Chapter 1. Geometry
7.1 Introduction – basic formulas in geometry
In this section we will look at different geometric figures commonly used in physics. Geometric figures are bounded shapes in two or three dimensions (e.g. circles, triangles, spheres, cylinders etc.).
The lengths, areas or volumes of different geometric figures are governed by specific ratios and these ratios are used as a basic analytical tool in physics. For example, the characteristic ratios within triangles give us the laws of trigonometry, we will look at this in more detail later on. We will also use similar skills in working with vectors – essential for analyzing motion in two or three dimensions.
Circles and spheres are essential for understanding, among other concepts, angular momentum and the probability densities of quantum mechanics.
7.2 The circle
Circumference – the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter is a number, π, which has the approximate value
π = 3.141592
This means we can relate a circle’s circumference, C, its diameter, d and radius, r by
C=πd=2πr Circumference of a circle
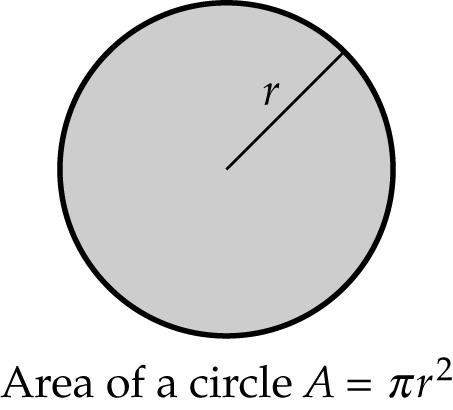
Area – The area of a circle, A, is given by
A=πr2 Area of a circle
7.3 The Parallelogram
Area - The area of a parallelogram is the base, b, multiplied by the height, h
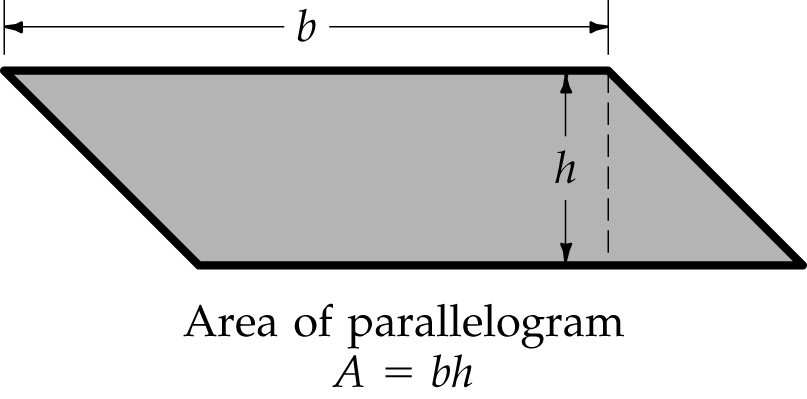
A=bh Area of parallelogram
7.4 The Triangle
In most physics problems you will complete throughout the book you will need to write an numerical answer with the correct number of significant figures. This will involve deciding how many significant figures your answer should include.
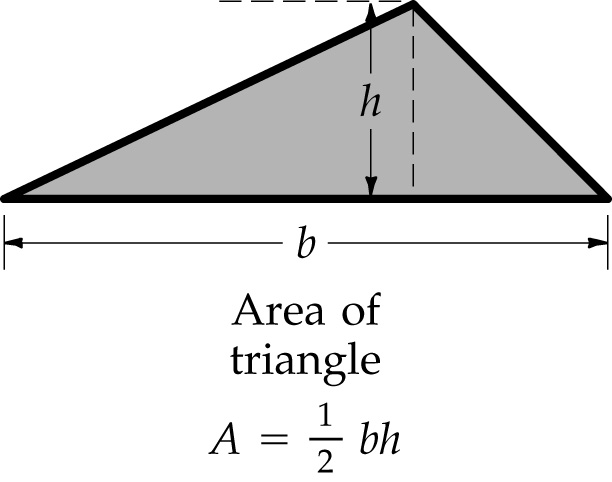
A=½bh Area of triangle
Try it yourself 1, two dimensional figures
Question Sequence
Question 1.
A wheel with a 0.25m radius rolls down a 5m long slope without slipping. How many turns of the wheel does it take to reach to bottom of the slope?
7.5 The Sphere
Surface area – A sphere of radius, r, has a surface area given by
A = 4πr2 Surface area of a sphere
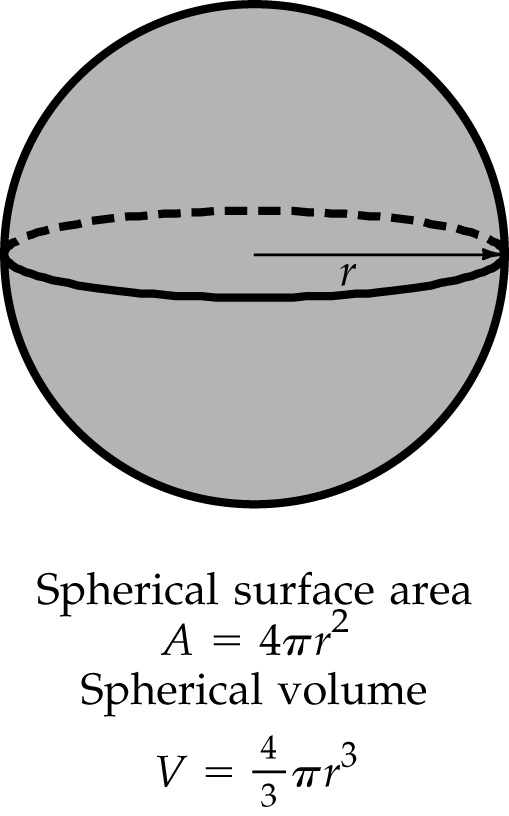
Volume – A sphere of radius, r, has a volume of,
V = 4/3 πr3 Volume of a sphere
Worked example
{Put Example M8 from the book here}
7.5 The Cylinder
Surface area – A cylinder of radius, r, and length, L, has a surface area not including the end faces of
A = 2 πrL Surface area of a cylinder
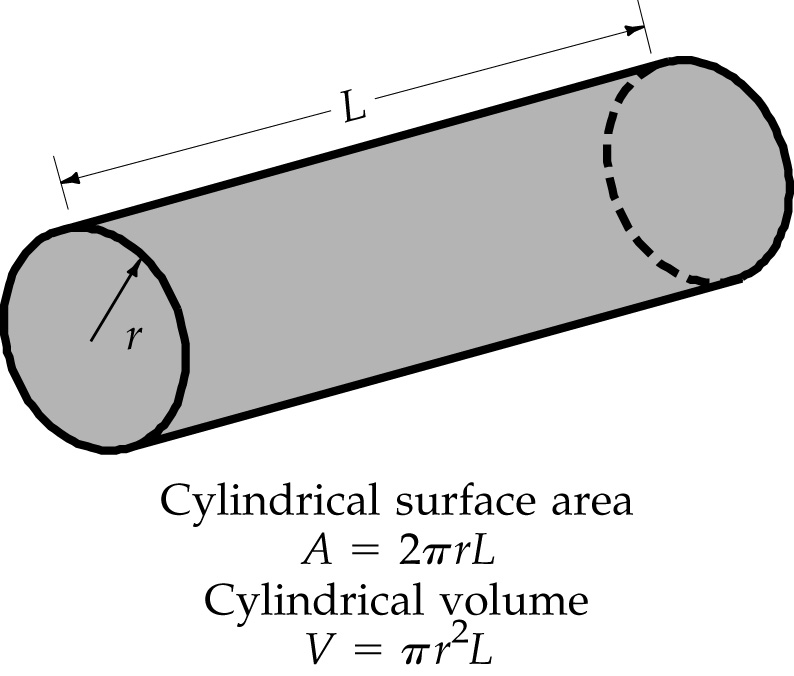
Volume – A cylinder of radius, r, and length, L, has a volume of,
V = πr2L Volume of a cylinder
Try it yourself 2, three dimensional figures
Question Sequence
Question 6.
A cylindrical copper wire, with a diameter of 3mm is used to make a circuit. What is the cross-sectional area of the wire in mm^2?