APPLICATION QUESTIONS AND PROBLEMS
Question 12
*12.Assume that the number of different types of bases in RNA is four. What would be the minimum codon size (number of nucleotides) required to specify all amino acids if the number of different types of amino acids in proteins were (a) 2, (b) 8, (c) 17, (d) 45, (e) 75?
Question 13
*13.How many codons would be possible in a triplet code if only three bases (A, C, and U) were used?
Question 14
14.Using the genetic code presented in Figure 11.5, indicate which amino acid is encoded by each of the following mRNA codons.
5′—CCC—
3′ 5′—UUG—
3′ 5′—CUG—
3′ 5′—AGA—
5′ 5′—UAA—
3′
Question 15
*15.Referring to the genetic code presented in Figure 11.5, give the amino acids specified by the following bacterial mRNA sequences, and indicate the amino and carboxyl ends of the polypeptide produced. Hint: Remember that AUG is the initiation codon.
5′—AUGUUUAAAUUUAAAUUUUGA—
3′ 5′—AGGGAAAUCAGAUGUAUAUAUAUAUAUGA—
3′ 5′—UUUGGAUUGAGUGAAACGAUGGAUGAAAGAUUUCUCGCUUGA—
3′ 5′—GUACUAAGGAGGUUGUAUGGGUUAGGGGACAUCAUUUUGA—
3′
Question 16
16.A nontemplate strand of bacterial DNA has the following base sequence. What amino acid sequence will be encoded by this sequence?
5′—ATGATACTAAGGCCC—
Question 17
*17.The following amino acid sequence is found in a tripeptide: Met-
Question 18
18.How many different mRNA sequences can encode a polypeptide chain with the amino acid sequence Met-
Question 19
19.The following anticodons are found in a series of tRNAs. Refer to the genetic code in Figure 11.5 and give the amino acid carried by each of these tRNAs.
5′—GUA—
3′ 5′—AUU—
3′ 5′—GGU—
3′ 5′—CCU—
3′
Question 20
20.Which of the following amino acid changes could result from a mutation that changed a single base? For each change that could result from the alteration of a single base, determine which position of the codon (first, second, or third nucleotide) in the mRNA must be altered for the change to result.
Leu → Gln
Phe → Ser
Phe → Ile
Pro → Ala
Asn → Lys
Ile → Asn
Question 21
*21.Arrange the following components of translation in the approximate order in which they would appear or be used in prokaryotic protein synthesis:
70S initiation complex
30S initiation complex
Release factor 1
Elongation factor Tu
Initiation factor 3
Elongation factor G
fMet-
Question 22
22.The following diagram illustrates a step in the process of translation. Identify the following elements on the diagram.
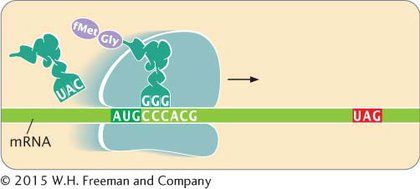
5′ and 3′ ends of the mRNA
A, P, and E sites
Start codon
Stop codon
Amino and carboxyl ends of the newly synthesized polypeptide chain
Approximate location of the next peptide bond that will be formed
Place on the ribosome where release factor 1 will bind
Question 23
23.Refer to the diagram in Problem 22 to answer the following questions.
What will be the anticodon of the next tRNA added to the A site of the ribosome?
What will be the next amino acid added to the growing polypeptide chain?
Question 24
*24.A synthetic mRNA added to a cell-
Initiation factor 3
Initiation factor 2
Elongation factor Tu
Elongation factor G
Release factors RF-
1, RF- 2, and RF- 3 ATP
GTP
Question 25
25.For each of the sequences in the following table, place a check mark in the appropriate space to indicate the process most immediately affected by deleting the sequence. Choose only one process for each sequence (i.e., one check mark per sequence).
| Process most immediately affected by deletion | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sequence deleted | Replication | Transcription | RNA processing | Translation |
| a. ori site | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ |
| b. 3′ splice- |
______ | ______ | ______ | ______ |
| c. Poly(A) tail | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ |
| d. Terminator | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ |
| e. Start codon | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ |
| f. −10 consensus | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ |
| g. Shine– Dalgarno | ______ | ______ | ______ | ______ |
Question 26
26.Give the amino acid sequence of the protein encoded by the mRNA in Figure 11.13.