WORKED PROBLEMS
WORKED PROBLEMS
Problem 1
If there were five different types of bases in mRNA instead of four, what would be the minimum codon size (number of nucleotides) required to specify the following numbers of different amino acid types: (a) 4, (b) 20, (c) 30?
Solution Strategy
What information is required in your answer to the problem?
The minimum codon size if there were five bases instead of four.
What information is provided to solve the problem?
There are five different types of bases in mRNA.
The number of different amino acids that need to be specified by the code.
For help with this problem, review:
Solution Steps
Hint: The number of possible codons must be greater than or equal to the number of amino acids specified.
To answer this question, we must determine the number of combinations (codons) possible when there are different numbers of bases and different codon lengths. In general, the number of different codons possible will be equal to
blg
where b equals the number of different types of bases and lg equals the number of nucleotides in each codon (codon length). If there are five different types of bases, then
51 = 5 possible codons
52 = 25 possible codons
53 = 125 possible codons
A codon length of one nucleotide could specify 4 different amino acids, a codon length of two nucleotides could specify 20 different amino acids, and a codon length of three nucleotides could specify 30 different amino acids: (a) one, (b) two, (c) three.
Problem 2
A template strand in bacterial DNA has the following base sequence
5′—AGGTTTAACGTGCAT—
What amino acids are encoded by this sequence?
Solution Strategy
What information is required in your answer to the problem?
The list of amino acids encoded by the given sequence.
What information is provided to solve the problem?
The DNA sequence of the template strand.
The 5′ and 3′ ends of the template sequence.
The amino acids encoded by different codons (Figure 11.5).
For help with this problem, review:
The Degeneracy of the Code in Section 11.2.
Recall: The mRNA is antiparallel and complementary to the DNA template strand.
Solution Steps
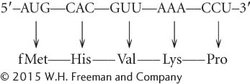
To answer this question, we must first work out the mRNA sequence that will be transcribed from this DNA sequence.
| DNA template strand: | 5′—AGGTTTAACGTGCAT— |
| mRNA copied from DNA: | 3′—UCCAAAUUGCACGUA— |
An mRNA is translated 5′ → 3′; so it will be helpful if we turn the RNA molecule around with the 5′ end on the left:
mRNA copied from DNA: 5′—AUGCACGUUAAACCU—
The codons consist of groups of three nucleotides that are read successivvely after the first AUG codon; by referring to Figure 11.5, we can determine that the amino acids are