Pregnancy depends on the occurrence of a great many events, relating to the production of sperm and eggs, fertilization, and implantation of the zygote in the uterus. Contraception, or birth control, is the attempt to prevent pregnancy. Although a wide variety of contraception strategies are used—
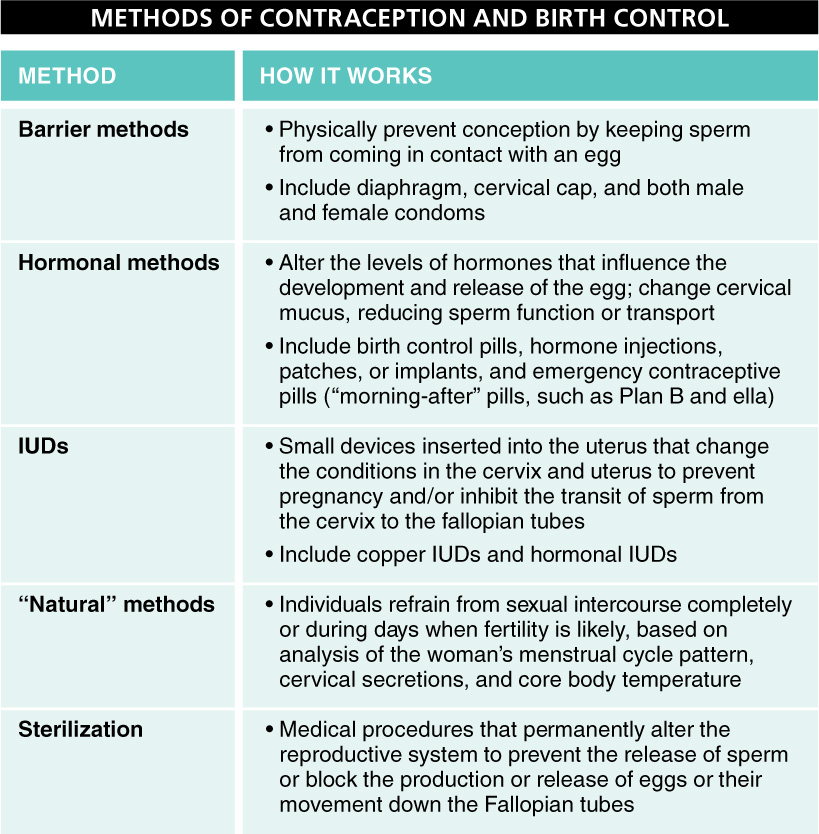
Barrier Methods Barrier methods physically prevent conception by keeping sperm from coming in contact with an egg. They include the diaphragm, cervical cap, and both male and female condoms.
Diaphragm or cervical cap. A diaphragm or cervical cap—
Condoms. The condom—
Hormonal Methods Hormonal methods alter the levels of female hormones that influence the development and release of an egg. They may also change cervical mucus, reducing sperm function or transport. They include birth control pills, hormone injections, patches, or implants, and emergency contraceptive pills (or “morning-
Birth control pills. Available since 1960, “the pill” is among the most effective of all methods of contraception, with a failure rate of 1% to 8%; that is, among 100 women using birth control pills over the course of one year, there would be 1–
1024
How do birth control pills work?
Two chief varieties of birth control pills, or oral contraceptives, are available, one that contains synthetic versions of estrogen and progesterone, and one that contains only a synthetic progesterone. The estrogen-
Taking the pill at the same time every day is essential. If more than 24 hours go by between pills, the estrogen level in the body begins to drop; if it gets below a critical level, FSH release by the pituitary is triggered, which can lead to ovulation and the risk of pregnancy.
The long-
Although the birth control pill is one of the most commonly used contraceptives, recent research has revealed that its hormones may alter women’s attraction to men. When not taking birth control pills, most women prefer the odor of men who have certain genetic combinations that are most different from their own. When taking the pill, however, their preference switches to the odor of men with genetic combinations most similar to their own. Much additional research in this area is under way.
Hormone injections or implants. Injections or capsule implants, just under the skin, of synthetic estrogen and progesterone, or progesterone only, represent a slight variation on birth control pills. The prevention of pregnancy works in the same way, but with the added convenience of not having to take a pill every day. Some implants, in fact, need to be replaced only once every three years. These methods are slightly more effective than birth control pills, because much of the user error is eliminated.
What is the “morning-
Emergency contraceptive pills. Not recommended as a long-
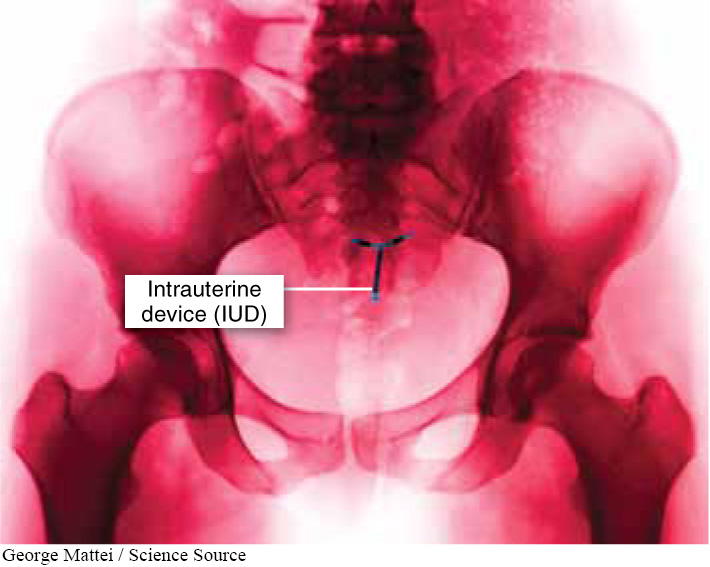
Intrauterine Devices (IUDs) An IUD is a small, T-
1025
“Natural” Methods “Natural” methods of contraception describe those in which individuals refrain from sexual intercourse completely or on days when fertility is likely, based on analysis of the woman’s menstrual cycle pattern, cervical secretions, and core body temperature.
Abstinence—
Sterilization Sterilization is the permanent alteration of the reproductive system to prevent the release of sperm or the movement of eggs down the Fallopian tubes. In a tubal ligation, the woman’s oviducts are cut and tied so that eggs cannot reach the uterus. In a vasectomy, the man’s vas deferens on each side is cut and tied so that sperm cannot reach the urethra, thereby causing the semen to carry no sperm. There are no side effects in either case. Each of these procedures, however, should be considered permanent (although in rare cases, the procedure can be successfully reversed).
In contrast to the contraception methods described above, the drug RU486—
TAKE-HOME MESSAGE 25.10
Pregnancy can be prevented by numerous methods, of five general types: barrier methods, hormonal methods, intrauterine devices (IUDs), “natural” methods, or sterilization.
There are three general strategies used in birth control. One of them is preventing ovulation, which can be accomplished by the introduction of synthetic hormones through birth control pills, injections, or implants. List the other two general strategies, and give at least two examples of each.
Preventing fertilization can be accomplished with condoms, diaphragms, cervical caps, sterilization, or abstinence. Preventing implantation can be accomplished through the use of an intrauterine device (IUD) or the “morning-after” pill.