The Binding of Amino Acids To Transfer RNAs
The first stage of translation is the binding of tRNA molecules to their appropriate amino acids. As we have seen, although there may be several different tRNAs for a particular amino acid, each tRNA is specific for only one amino acid. The key to specificity between an amino acid and its tRNA is a set of enzymes called aminoacyl-
The attachment of a tRNA to its appropriate amino acid, termed tRNA charging, requires energy, which is supplied by adenosine triphosphate (ATP):
amino acid + tRNA + ATP → aminoacyl-tRNA
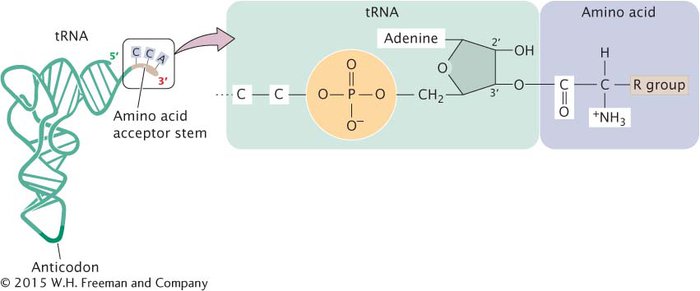
The carboxyl group (COO−) of the amino acid is attached to the adenine nucleotide at the 3′ end of the tRNA (Figure 11.8). To identify the resulting aminoacylated tRNA, we write the three-
CONCEPTS
Amino acids are attached to specific tRNAs by aminoacyl-
 CONCEPT CHECK 4
CONCEPT CHECK 4
Amino acids bind to which part of the tRNA?
anticodon
codon
3′ end
5′ end
c