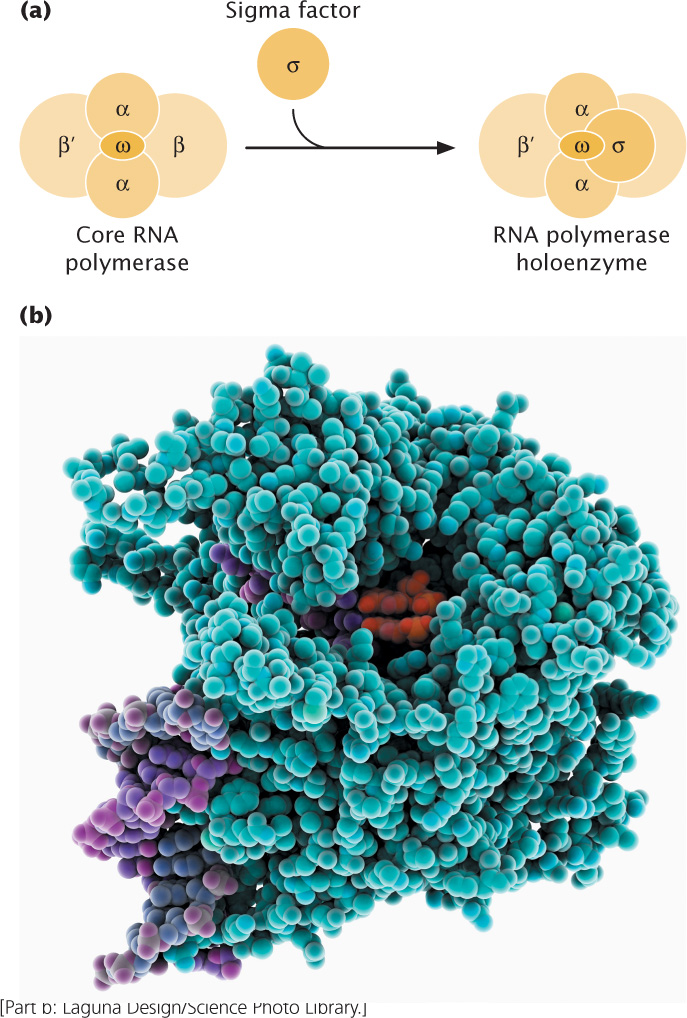
Figure 13.9: In bacterial RNA polymerase, the core enzyme consists of five subunits: two copies of alpha (α), a single copy of beta (β), a single copy of beta prime (β′), and a single copy of omega (ω). The core enzyme catalyzes the elongation of the RNA molecule by the addition of RNA nucleotides. (a) The sigma factor (σ) joins the core to form the holoenzyme, which is capable of binding to a promoter and initiating transcription. (b) The molecular model shows RNA polymerase (blue), binding DNA (purple), and synthesizing mRNA (red).
[Part b: Laguna Design/Science photo Library.]