During the first few weeks after fertilization, surprisingly little distinguishes males from females. Then, about four weeks into embryonic development in mammals, a gene carried on the Y chromosome, called SRY (for sex-
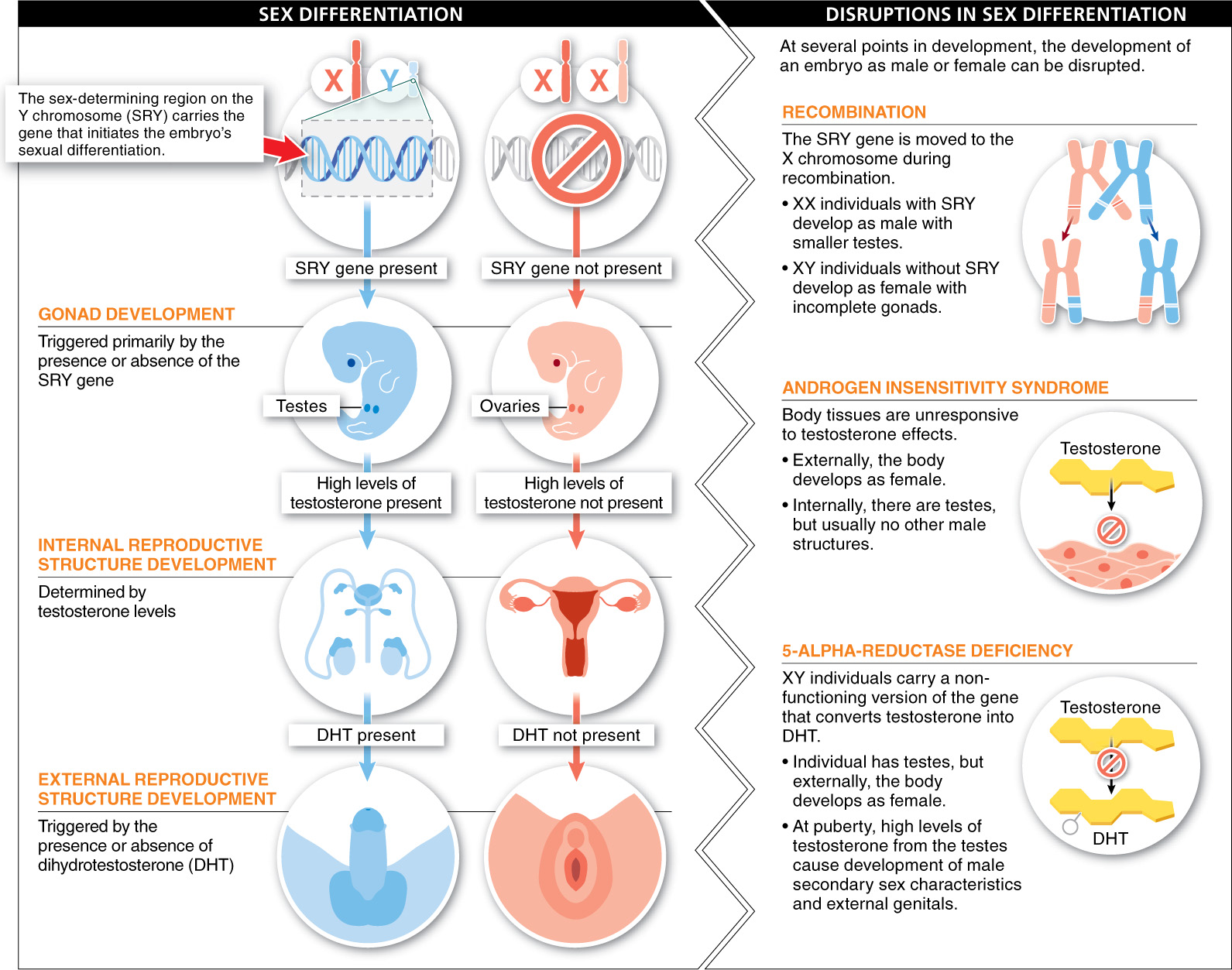
Once the fetal gonads develop, they start producing steroid hormones. If testes, they produce testosterone. If ovaries, they produce estrogen. The presence of high levels of testosterone causes ducts that connect the gonads and the outside of the body to develop into the male internal reproductive organs, including the vas deferens (on each side), ejaculatory duct, and prostate. In the absence of testosterone, adjoining ducts become the female reproductive organs, including the uterus, cervix, and Fallopian tubes.
Following development of the internal reproductive organs, undifferentiated external genitals develop. If testosterone is present and is modified slightly (by an enzyme called 5-
At several points, the development of an embryo as male or female can be disrupted. Disruptions of this type occur in several genetic disorders.
1. Recombination leading to XX individuals with the SRY gene or XY individuals lacking SRY. It is possible, during the production of sperm, for crossing over to occur between the X and Y chromosomes. If this crossover causes the SRY gene to be moved to the X chromosome, and if the sperm cell carrying the X with SRY or the Y without SRY fertilizes an egg, irregular development occurs. In XX individuals with the SRY gene, the individual appears to develop as a male. Although testes develop, they are smaller than average. These individuals are infertile and also tend to be shorter than XY males. In XY individuals without the SRY gene, the gonads develop incompletely. These individuals appear to develop as female. At puberty, however, they are taller than average, do not develop secondary sex characteristics, and do not menstruate.
2. Androgen insensitivity syndrome. Some XY individuals (approximately 1 in 20,000) carry a nonfunctioning copy of the androgen receptor. Although the SRY gene triggers the development of testes, this X-
1031
3. 5-
TAKE-HOME MESSAGE 25.13
Mammalian embryos develop female internal and external reproductive organs unless a gene on the Y chromosome stimulates fetal gonads to develop as testes, leading to testosterone production, which then stimulates the development of male reproductive organs.
What are three ways that development of an embryo as male or female can be disrupted?
Disruptions of this type occur in several genetic disorders: recombination leading to XX individuals with the SRY gene or XY individuals lacking SRY, androgen insensitivity syndrome, and also 5-Alpha-reductase deficiency.
1032