tract. The central nervous system controls both the somatic and the autonomic nervous systems.
Because it enables you to initiate movements consciously, the somatic nervous system is commonly referred to as the voluntary nervous system. When a sensory neuron in the peripheral nervous system—
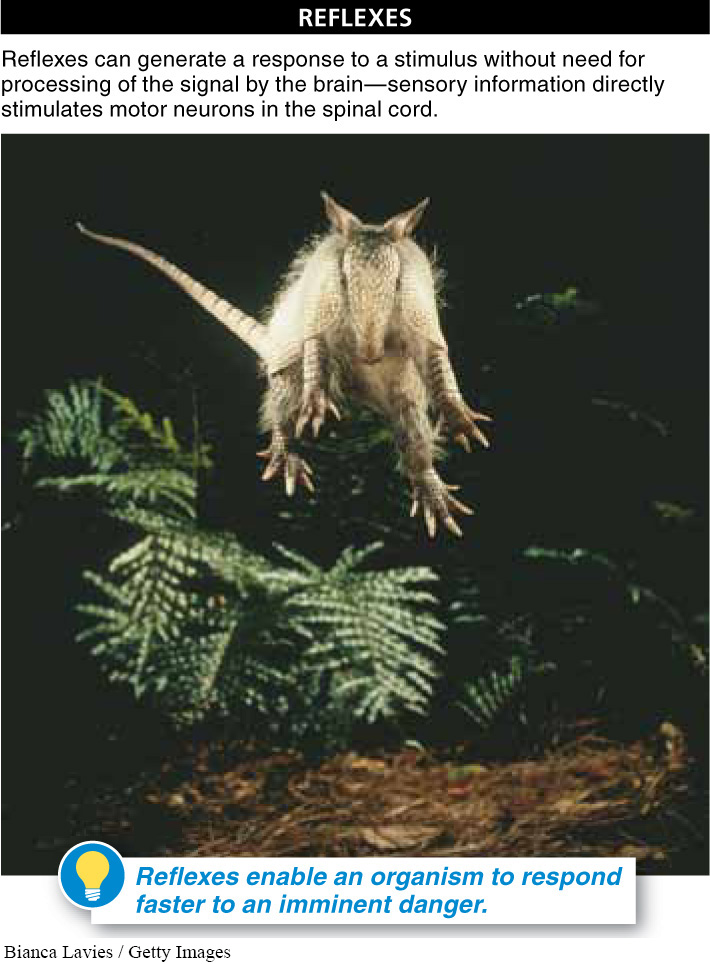
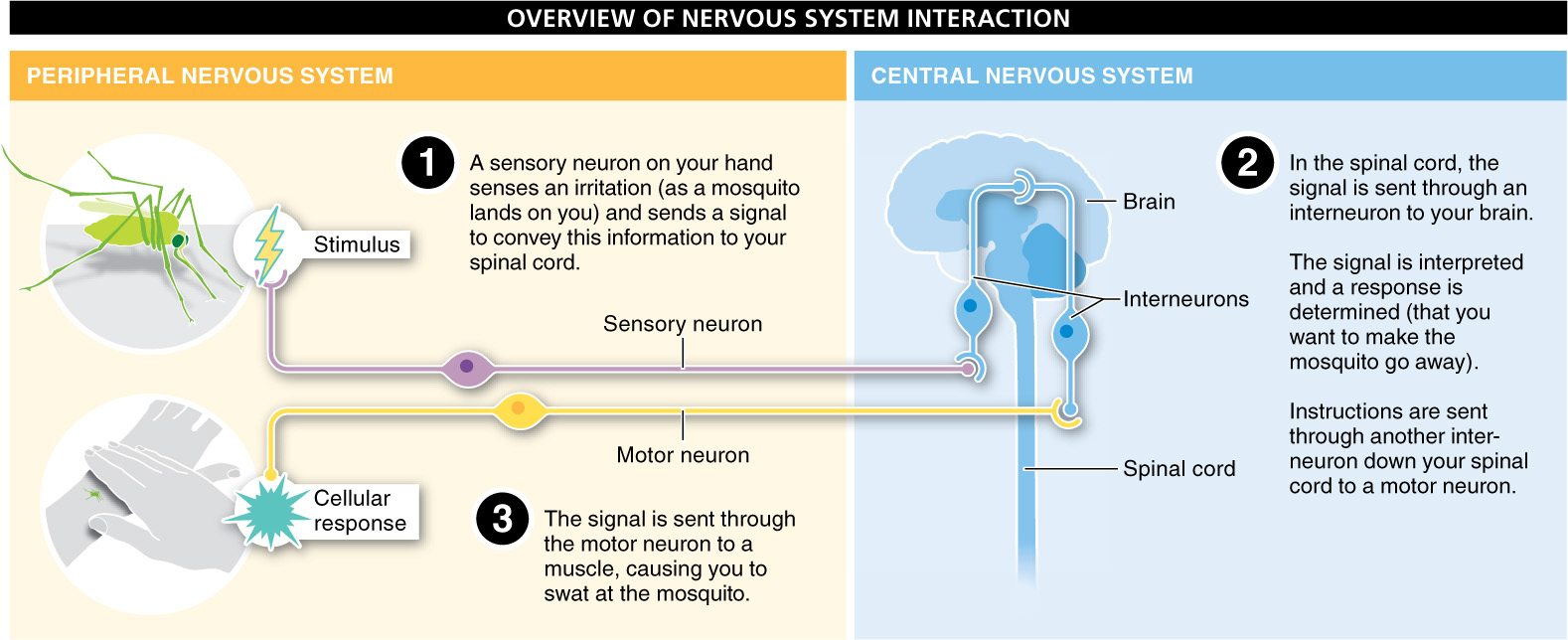

Within the somatic nervous system, some signals can bypass the brain, with sensory information stimulating the motor neuron through the spinal cord. This kind of direct sensory-
In contrast to the somatic nervous system, the autonomic nervous system—
Two components make up the autonomic nervous system: the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system. The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for coordinating the body’s fight-
923
TAKE-HOME MESSAGE 23.3
In all vertebrates, the nervous system is divided into the peripheral nervous system and the central nervous system. The central nervous system is made up of the spinal cord and brain. The peripheral nervous system carries signals to and from the sensory and motor pathways. The motor pathways carry signals from both the somatic and autonomic nervous systems, which relay signals that can be controlled consciously and other signals that cannot be controlled consciously.
While cooking dinner, you accidentally place your hand on a hot burner, but you immediately pull your hand away. What parts of your nervous system were involved in this involuntary reaction?
The peripheral nervous system is the network that receives information (sensory neurons) and transmits signals (motor neurons) to effectors that respond to a stimulus. The somatic nervous system is one of two major divisions of the motor pathways of the peripheral nervous system (the other being the autonomic nervous system). In the somatic nervous system, some signals can generate a special response by traveling directly from a sensory neuron to a motor neuron. This direct sensory-motor response, known as a reflex, does not need to be processed through the brain and enables you to respond faster to imminent danger—in this case, a hot burner on your stove.
924