The Initiation of Translation
The second stage in the process of protein synthesis is initiation. At this stage, all the components necessary for protein synthesis assemble: (1) mRNA; (2) the small and large subunits of the ribosome; (3) a set of three proteins called initiation factors; (4) initiator tRNA with N-formylmethionine attached (fMet-
INITIATION IN BACTERIA The functional ribosome of bacteria exists as two subunits, the small 30S subunit and the large 50S subunit (Figure 11.9a). An mRNA molecule can bind to the small ribosome subunit only when the subunits are separate. Initiation factor 3 (IF-
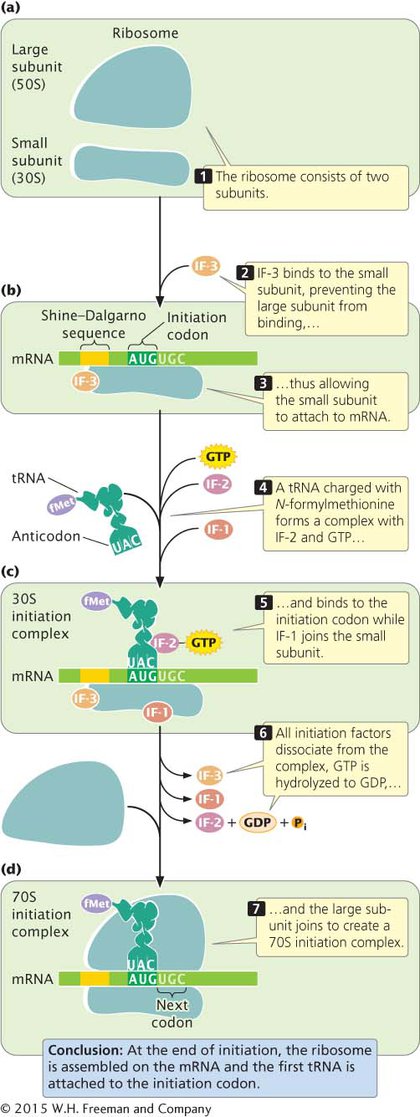
The initiator tRNA, fMet-
At this point, the initiation complex consists of (1) the small subunit of the ribosome; (2) the mRNA; (3) the initiator tRNA with its amino acid (fMet-
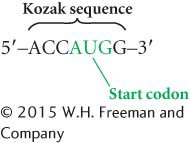
INITIATION IN EUKARYOTES Similar events take place in the initiation of translation in eukaryotic cells, but there are some important differences. In bacterial cells, sequences in 16S rRNA of the small subunit of the ribosome bind to the Shine–Dalgarno sequence in mRNA. No analogous consensus sequence exists in eukaryotic mRNA. Instead, the cap at the 5′ end of eukaryotic mRNA plays a critical role in the initiation of translation. The small subunit of the eukaryotic ribosome, initiation factors, and the initiator tRNA with its amino acid (Met-
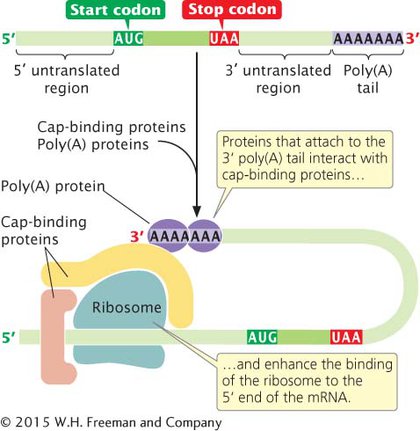
Another difference is that eukaryotic initiation requires at least seven initiation factors. The poly(A) tail at the 3′ end of eukaryotic mRNA also plays a role in the initiation of translation. During initiation, proteins that attach to the poly(A) tail interact with proteins that bind to the 5′ cap, enhancing the binding of the small subunit of the ribosome to the 5′ end of the mRNA. This interaction indicates that the 3′ end of the mRNA bends over and associates with the 5′ cap during the initiation of translation, forming a circular structure known as the closed loop (Figure 11.10).
CONCEPTS
In the initiation of translation in bacterial cells, the small ribosomal subunit attaches to mRNA, and initiator tRNA attaches to the initiation codon. This process requires several initiation factors (IF-
 CONCEPT CHECK 5
CONCEPT CHECK 5
During the initiation of translation in bacteria, the small ribosomal subunit binds to which consensus sequence?
The Shine–Dalgarno sequence