WORKED PROBLEMS
WORKED PROBLEMS
Problem 1
DNA from a eukaryotic gene was isolated, the two strands separated, and then hybridized to the mRNA transcribed from the gene. When the hybridized structure was observed with an electron microscope, it looked like this:
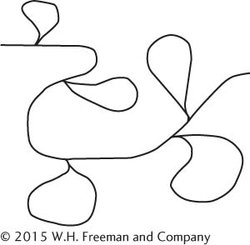
How many introns and exons are there in this gene? Explain your answer.
Identify the exons and introns in this hybridized structure.
Solution Strategy
What information is required in your answer to the problem?
The number of introns and exons and how you arrived at your answer.
The locations of the introns and exons labeled on the figure.
What information is provided to solve the problem?
The DNA and mRNA are from a eukaryote.
The DNA was denatured and hybridized to the mRNA.
A picture of the hybridized structure.
Recall: Introns are noncoding sequences found within eukaryotic genes.
Hint: The number of introns will be one less than the number of exons.
For help with this problem, review:
Introns in Section 10.4 and Figure 10.15.
Solution Steps
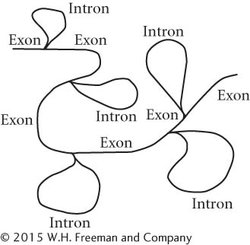
Each of the loops represents a region in which sequences in the DNA do not have corresponding sequences in the RNA; these regions are introns. There are five loops in the hybridized structure; so there must be five introns in the DNA and six exons.
Problem 2
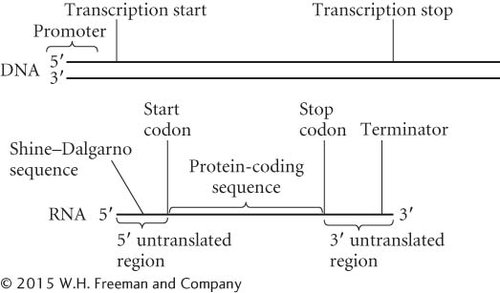
Draw a typical bacterial mRNA and the gene from which it was transcribed. Identify the 5′ and 3′ ends of the RNA and DNA molecules, as well as the following regions or sequences:
Promoter
5′ untranslated region
3′ untranslated region
Protein-
coding sequence Transcription start and termination sites
Terminator
Shine–Dalgarno sequence
Start and stop codons
Solution Strategy
What information is required in your answer to the problem?
A drawing of the mRNA and the gene from which it is transcribed. The 5′ and 3′ ends of the mRNA and DNA molecules. Locations of the listed structures on the drawing.
What information is provided to solve the problem?
The gene is from a bacterium.
Different parts of the DNA and RNA that are to be labeled.
For help with this problem, review:
Hint: Review the structure of a transcription unit in Figure 10.6 and the structure of mRNA in Figure 10.17.
The Template in Section 10.2 and The Structure of mRNA in Section 10.5.
Solution Steps