Application Questions and Problems
Introduction
Question 2.20
Answer the following questions regarding the Blind Men’s Riddle, presented at the beginning of the chapter.
- a. What do the two socks of a pair represent in the cell cycle?
- b. In the riddle, each blind man buys his own pairs of socks, but the clerk places all pairs into one bag. Thus, there are two pairs of socks of each color in the bag (two black pairs, two blue pairs, two gray pairs, etc.). What do the two pairs (four socks in all) of each color represent?
- c. In the cell cycle, what is the thread that connects the two socks of a pair?
- d. In the cell cycle, what is the molecular knife that cuts the thread holding the two socks of a pair together?
- e. What in the riddle performs the same function as spindle fibers?
- f. What would happen if one man failed to grasp his sock of a particular pair and how does it relate to events in the cell cycle?
Section 2.1
Question 2.21
A cell has a circular chromosome and no nuclear membrane. Its DNA is complexed to some histone proteins. Does this cell belong to a eubacterium, archaea, or eukaryote? Explain your reasoning.
Section 2.2
Question 2.22
A certain species has three pairs of chromosomes: an acrocentric pair, a metacentric pair, and a submetacentric pair. Draw a cell of this species as it would appear in metaphase of mitosis.
Question 2.23
A biologist examines a series of cells and counts 160 cells in interphase, 20 cells in prophase, 6 cells in prometaphase, 2 cells in metaphase, 7 cells in anaphase, and 5 cells in telophase. If the complete cell cycle requires 24 hours, what is the average duration of the M phase in these cells? Of metaphase?
Section 2.3
Question 2.24
A certain species has three pairs of chromosomes: one acrocentric pair and two metacentric pairs. Draw a cell of this species as it would appear in the following stages of meiosis.
- a. Metaphase I
- b. Anaphase I
- c. Metaphase II
- d. Anaphase II
Question 2.25
Construct a table similar to that in Figure 2.12 for the different stages of meiosis, giving the number of chromosomes per cell and the number of DNA molecules per cell for a cell that begins with 4 chromosomes (two homologous pairs) in G1. Include the following stages in your table: G1, S, G2, prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, telophase I (after cytokinesis), prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, and telophase II (after cytokinesis).
Question 2.26
A cell in G1 of interphase has 12 chromosomes. How many chromosomes and DNA molecules will be found per cell when this original cell progresses to the following stages?
- a. G2 of interphase
- b. Metaphase I of meiosis
- c. Prophase of mitosis
- d. Anaphase I of meiosis
- e. Anaphase II of meiosis
- f. Prophase II of meiosis
- g. After cytokinesis following mitosis
- h. After cytokinesis following meiosis II
Question 2.27
How are the events that take place in spermatogenesis and oogenesis similar? How are they different?
Question 2.28
All of the following cells, shown in various stages of mitosis and meiosis, come from the same rare species of plant.
- a. What is the diploid number of chromosomes in this plant?
- b. Give the names of each stage of mitosis or meiosis shown.
- c. Give the number of chromosomes and number of DNA molecules per cell present at each stage.
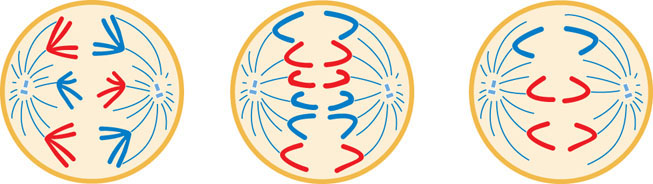
Question 2.29
The amount of DNA per cell of a particular species is measured in cells found at various stages of meiosis, and the following amounts are obtained:
Amount of DNA per cell
_______3.7 pg ______7.3 pg _______14.6 pg
Match the amounts of DNA above with the corresponding stages of the cell cycle (a through f). You may use more than one stage for each amount of DNA.
Stage of meiosis
- a. G1
- b. Prophase I
- c. G2
- d. Following telophase II and cytokinesis
- e. Anaphase I
- f. Metaphase II
Question 2.30
How would each of the following events affect the outcome of mitosis or meiosis?
- a. Mitotic cohesin fails to form early in mitosis.
- b. Shugoshin is absent during meiosis.
- c. Shugoshin does not break down after anaphase I of meiosis.
- d. Separase is defective.
Question 2.31
A cell in prophase II of meiosis contains 12 chromosomes. How many chromosomes would be present in a cell from the same organism if it were in prophase of mitosis? Prophase I of meiosis?
Question 2.32
A cell has 8 chromosomes in G1 of interphase. Draw a picture of this cell with its chromosomes at the following stages. Indicate how many DNA molecules are present at each stage.
- a. Metaphase of mitosis
- b. Anaphase of mitosis
- c. Anaphase II of meiosis
- d. Diplotene of meiosis I
Question 2.33
The fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster (left) has four pairs of chromosomes, whereas the house fly Musca domestica (right) has six pairs of chromosomes. In which species would you expect to see more genetic variation among the progeny of a cross? Explain your answer.

Question 2.34
A cell has two pairs of submetacentric chromosomes, which we will call chromosomes Ia, Ib, IIa, and IIb (chromosomes Ia and Ib are homologs, and chromosomes IIa and IIb are homologs). Allele M is located on the long arm of chromosome Ia, and allele m is located at the same position on chromosome Ib. Allele P is located on the short arm of chromosome Ia, and allele p is located at the same position on chromosome Ib. Allele R is located on chromosome IIa and allele r is located at the same position on chromosome IIb.
- a. Draw these chromosomes, identifying genes M, m, P, p, R, and r, as they might appear in metaphase I of meiosis. Assume that there is no crossing over.
- b. Taking into consideration the random separation of chromosomes in anaphase I, draw the chromosomes (with genes identified) present in all possible types of gametes that might result from this cell’s undergoing meiosis. Assume that there is no crossing over.
Question 2.35
A horse has 64 chromosomes and a donkey has 62 chromosomes. A cross between a female horse and a male donkey produces a mule, which is usually sterile. How many chromosomes does a mule have? Can you think of any reasons for the fact that most mules are sterile?
Question 2.36
Normal somatic cells of horses have 64 chromosomes (2n = 64). How many chromosomes and DNA molecules will be present in the following types of horse cells?

| Cell type | Number of chromosomes | Number of DNA molecules |
|---|---|---|
| a. Spermatogonium | ________ | _______ |
| b. First polar body | ________ | _______ |
| c. Primary oocyte | ________ | _______ |
| d. Secondary spermatocyte | ________ | _______ |
Question 2.37
Indicate whether each of the following cells is haploid or diploid.
| Cell Type | Haploid or Diploid? |
|---|---|
| Microspore | ________ |
| Primary spermatocyte | ________ |
| Microsporocyte | ________ |
| First polar body | ________ |
| Oogonium | ________ |
| Spermatid | ________ |
| Megaspore | ________ |
| Ovum | ________ |
| Secondary oocyte | ________ |
| Spermatogonium | ________ |
Question 2.38
A primary oocyte divides to give rise to a secondary oocyte and a first polar body. The secondary oocyte then divides to give rise to an ovum and a second polar body.
- a. Is the genetic information found in the first polar body identical with that found in the secondary oocyte? Explain your answer.
- b. Is the genetic information found in the second polar body identical with that in the ovum? Explain your answer.