APPLICATION QUESTIONS AND PROBLEMS
Question 12
12.A codon that specifies the amino acid Gly undergoes a single-
Question 13
*13.Refer to the genetic code in Figure 11.5 to answer the following questions:
If a single transition occurs in a codon that specifies Phe, what amino acids can be specified by the mutated sequence?
If a single transversion occurs in a codon that specifies Phe, what amino acids can be specified by the mutated sequence?
If a single transition occurs in a codon that specifies Leu, what amino acids can be specified by the mutated sequence?
If a single transversion occurs in a codon that specifies Leu, what amino acids can be specified by the mutated sequence?
Question 14
14.Hemoglobin is a complex protein that contains four polypeptide chains. The normal hemoglobin found in adults—
Question 15
*15.The following nucleotide sequence is found on the template strand of DNA. First, determine the amino acids of the protein encoded by this sequence by using the genetic code provided in Figure 11.5. Then give the altered amino acid sequence of the protein that will be found in each of the following mutations:

Mutant 1: A transition at nucleotide 11
Mutant 2: A transition at nucleotide 13
Mutant 3: A one-
nucleotide deletion at nucleotide 7 Mutant 4: A T → A transversion at nucleotide 15
Mutant 5: An addition of TGG after nucleotide 6
Mutant 6: A transition at nucleotide 9
Question 16
16.Draw a hairpin structure like that shown in Figure 13.5 for the repeated sequence found in fragile-
Question 17
*17.A polypeptide has the following amino acid sequence.
Met-
The amino acid sequence of this polypeptide was determined in a series of mutants listed in parts a through e. For each mutant, indicate the type of mutation that occurred in the DNA (single-
Mutant 1: Met-
Ser- Ser- Arg- Leu- Glu- Gly Mutant 2: Met-
Ser- Pro Mutant 3: Met-
Ser- Pro- Asp- Trp- Arg- Asp- Lys Mutant 4: Met-
Ser- Pro- Glu- Gly Mutant 5: Met-
Ser- Pro- Arg- Leu- Leu- Glu- Gly
Question 18
18.A gene encodes a protein with the following amino acid sequence:
Met-
A mutation occurs in the gene. The mutant protein has the following amino acid sequence:
Met-
An intragenic suppressor restores the amino acid sequence to that of the original protein:
Met-
Give at least one example of base changes that could produce the original mutation and the intragenic suppressor. (Consult the genetic code in Figure 11.5).
Question 19
19.The following nucleotide sequence is found in a short stretch of DNA:
5′—ATGT—
3′—TACA—
If this sequence is treated with hydroxylamine, what sequences will result after replication?
Question 20
*20.The following nucleotide sequence is found in a short stretch of DNA:
5′—AG—
3′—TC—
Give all the mutant sequences that can result from spontaneous depurination in this stretch of DNA.
Give all the mutant sequences that can result from spontaneous deamination in this stretch of DNA.
Question 21
21. Mary Alexander studied the effects of radiation on mutation rates in the sperm of Drosophila melanogaster. She irradiated Drosophila larvae with either 3000 roentgens (3000 r) or 3975 r, collected the adult males that developed from irradiated larvae, mated them with nonirradiated females, and then counted the number of mutant F1 offspring produced by each male. All mutant flies that appeared were used in subsequent crosses to determine if their mutant phenotypes were genetic. She obtained the following results (M. L. Alexander. 1954. Genetics 39:409–428):
Mary Alexander studied the effects of radiation on mutation rates in the sperm of Drosophila melanogaster. She irradiated Drosophila larvae with either 3000 roentgens (3000 r) or 3975 r, collected the adult males that developed from irradiated larvae, mated them with nonirradiated females, and then counted the number of mutant F1 offspring produced by each male. All mutant flies that appeared were used in subsequent crosses to determine if their mutant phenotypes were genetic. She obtained the following results (M. L. Alexander. 1954. Genetics 39:409–428):
|
Group |
Number of offspring |
Offspring with a genetic mutation |
|---|---|---|
| Control (0 r) | 45,504 | 0 |
| Irradiated (3000 r) | 49,512 | 71 |
| Irradiated (3975 r) | 50,159 | 70 |
Calculate the mutation rates of the control group and the two groups of irradiated flies.
On the basis of these data, do you think radiation has any effect on mutation? Explain your answer.
Question 22
22.What conclusion would you draw if the number of bacterial colonies in Figure 13.21 were the same on the control plate and the treatment plate? Explain your reasoning.
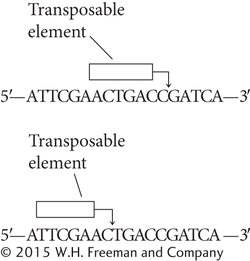
Question 23
*23.A particular transposable element generates flanking direct repeats that are 4 bp long. Give the sequence that will be found on both sides of the transposable element if this transposable element inserts at the position indicated on each of the following sequences.
Question 24
24.What factor determines the length of the flanking direct repeats that are produced in a transposition?
Question 25
25.Zidovudine (AZT) is a drug used to treat patients with AIDS. AZT works by blocking the reverse-
Question 26
26.A transposable element is found to encode a reverse-
Question 27
*27.A plant breeder wants to isolate mutants in tomatoes that are defective in DNA repair. However, this breeder does not have the expertise or equipment to study enzymes in DNA-