Chapter 9
5 minutes.
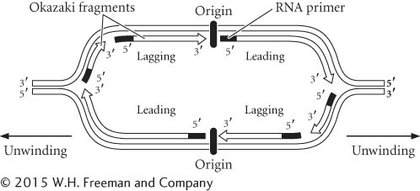
More errors in replication.
Primers would not be removed.
Primers that had been removed would not be replaced.
If DNA polymerase inserts an incorrect nucleotide, the 3′-OH group of the mismatched nucleotide is improperly positioned within the enzyme’s active site for the addition of the next nucleotide, thus stalling the polymerase. The 3′→5′ exonuclease function of the DNA polymerase then removes the mismatched base, and the polymerase can now insert the correct nucleotide. To proofread, DNA polymerase requires a 3′-OH group from a previously inserted nucleotide. This prevents DNA polymerase from starting replication, because initiation requires the ability to add a nucleotide without an existing 3′-OH. Thus an enzyme cannot have both the ability to initiate replication and to proofread; these two functions are incompatible.
The RNA part of telomerase is needed to provide the template for synthesizing complementary DNA telomere sequences at the ends of the chromosomes. A deletion of the gene that encodes the RNA part of telomerase would eliminate the template and prevent telomere synthesis at the ends of the chromosomes.