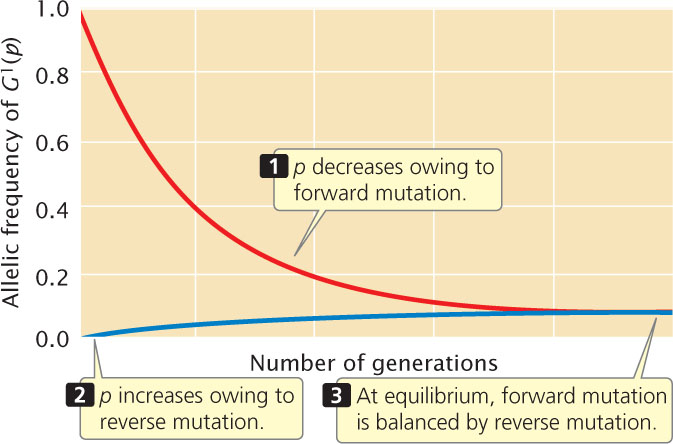
Figure 25.9: Change due to recurrent mutation slows as the frequency of p drops. Allelic frequencies approach mutational equilibrium at typical low mutation rates. The allelic frequency of G1 decreases as a result of forward (G1 → G2) mutation at rate of 0.0001 and increases as a result of reverse (G2 → G1) mutation at rate of 0.00001. Owing to the low rate of mutations, eventual equilibrium takes many generations to be reached.