3.8–3.11
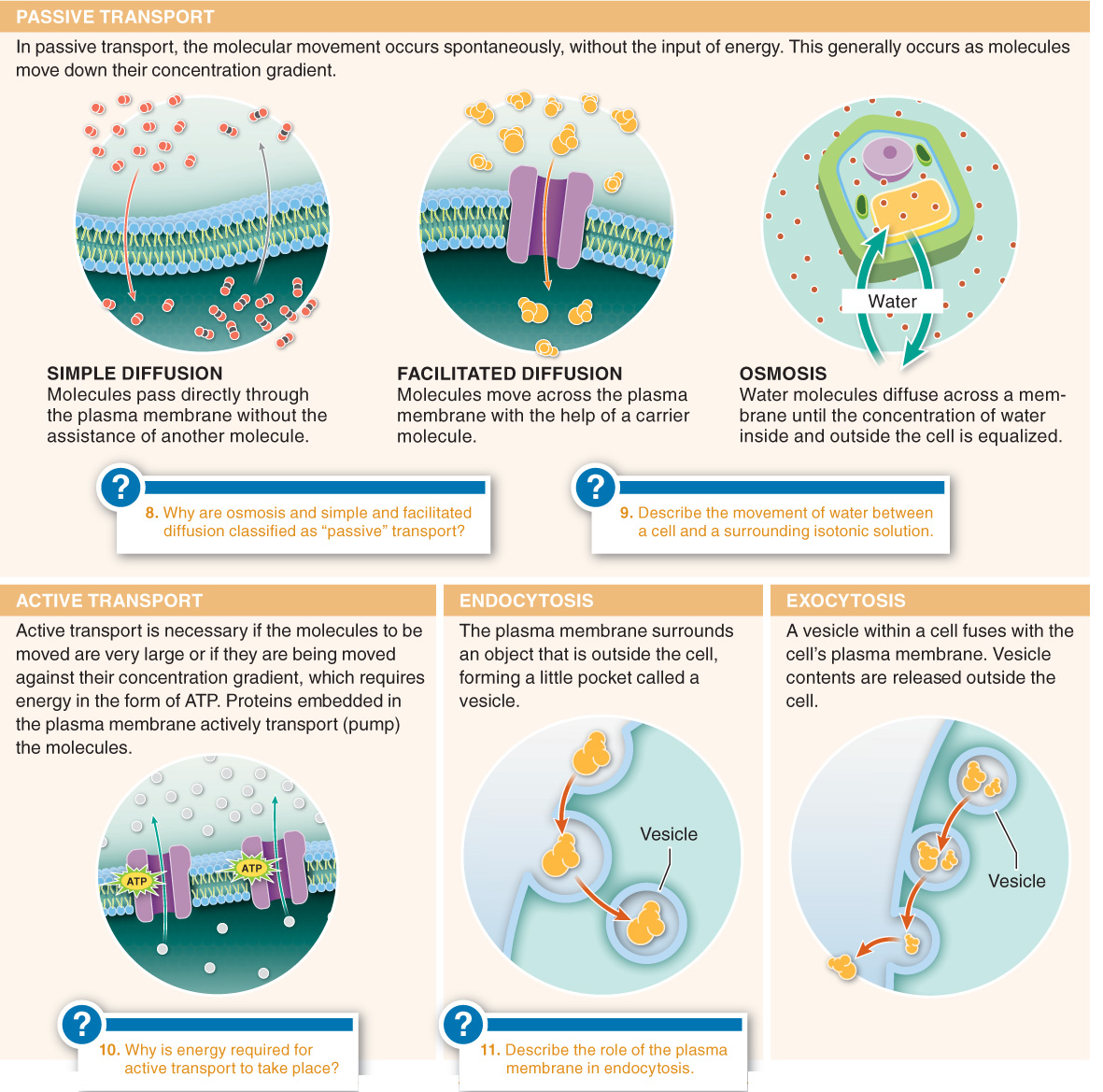
3.8–Molecules move across membranes in several ways.
Cells must import food molecules and other necessary materials from outside the cell and export metabolic waste and molecules produced for use elsewhere.
Q
Hydrophobic molecules can pass freely through the plasma membrane, but ions and polar molecules are impeded by the hydrophobic core. For this reason, plasma membranes can be considered:
- a) partially permeable.
- b) impermeable.
- c) hydrophobic.
- d) hydrophilic.
- e) None of these terms properly describe plasma membranes.

Drugs called beta-
- a) reduce high blood pressure.
- b) block signaling through adrenaline receptors.
- c) reduce outward symptoms of anxiety.
- d) bind to the cytoplasmic side of a receptor protein.
- e) reduce the effects of adrenaline on the heart.

Cellular “fingerprints”:
- a) are exposed on the cytoplasmic side of the membrane.
- b) are made from cholesterol.
- c) are “erased” by HIV.
- d) can help the immune system distinguish “self” from “non-
self.” - e) All of the above are correct.

The movement of molecules across a membrane from an area of high concentration to one of low concentration is best described as:
- a) active transport.
- b) inactivated transport.
- c) passive transport.
- d) channel-
mediated diffusion. - e) electron transport.

The transport of water across a membrane from a solution of lower solute concentration to a solution of higher solute concentration is best described as:
- a) osmosis.
- b) facilitated diffusion.
- c) receptor-
mediated transport. - d) active transport.
- e) general diffusion.

132