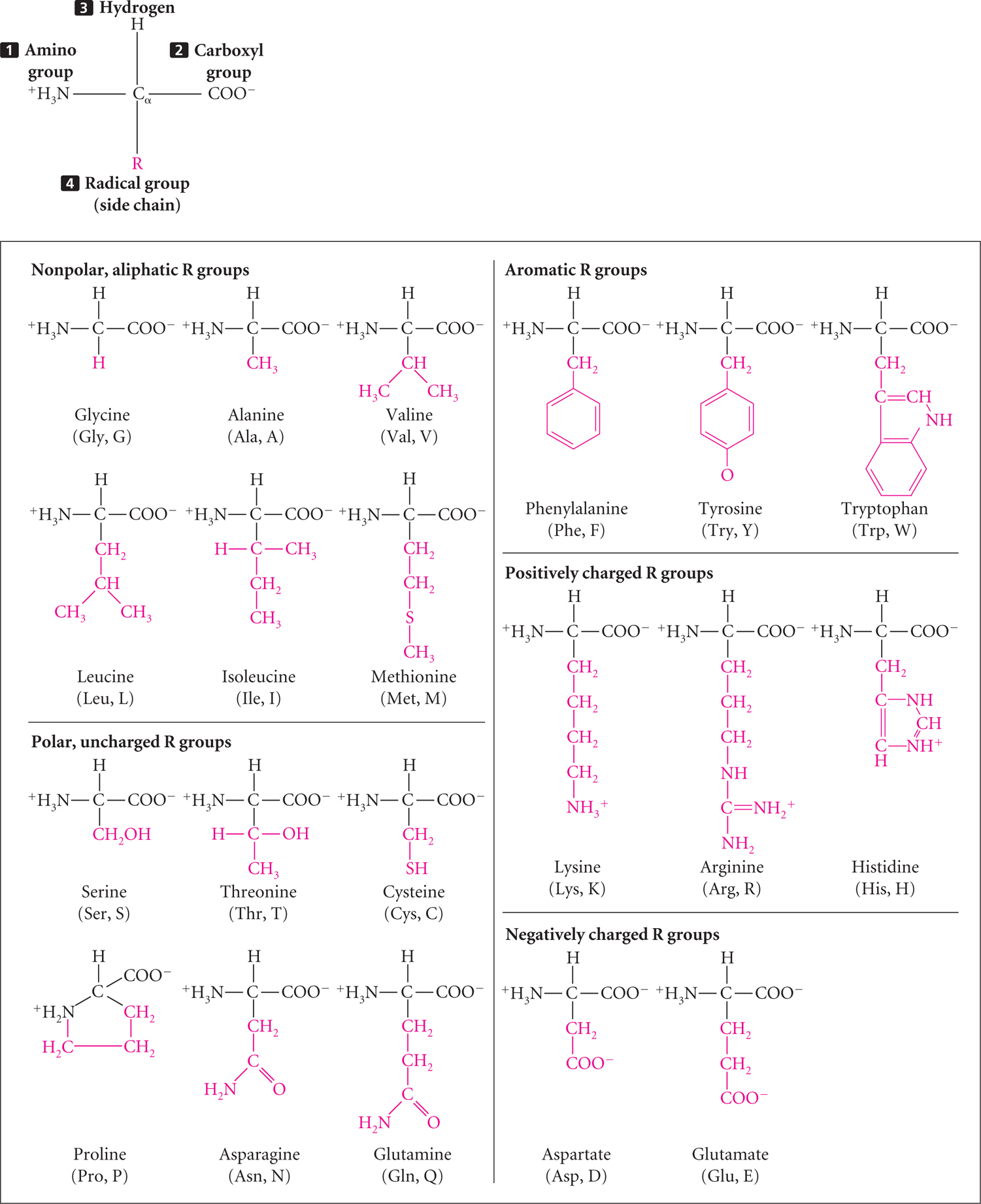
Figure 15.5: The common amino acids have similar structures. Each amino acid consists of a central carbon atom (Ca) attached to: (1) an amino group (NH3+); (2) a carboxyl group (COO−); (3) a hydrogen atom (H); and (4) a radical group, designated R. In the structures of the 20 common amino acids, the parts in black are common to all amino acids and the parts in red are the R groups.