Many substances are just too big to get into or out of a cell by passive or active transport. To absorb large particles, such as bacterial invaders, cells engulf them with their plasma membrane in a process called endocytosis. To export large particles, such as digestive enzymes manufactured for use elsewhere in the body, they often use the process of exocytosis.
There are three types of endocytosis: phagocytosis, pinocytosis, and receptor-
Phagocytosis and Pinocytosis Relatively large particles are engulfed by cells in a process called phagocytosis (FIGURE 3-22). Amoebas and other unicellular protists, as well as white blood cells, use phagocytosis to consume entire organisms, either as food or as their way of defending against pathogens (disease-
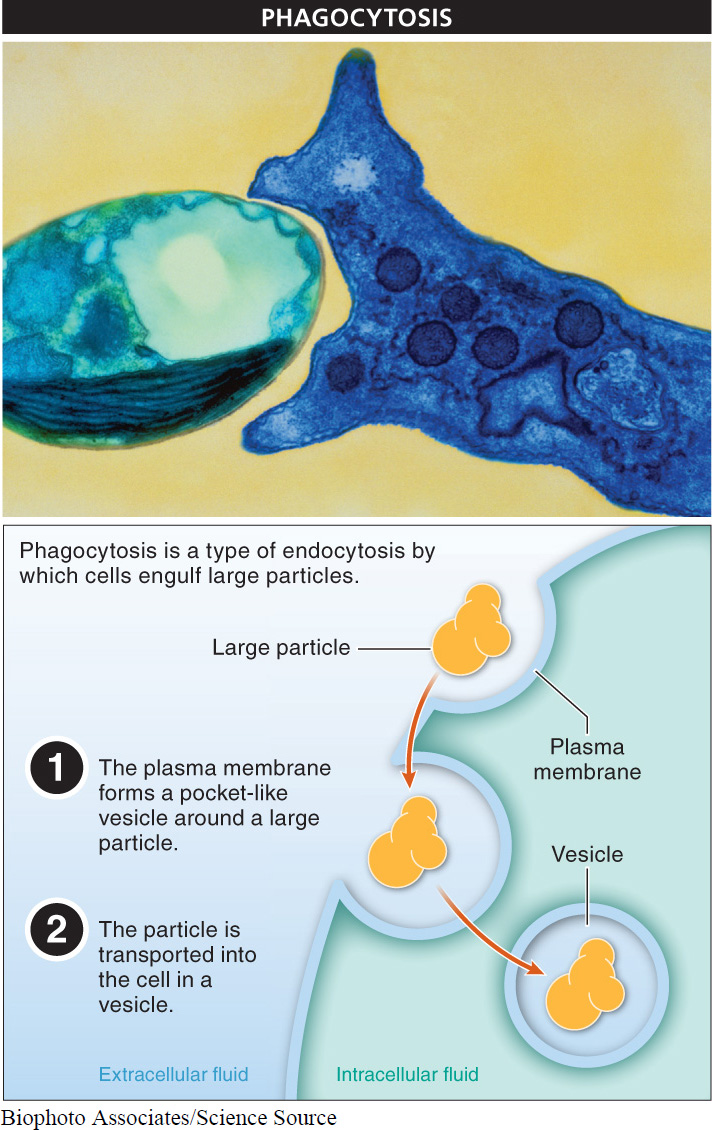
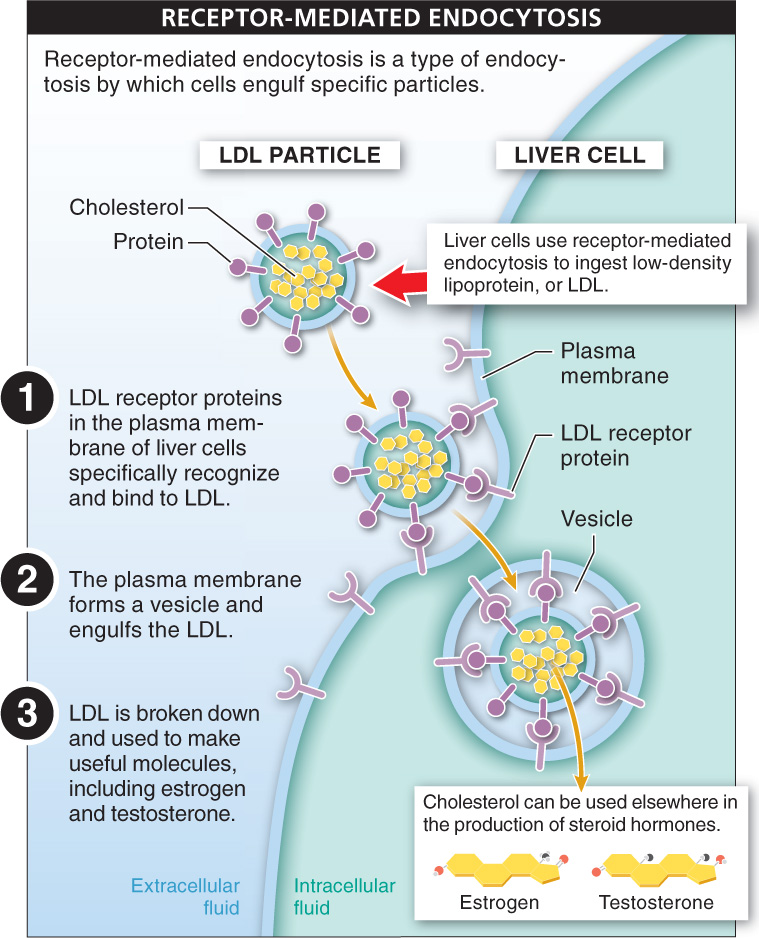
Receptor-
One of the most important examples of receptor-
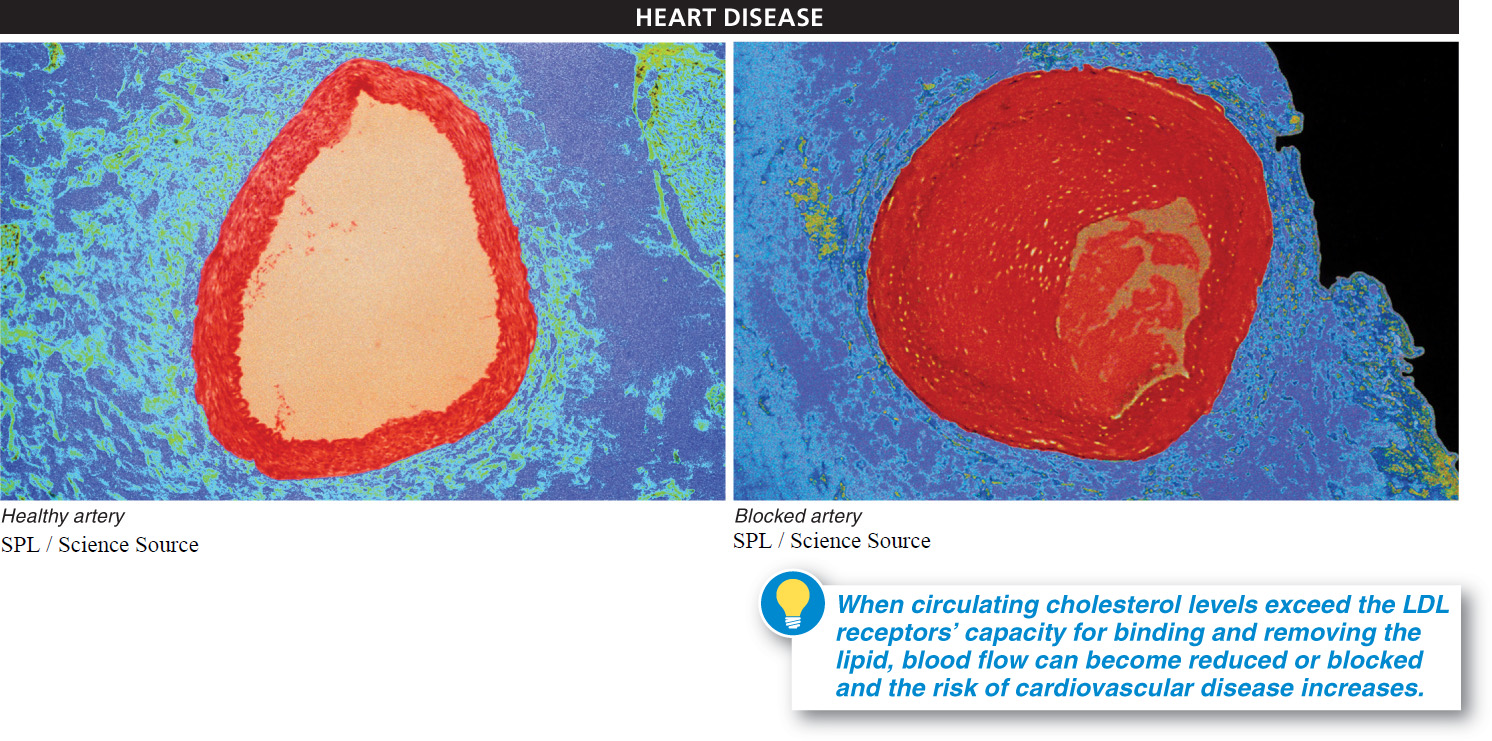
Faulty cell membranes are a primary cause of cardiovascular disease. What modification to these membranes might be an effective treatment?
Circulating cholesterol often builds up on the walls of arteries, reducing blood flow and causing the artery to harden. Too much circulating cholesterol in LDL molecules can lead to cardiovascular disease and death (FIGURE 3-24). Individuals lucky enough to have large numbers of LDL receptors on the plasma membranes of their liver cells have a significantly lower risk of cardiovascular disease.
108
Conversely, some individuals are at risk of early onset of cardiovascular disease because they consume food laden with too much cholesterol (such as egg yolks, cheese, and sausages) or have the misfortune of inheriting genes that code for faulty liver cell membranes that have few LDL receptors—
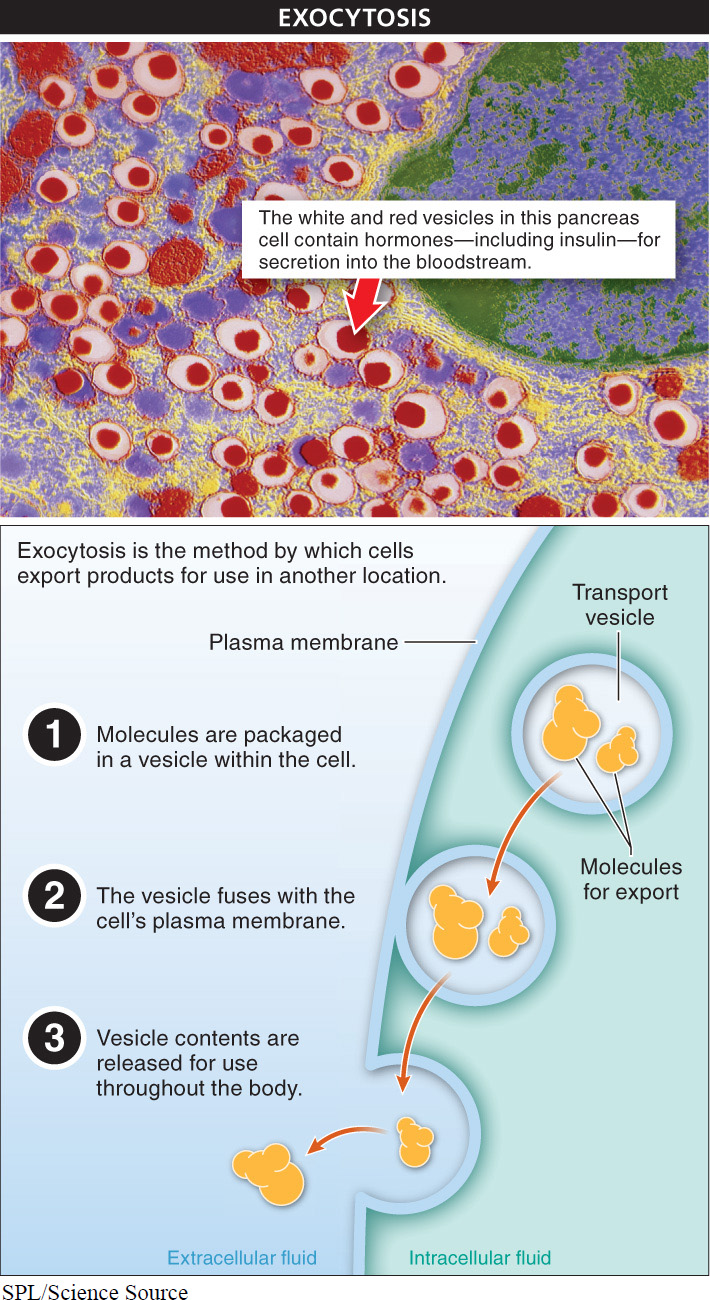
Exocytosis The movement of molecules out of cells takes place throughout the body. For example, cells in the pancreas produce a chemical called insulin that moves throughout the circulatory system. Insulin informs body cells that there is glucose in the bloodstream that ought to be taken in and used for energy. The insulin molecule is much too large to pass out through the plasma membranes of the cells where it is manufactured. As a result, after molecules of insulin are produced, they are coated with a phospholipid membrane to form a vesicle. The insulin-
109
Exocytosis is not restricted to large molecules. In the brain and other parts of the nervous system, for example, communication between cells occurs as one cell releases large numbers of very small molecules, called neurotransmitters, by exocytosis.
TAKE-HOME MESSAGE 3.11
When materials cannot get into a cell by diffusion or through a pump (for example, when the molecules are too big), cells can engulf the molecules or particles with their plasma membrane in a process called endocytosis. Similarly, molecules can be moved out of a cell by exocytosis. In both processes, the plasma membrane moves to surround the molecules or particles and forms a little vesicle that is pinched off inside the cell (endocytosis) or fuses with the plasma membrane and dumps its contents outside the cell (exocytosis).
Give two examples of cases in which cells of your body use endocytosis.
The textbook describes white blood cells consuming foreign cells through phagocytosis, as well as the uptake of cholesterol-containing LDL particles by receptor-mediated endocytosis in liver cells.
110