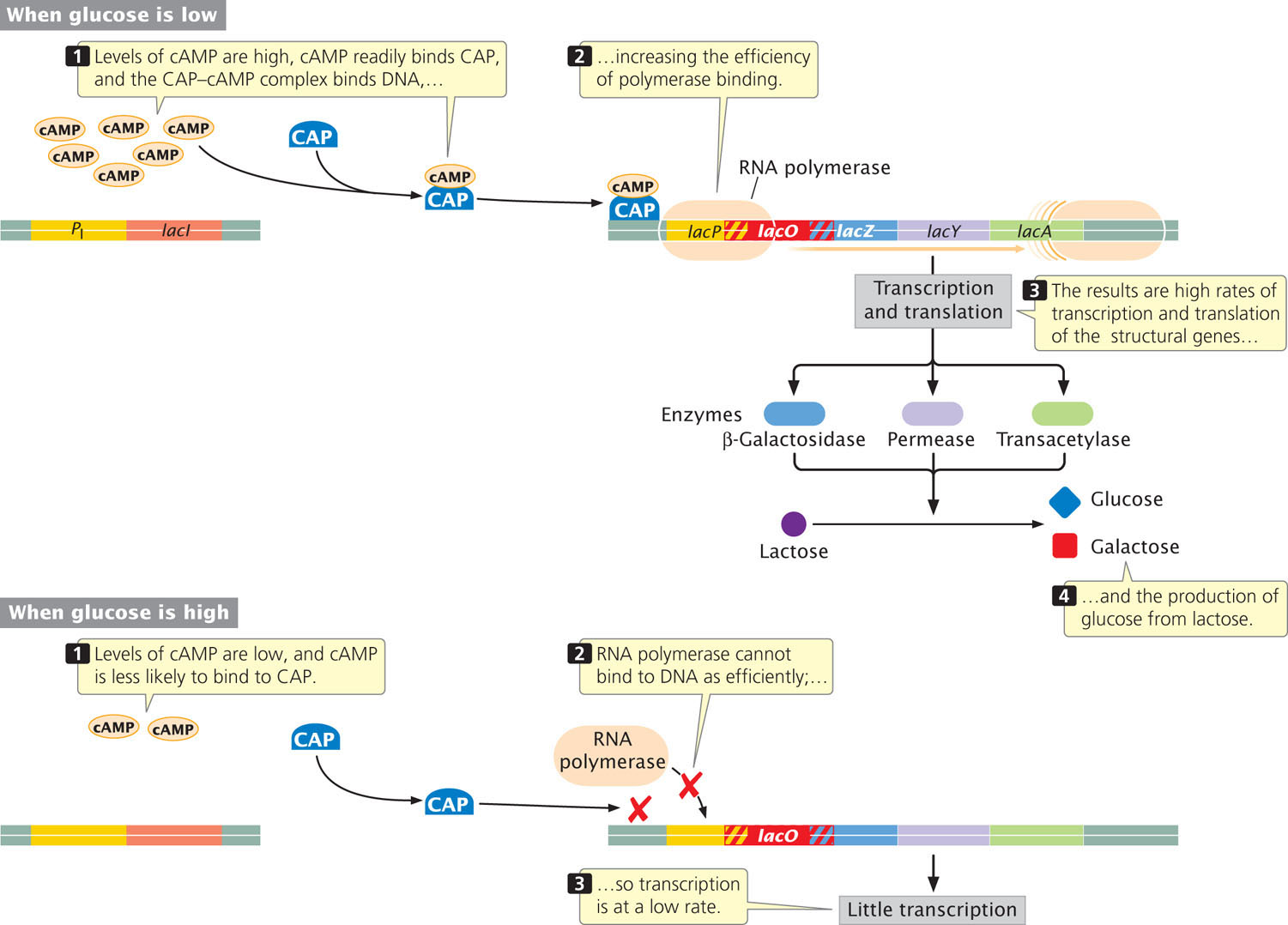
Figure 16.13: The catabolite activator protein (CAP) binds to the promoter of the lac operon and stimulates transcription. CAP must complex with adenosine-3′, 5′-cyclic monophosphate (cAMP) before binding to the promoter of the lac operon. The binding of cAMP-CAP to the promoter activates transcription by facilitating the binding of RNA polymerase. Levels of cAMP are inversely related to glucose: low glucose stimulates high cAMP; high glucose stimulates low cAMP.