4.5–4.11
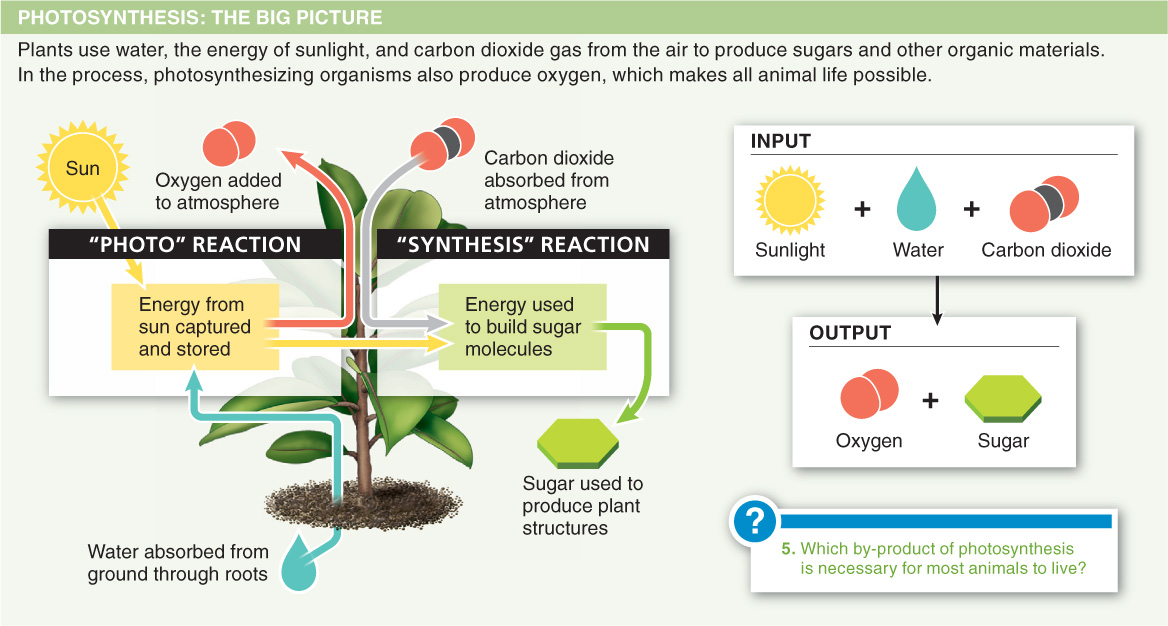
4.5–Photosynthesis uses energy from sunlight to make food.
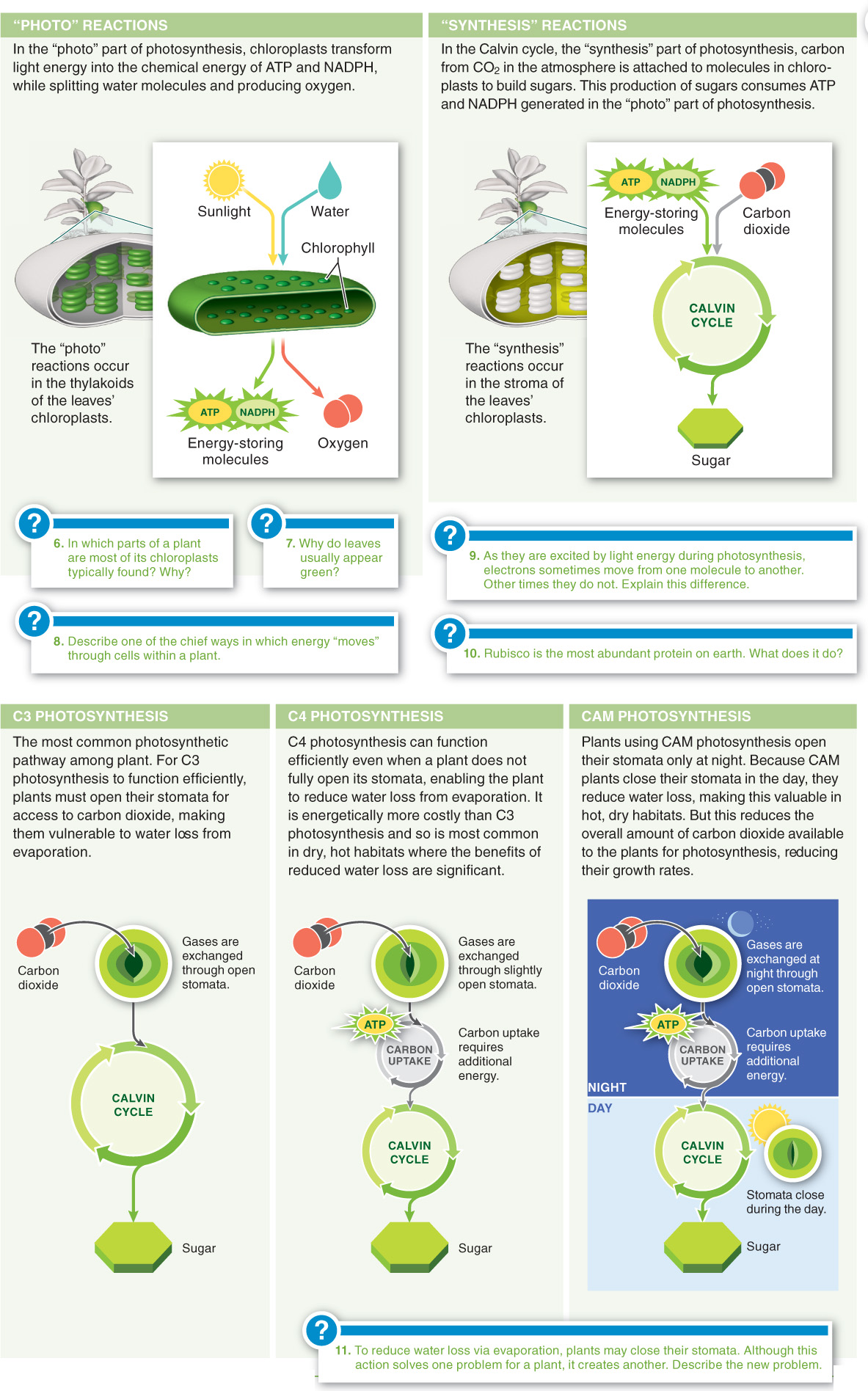
In photosynthesis, plants transform light energy into the chemical energy of ATP and NADPH, while splitting water molecules and producing oxygen.
173
Q
In your body, when energy is released during the breakdown of glucose:
- a) adenosine monophosphate is created.
- b) adenosine diphosphate is created.
- c) some energy may be harnessed to build high-
energy bonds that attach phosphate groups to ADP molecules. - d) molecules of ATP capture and absorb the heat from the reaction.
- e) it forms adenosine-
CoA.

A green plant can carry out photosynthesis if given nothing more than:
- a) water, light, and carbon dioxide.
- b) water, light, and oxygen.
- c) carbon dioxide.
- d) oxygen.
- e) oxygen and carbon dioxide.

The actual production of sugars during photosynthesis takes place:
- a) in the chloroplast outer membrane.
- b) within the stroma, inside the thylakoids of the chloroplast.
- c) within the stroma, outside the thylakoids of the chloroplast.
- d) within the mitochondria.
- e) within the thylakoid membranes.

The leaves of plants can be thought of as “eating” sunlight because:
- a) light energy, like chemical energy released when the bonds of food molecules are broken, is a type of kinetic energy.
- b) both light energy and food energy can be interconverted without heat loss.
- c) the carbon-
oxygen bonds within a photon of light release energy when broken by the enzymes in chloroplasts. - d) the carbon-
hydrogen bonds within a photon of light release energy when broken by the enzymes in chloroplasts. - e) photons contain hydrocarbons.

A molecule of chlorophyll increases in potential energy:
- a) when it binds to a photon.
- b) when a photon strikes it, boosting electrons to a higher-
energy excited state. - c) when it loses an electron.
- d) only in the presence of oxygen.
- e) None of the above. The potential energy of a molecule cannot change.

174