To many microbes, the human genitals and reproductive tract represent a desirable place to find shelter, nourishment, and opportunities for reproducing and dispersing. Unfortunately, these microbes can cause problems for humans in the form of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). STDs produce symptoms of varying severity, from mild to extreme discomfort to sterility or even death. It is estimated that, worldwide, more than 300 million new cases of STDs occur each year.
Sexually transmitted diseases are caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, protists, and even some arthropods. The organisms are passed from the mucous membranes (of the genitals, as well as of the anus and mouth) of one individual to those of another during sexual contact; sometimes they can also be transmitted by needles used for drug injections.
1026
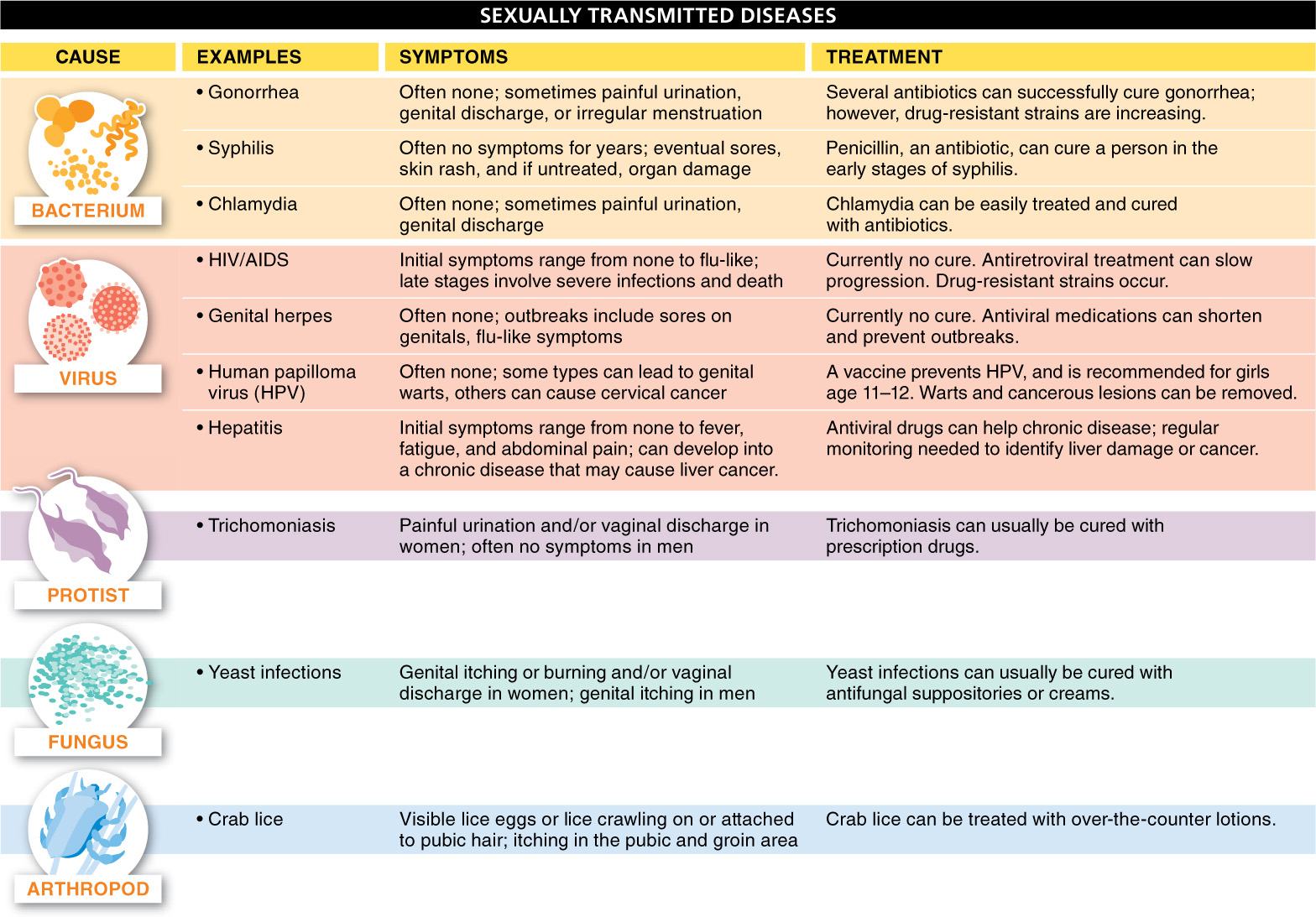
Some of the most common STDs, with their symptoms and treatments, are listed in FIGURE 25-22. Although most are curable with antibiotics, antifungal drugs, or anti-
TAKE-HOME MESSAGE 25.11
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are caused by a variety of organisms, including bacteria, viruses, protists, fungi, and arthropods. Worldwide, more than 300 million people are newly infected each year. The symptoms of STDs range from nonexistent to mild to extreme discomfort, sterility, or even death.
What two characteristics of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) make them nearly impossible to completely eliminate from a population?
Symptoms can be mild or even completely absent, resulting in transmission from individuals who are unaware that they are infected. In addition, treatments often are ineffective when sexual partners are not treated simultaneously. Also, the populations of microbes that cause these diseases can evolve quickly, becoming resistant to existing treatments.
1027