Chapter 15
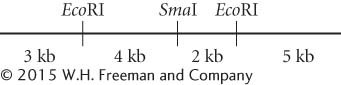
5′—ATTTACCGCAATACCCTAGTTAAAAC—
3′
Genes 2 and 24 are expressed at far higher levels in the antibiotic-
resistant bacteria than in the nonresistant cells. Conversely, genes 4, 17, and 22 are downregulated. All of these genes may be involved in antibiotic resistance. The upregulated genes may be involved in metabolism of the antibiotic or may perform functions that are inhibited by the antibiotic. The downregulated genes may be involved in uptake of the antibiotic or represent a cellular mechanism that accentuates the potency of the antibiotic. Characterization of these genes might lead to information regarding the mechanism of antibiotic resistance, and thus to the design of new antibiotics that can circumvent this resistance mechanism.
Any association between genome size and number of protein-
encoding genes among the 12 Drosophila species is weak at best. This observation is consistent with the pattern seen among eukaryotic organisms in general, in which there is no general association between genome size and number of genes. 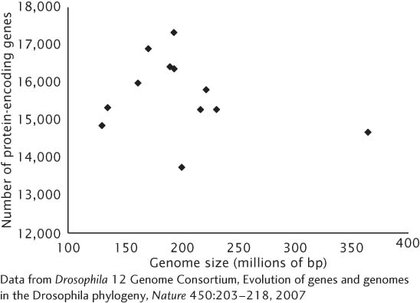
Proteomes. Generally, the genomes of two cells from the same person are genetically identical. However, the proteins in the two cells are likely to differ widely because different genes are expressed in each cell type.