Chemically Induced Mutations
Although many mutations arise spontaneously, a number of environmental agents, including certain chemicals and radiation, are capable of damaging DNA. Any environmental agent that significantly increases the rate of mutation above the spontaneous rate is called a mutagen.
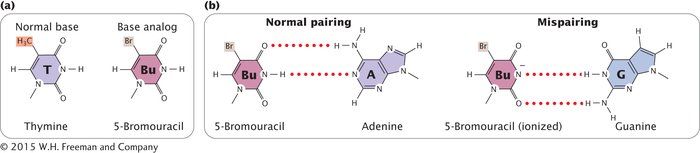
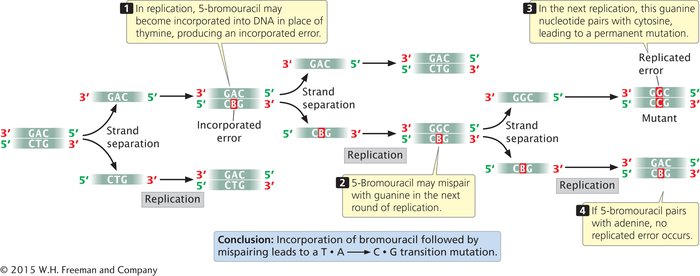
BASE ANALOGS One class of chemical mutagens consists of base analogs, chemicals with structures similar to those of any of the four standard bases of DNA. DNA polymerases cannot distinguish these analogs from the standard bases, so if base analogs are present during replication, they may be incorporated into newly synthesized DNA molecules. For example, 5-
ALKYLATING AGENTS Alkylating agents are chemicals that donate alkyl groups, such as methyl (CH3) and ethyl (CH3–CH2) groups, to nucleotide bases. For example, ethylmethylsulfonate (EMS) adds an ethyl group to guanine, producing O6-ethylguanine, which pairs with thymine (Figure 13.18a). Thus, EMS produces C • G → T • A transitions. Ethylmethylsulfonate is also capable of adding an ethyl group to thymine, producing 4-
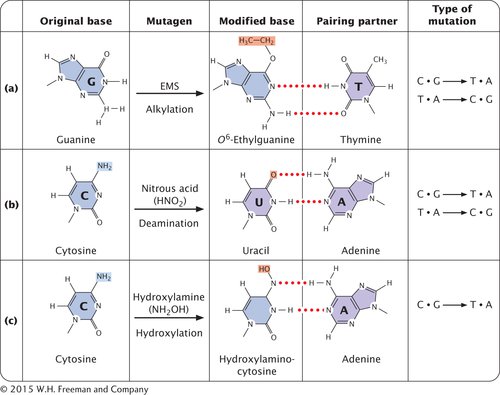
DEAMINATION In addition to its spontaneous occurrence (see Figure 13.15), deamination can be induced by some chemicals. For instance, nitrous acid deaminates cytosine, creating uracil, which in the next round of replication pairs with adenine (Figure 13.18b), producing a C • G → T • A transition mutation. Nitrous acid also changes adenine into hypoxanthine, which pairs with cytosine, leading to a T • A → C • G transition. In addition, nitrous acid deaminates guanine, producing xanthine, which pairs with cytosine just as guanine does; however, xanthine can also pair with thymine, leading to a C • G → T • A transition. Nitrous acid produces exclusively transition mutations, and because both C • G → T • A and T • A → C • G transitions are produced, these mutations can be reversed with nitrous acid.
HYDROXYLAMINE Hydroxylamine is a very specific base-
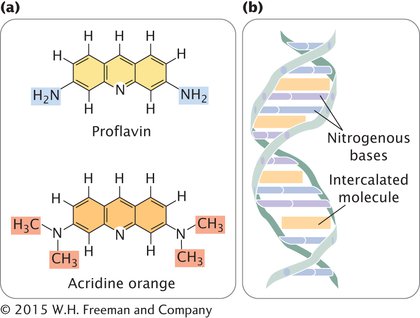
INTERCALATING AGENTS Proflavin, acridine orange, ethidium bromide, and dioxin are intercalating agents (Figure 13.19a), which produce mutations by sandwiching themselves (intercalating) between adjacent bases in DNA, distorting the three-
CONCEPTS
Chemicals can produce mutations by a number of mechanisms. Base analogs are incorporated into DNA and frequently pair with the wrong base. Alkylating agents, deaminating chemicals, hydroxylamine, and other chemicals change the structure of DNA bases, thereby altering their pairing properties. Intercalating agents wedge between the bases and cause single-
 CONCEPT CHECK 3
CONCEPT CHECK 3
Base analogs are mutagenic because of which characteristic?
They produce changes in DNA polymerase that cause it to malfunction.
They distort the structure of DNA.
They are similar in structure to the normal bases.
They chemically modify the normal bases.
c