APPLICATION QUESTIONS AND PROBLEMS
Question 12
12.If nondisjunction of the sex chromosomes takes place in meiosis I in the male in Figure 4.5, what sexual phenotypes and proportions of offspring will be produced?
Question 13
13.What will be the phenotypic sex of a human with the following genes or chromosomes or both?
XY with the SRY gene deleted
XY with the SRY gene located on an autosome
XX with a copy of the SRY gene on an autosome
XO with a copy of the SRY gene on an autosome
XXY with the SRY gene deleted
XXYY with one copy of the SRY gene deleted
Question 14
*14.Joe has classic hemophilia, an X-
| Yes | No | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| a. | His mother’s mother | ________ | ________ |
| b. | His mother’s father | ________ | ________ |
| c. | His father’s mother | ________ | ________ |
| d. | His father’s father | ________ | ________ |
Question 15
*15.In Drosophila, yellow body color is due to an X-

A homozygous gray female is crossed with a yellow male. The F1 are intercrossed to produce F2. Give the genotypes and phenotypes, along with the expected proportions, of the F1 and F2 progeny.
A yellow female is crossed with a gray male. The F1 are intercrossed to produce the F2. Give the genotypes and phenotypes, along with the expected proportions, of the F1 and F2 progeny.
Question 16
16.Coat color in cats is determined by genes at several different loci. At one locus on the X chromosome, one allele (X+) encodes black fur; another allele (Xo) encodes orange fur. Females can be black (X+X+), orange (XoXo). or a mixture of orange and black called tortoiseshell (X+Xo). Males are either black (X+Y) or orange (XoY), Bill has a female tortoiseshell cat named Patches. One night Patches escapes from Bill’s house, spends the night out, and mates with a stray male. Patches later gives birth to the following kittens: one orange male, one black male, two tortoiseshell females, and one orange female. Give the genotypes of Patches, her kittens, and the stray male with which Patches mated.
Question 17
17.Red–green color blindness in humans is due to an X-
Question 18
18. The following pedigree illustrates the inheritance of Nance–Horan syndrome, a rare genetic condition in which affected persons have cataracts and abnormally shaped teeth.
The following pedigree illustrates the inheritance of Nance–Horan syndrome, a rare genetic condition in which affected persons have cataracts and abnormally shaped teeth.
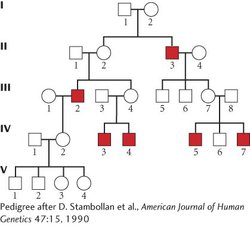
On the basis of this pedigree, what do you think is the most likely mode of inheritance for Nance–Horan syndrome?
If couple III-
7 and III- 8 have another child, what is the probability that the child will have Nance–Horan syndrome? If III-
2 and III- 7 were to mate, what is the probability that one of their children would have Nance–Horan syndrome?
Question 19
*19.Bob has XXY chromosomes (Klinefelter syndrome) and is color blind. His mother and father have normal color vision, but his maternal grandfather is color blind. Assume that Bob’s chromosome abnormality arose from nondisjunction in meiosis. In which parent and in which meiotic division did nondisjunction take place? Assume that no crossing over has taken place. Explain your answer.
Question 20
20.The Talmud, an ancient book of Jewish civil and religious laws, states that if a woman bears two sons who die of bleeding after circumcision (removal of the foreskin from the penis), any additional sons that she has should not be circumcised. (The bleeding is most likely due to the X-
Question 21
21. Craniofrontonasal syndrome (CFNS) is a birth defect in which premature fusion of the cranial sutures leads to abnormal head shape, widely spaced eyes, nasal clefts, and various other skeletal abnormalities. George Feldman and his colleagues looked at several families in which CFNS occurred and recorded the results shown in the following table (G. J. Feldman. 1997. Human Molecular Genetics 6:1937–1941).
Craniofrontonasal syndrome (CFNS) is a birth defect in which premature fusion of the cranial sutures leads to abnormal head shape, widely spaced eyes, nasal clefts, and various other skeletal abnormalities. George Feldman and his colleagues looked at several families in which CFNS occurred and recorded the results shown in the following table (G. J. Feldman. 1997. Human Molecular Genetics 6:1937–1941).
| Family number | Offspring | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parents | Normal | CFNS | ||||
| Father | Mother | Male | Female | Male | Female | |
| 1 | normal | CFNS | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 |
| 5 | normal | CFNS | 0 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| 6 | normal | CFNS | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| 8 | normal | CFNS | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 10a | CFNS | normal | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| 10b | normal | CFNS | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 |
| 12 | CFNS | normal | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 13a | normal | CFNS | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| 13b | CFNS | normal | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| 7b | CFNS | normal | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
On the basis of the families given, what is the most likely mode of inheritance for CFNS?
Give the most likely genotypes of the parents in families 1 and 10a.
Question 22
22.How many Barr bodies would you expect to see in a human cell containing the following chromosomes?
XX
XY
XO
XXY
XXYY
XXXY
XYY
XXX
XXXX
Question 23
23.What is the most likely sex and genotype of the cat shown in Figure 4.12?
Question 24
24.Red–green color blindness is an X-
Question 25
*25.Miniature wings in Drosophila result from an X-
A female fly that has miniature wings and sepia eyes is crossed with a male that has normal wings and is homozygous for red eyes. The F1 are intercrossed to produce the F2. Give the phenotypes and their proportions expected in the F1 and F2 flies from this cross.
A female fly that is homozygous for normal wings and has sepia eyes is crossed with a male that has miniature wings and is homozygous for red eyes. The F1 are intercrossed to produce the F2. Give the phenotypes and their proportions expected in the F1 and F2 flies from this cross.
Question 26
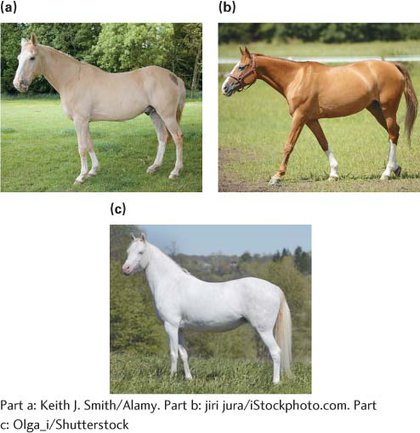
*26.Palomino horses have a golden yellow coat, chestnut horses have a brown coat, and cremello horses have a coat that is almost white. A series of crosses between the three different types of horses produced the following offspring:
| Cross | Offspring |
|---|---|
| palomino × palomino | 13 palomino, 6 chestnut, 5 cremello |
| chestnut × chestnut | 16 chestnut |
| cremello × cremello | 13 cremello |
| palomino × chestnut | 8 palomino, 9 chestnut |
| palomino × cremello | 11 palomino, 11 cremello |
| chestnut × cremello | 23 palomino |
Explain the inheritance of the palomino, chestnut, and cremello phenotypes in horses.
Assign symbols for the alleles that determine these phenotypes, and list the genotypes of all parents and offspring given in the preceding table.

Question 27
27.The LM and LN alleles at the MN blood group locus exhibit codominance. Give the expected genotypes and phenotypes and their ratios in progeny resulting from the following crosses.
LMLM × LMLN
LNLN × LNLN
LMLN × LMLN
LMLN × LNLN
LMLM × LNLN
Question 28
*28.Assume that long earlobes in humans are an autosomal dominant trait that exhibits 30% penetrance. A person who is heterozygous for long earlobes mates with a person who is homozygous for normal earlobes. What is the probability that their first child will have long earlobes?
Question 29
*29.When a Chinese hamster with white spots is crossed with another hamster that has no spots, approximately ½ of the offspring have white spots and ½ have no spots. When two hamsters with white spots are crossed, 2/3 of the offspring possess white spots and 1/3 have no spots.
What is the genetic basis of white spotting in Chinese hamsters?
How might you go about producing Chinese hamsters that breed true for white spotting?
Question 30
30. In the early 1900s, Lucien Cuénot, a French scientist working at the University of Nancy, studied the genetic basis of yellow coat color in mice. He carried out a number of crosses between two yellow mice and obtained what he thought was a 3 : 1 ratio of yellow to gray mice in the progeny. The following table gives Cuénot’s actual results, along with the results of a much larger series of crosses carried out by William Castle and Clarence Little (W. E. Castle and C. C. Little. 1910. Science 32:868–870).
In the early 1900s, Lucien Cuénot, a French scientist working at the University of Nancy, studied the genetic basis of yellow coat color in mice. He carried out a number of crosses between two yellow mice and obtained what he thought was a 3 : 1 ratio of yellow to gray mice in the progeny. The following table gives Cuénot’s actual results, along with the results of a much larger series of crosses carried out by William Castle and Clarence Little (W. E. Castle and C. C. Little. 1910. Science 32:868–870).
| Investigators | Yellow progeny | Nonyellow progeny | Total progeny |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cuénot | 263 | 100 | 363 |
| Castle and Little | 800 | 435 | 1235 |
| Both combined | 1063 | 535 | 1598 |
Using a chi-
square test, determine whether Cuénot’s results are significantly different from the 3 : 1 ratio that he thought he observed. Are they different from a 2 : 1 ratio? Determine whether Castle and Little’s results are significantly different from a 3 : 1 ratio. Are they different from a 2 : 1 ratio?
Combine the Castle and Little results with those of Cuénot and determine whether they are significantly different from a 3 : 1 ratio and a 2 : 1 ratio.
Offer an explanation for the different ratios obtained by Cuénot and by Castle and Little.
Question 31
31.In rabbits, an allelic series helps to determine coat color: C (full color), cch (chinchilla, gray color), ch (Himalayan, white with black extremities), and c (albino, all white). The C allele is dominant over all others, cch is dominant over ch and c, ch is dominant over c, and c is recessive to all the other alleles. This dominance hierarchy can be summarized as C > cch > ch > c. The rabbits in the list below are crossed and produce the progeny shown. Give the genotypes of the parents for each cross.
| Phenotypes of parents | Phenotypes of offspring | |
|---|---|---|
| a. | full color × albino | ½ full color, ½ albino |
| b. | Himalayan × albino | ½ Himalayan, ½ albino |
| c. | full color × albino | ½ full color, ½ chinchilla |
| d. | full color × Himalayan | ½ full color, ¼ Himalayan, ¼ albino |
| e. | full color × full color | ¾ full color, ¼ albino |
Question 32
*32.In this chapter, we considered Joan Barry’s paternity suit against Charlie Chaplin and how, on the basis of blood types, Chaplin could not have been the father of her child.
What blood types are possible for the father of Barry’s child?
If Chaplin had possessed one of these blood types, would that prove that he fathered Barry’s child?
Question 33
*33.In chickens, comb shape is determined by alleles at two loci (R, r and P, p). A walnut comb is produced when at least one dominant allele R is present at one locus and at least one dominant allele P is present at a second locus (genotype R_ P_). A rose comb is produced when at least one dominant allele is present at the first locus and two recessive alleles are present at the second locus (genotype R_ pp). A pea comb is produced when two recessive alleles are present at the first locus and at least one dominant allele is present at the second (genotype rr P_). If two recessive alleles are present at the first locus and at the second locus (rr pp), a single comb is produced. Progeny with what types of combs and in what proportions will result from the following crosses?

RR PP × rr pp
Rr Pp × rr pp
Rr Pp × Rr Pp
Rr pp × Rr pp
Rr pp × rr Pp
Rr pp × rr pp
Question 34
34. Tatuo Aida investigated the genetic basis of color variation in the medaka (Aplocheilus latipes), a small fish found in Japan (T. Aida. 1921. Genetics 6:554–573). Aida found that genes at two loci (B, b and R, r) determine the color of the fish: fish with a dominant allele at both loci (B_ R_) are brown, fish with a dominant allele at the B locus only (B_ rr) are blue, fish with a dominant allele at the R locus only (bb R_) are red, and fish with recessive alleles at both loci (bb rr) are white. Aida crossed a homozygous brown fish with a homozygous white fish. He then backcrossed the F1 with the homozygous white parent and obtained 228 brown fish, 230 blue fish, 237 red fish, and 222 white fish.
Tatuo Aida investigated the genetic basis of color variation in the medaka (Aplocheilus latipes), a small fish found in Japan (T. Aida. 1921. Genetics 6:554–573). Aida found that genes at two loci (B, b and R, r) determine the color of the fish: fish with a dominant allele at both loci (B_ R_) are brown, fish with a dominant allele at the B locus only (B_ rr) are blue, fish with a dominant allele at the R locus only (bb R_) are red, and fish with recessive alleles at both loci (bb rr) are white. Aida crossed a homozygous brown fish with a homozygous white fish. He then backcrossed the F1 with the homozygous white parent and obtained 228 brown fish, 230 blue fish, 237 red fish, and 222 white fish.
Give the genotypes of the backcross progeny.
Use a chi-
square test to compare the observed numbers of backcross progeny with the number expected. What conclusion can you make from your chi- square results? What results would you expect for a cross between a homozygous red fish and a white fish?
What results would you expect if you crossed a homozygous red fish with a homozygous blue fish and then backcrossed the F1 with a homozygous red parental fish?
Question 35
35. E. W. Lindstrom crossed two corn plants with green seedlings and obtained the following progeny: 3583 green seedlings, 853 virescent-
E. W. Lindstrom crossed two corn plants with green seedlings and obtained the following progeny: 3583 green seedlings, 853 virescent-
Give the genotypes for the green, virescent-
white, and yellow progeny. Explain how color is determined in these seedlings.
Does epistasis take place among the genes that determine color in the corn seedlings? If so, which gene is epistatic and which is hypostatic?
Question 36
*36.A summer-
Question 37
37.Some sweet-
Give genotypes for the purple and white flowers in these crosses.
Draw a hypothetical biochemical pathway to explain the production of purple and white flowers in sweet peas.
Question 38
*38.The direction of shell coiling in the snail Lymnaea peregra (discussed in the introduction to this chapter) results from a genetic maternal effect. An autosomal allele for a right-
Martha’s genotype must be ss.
Martha’s genotype cannot be s+s+.
All the offspring produced by Martha must be sinistral.
At least some of the offspring produced by Martha must be sinistral.
Martha’s mother must have been sinistral.
All of Martha’s brothers must be sinistral.
Question 39
39.If the F2 dextral snails with genotype S+s in Figure 4.21 undergo self-
Question 40
40.Which of the following statements is an example of a phenocopy? Explain your reasoning.
Phenylketonuria results from a recessive mutation that causes light skin as well as intellectual disability.
Human height is influenced by genes at many different loci.
Dwarf plants and mottled leaves in tomatoes are caused by separate genes that are linked.
Vestigial wings in Drosophila are produced by a recessive mutation. This trait is also produced by high temperature during development.
Intelligence in humans is influenced by both genetic and environmental factors.
Question 41
41.Match each of the following terms with its correct definition (parts a through h).
| phenocopy | sex- |
| pleiotropy | genetic maternal effect |
| polygenic trait | genomic imprinting |
| penetrance | sex- |
The percentage of individuals with a particular genotype that express the expected phenotype
A trait determined by an autosomal gene that is more easily expressed in one sex
A trait determined by an autosomal gene that is expressed in only one sex
A trait that is determined by an environmental effect and has the same phenotype as a genetically determined trait
A trait determined by genes at many loci
The expression of a trait affected by the sex of the parent that transmits the gene to the offspring
A gene affecting more than one phenotype
The influence of the genotype of the maternal parent on the phenotype of the offspring