Chapter 17
Discontinuous characteristic because only a few distinct phenotypes are present and alleles at a single locus determine the characteristic.
Discontinuous characteristic because there are only two phenotypes (dwarf and normal) and a single locus determines the characteristic.
Quantitative characteristic because susceptibility is a continuous trait determined by multiple genes and environmental factors (an example of a quantitative phenotype with a threshold effect).
Quantitative characteristic because it is determined by many loci (an example of a meristic characteristic).
Discontinuous characteristic because only a few distinct phenotypes are determined by alleles at a single locus.
All weigh 10 grams.
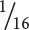 weighing 16 grams,
weighing 16 grams, 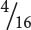 weighing 13 grams,
weighing 13 grams, 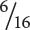 weighing 10 grams,
weighing 10 grams, 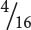 weighing 7 grams, and
weighing 7 grams, and 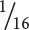 weighing 4 grams.
weighing 4 grams.
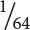 22 cm tall;
22 cm tall; 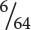 20 cm tall;
20 cm tall; 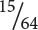 18 cm tall;
18 cm tall; 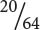 16 cm tall;
16 cm tall; 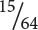 14 cm tall;
14 cm tall; 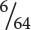 12 cm tall;
12 cm tall; 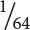 10 cm tall.
10 cm tall.
(a) 0.38; (b) 0.69.
The only reasonable conclusion is (d). Statement (a) is not justified because the heritability value does not apply to absolute height nor to an individual, but to the variance in height among Southwestern undergraduates. Statement (b) is not justified because the heritability has been determined only for Southwestern University students; students at other universities, with different ethnic backgrounds and from different regions of the country, may have different heritability for height. Statement (c) is again not justified because the heritability refers to the variance in height rather than absolute height. Statement (e) is not justified because the heritability has been determined for the range of variation in nongenetic factors experienced by the population under study; environmental variation outside this range (such as severe malnutrition) may have profound effects on height.
Use the equation R = h2 × S, where S is the selection differential. In this case, S = 10 cm − 4 cm = 6 cm, and we are given that the narrow-
sense heritability h2 is 0.6. Therefore, the response to selection R = 0.6 × 6 cm = 3.6 cm. The average wing length of the progeny should be the mean wing length of the population plus R: 4 cm + 3.6 cm = 7.6 cm.
0.75