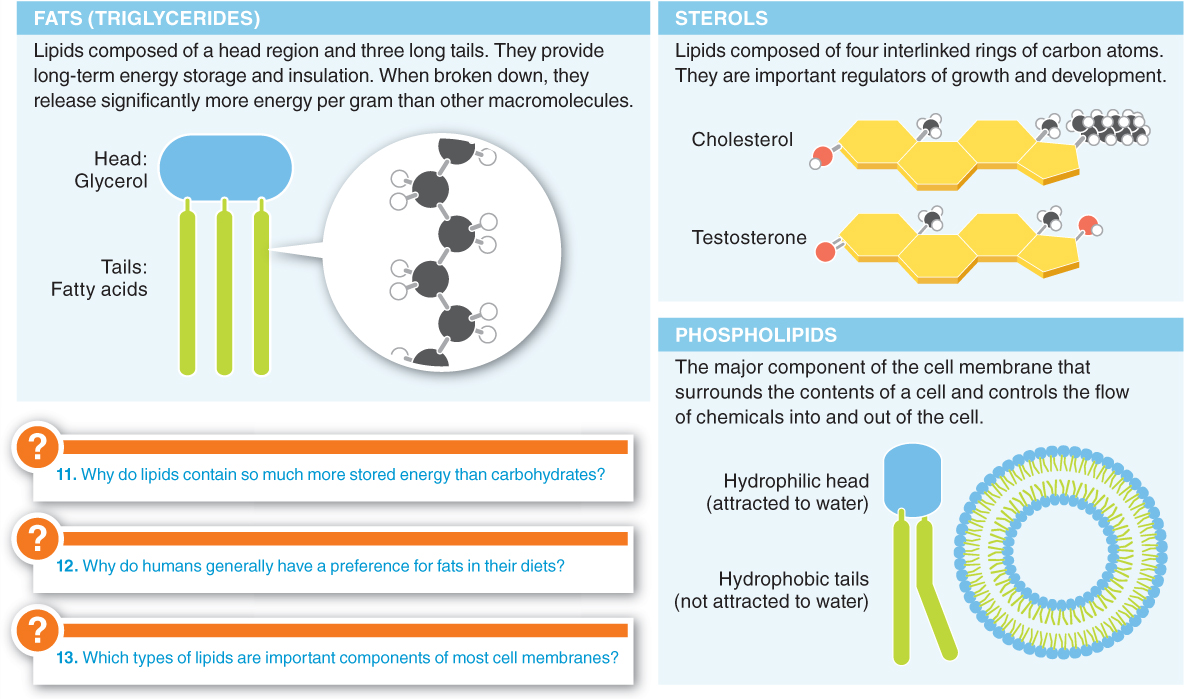
2.12–2.14
2.12–Lipids store energy for a rainy day.
Lipids are macromolecules—
Q
Which of the following statements about fiber is incorrect?
- a) Dietary fiber reduces the risk of colon cancer.
- b) Fiber in the diet slows the passage of food through the intestines.
- c) Humans cannot extract energy from fiber.
- d) The cellulose of celery stalks and lettuce leaves is fiber.
- e) Fiber scrapes the wall of the digestive tract, stimulating mucus secretion and aiding in the digestion of other molecules.

A dietary fatty acid is liquid at room temperature (i.e., it has a low melting point) and contains carbon-
- a) a plant
- b) a cow
- c) a pig
- d) a chicken
- e) a lamb

In an unsaturated fatty acid:
- a) carbon-
carbon double bonds are present in the hydrocarbon chain. - b) the hydrocarbon chain has an odd number of carbons.
- c) the hydrocarbon chain has an even number of carbons.
- d) no carbon-
carbon double bonds are present in the hydrocarbon chain. - e) not all carbons in the hydrocarbon chain are bonded to hydrogen.

Which statement about phospholipids is incorrect?
- a) They are used as organisms’ chief form of short-
term energy. - b) They are hydrophobic at one end.
- c) They are hydrophilic at one end.
- d) They are a major constituent of cell membranes.
- e) They contain glycerol linked to fatty acids.

Proteins are an essential component of a healthy diet for humans (and other animals). Their most common purpose is to serve as:
- a) raw material for growth.
- b) fuel for running the body.
- c) organic precursors for enzyme construction.
- d) long-
term energy storage. - e) inorganic precursors for enzyme construction.
