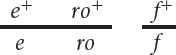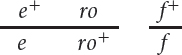APPLICATION QUESTIONS AND PROBLEMS
Question 8
8.In the snail Cepaea nemoralis, an autosomal allele causing a banded shell (BB) is recessive to the allele for an unbanded shell (BO). Genes at a different locus determine the background color of the shell; here, yellow (CY) is recessive to brown (CBw). A banded, yellow snail is crossed with a homozygous brown, unbanded snail. The F1 are then crossed with banded, yellow snails (a testcross).
What will the results of the testcross be if the loci that control banding and color are linked with no crossing over?
What will the results of the testcross be if the loci assort independently?
What will the results of the testcross be if the loci are linked and 20 m.u. apart?

Question 9
*9.In silkmoths (Bombyx mori), red eyes (re) and white-
| wild- |
418 |
| red eyes, wild- |
19 |
| wild- |
16 |
| red eyes, white- |
426 |
What phenotypic proportions would be expected if the genes for red eyes and for white-
banded wings were located on different chromosomes? What is the rate of recombination between the genes for red eyes and those for white-
banded wings?
Question 10
*10.A geneticist discovers a new mutation in Drosophila melanogaster that causes the flies to shake and quiver. She calls this mutation spastic (sps) and determines that it is due to an autosomal recessive gene. She wants to determine whether the gene encoding spastic is linked to the recessive gene for vestigial wings (vg). She crosses a fly homozygous for spastic and vestigial traits with a fly homozygous for the wild-
| vg+ | sps+ | 230 |
| vg | sps | 224 |
| vg | sps+ | 97 |
| vg+ | sps | 99 |
| Total | 650 |
Are the genes that cause vestigial wings and spastic linked? Do a chi-
Question 11
*11.In cucumbers, heart-
Question 12
12.In tomatoes, tall (D) is dominant over dwarf (d), and smooth fruit (P) is dominant over pubescent fruit (p), which is covered with fine hairs. A farmer has two tall and smooth tomato plants, which we will call plant A and plant B. The farmer crosses plants A and B with the same dwarf and pubescent plant and obtains the following numbers of progeny:
| Progeny of | ||
|---|---|---|
| Plant A | Plant b | |
| Dd Pp | 122 | 2 |
| Dd pp | 6 | 82 |
| dd Pp | 4 | 82 |
| dd pp | 124 | 4 |
What are the genotypes of plant A and plant B?
Are the loci that determine the height of the plant and pubescence linked? If so, what is the rate of recombination between them?
Explain why different proportions of progeny are produced when plant A and plant B are crossed with the same dwarf pubescent plant.
Question 13
13.Alleles A and a are at a locus on the same chromosome as is a locus with alleles B and b. Aa Bb is crossed with aa bb and the following progeny are produced:
| Aa Bb | 5 |
| Aa bb | 45 |
| aa Bb | 45 |
| aa bb | 5 |
What conclusion can be made about the arrangement of the genes on the chromosome in the Aa Bb parent?
Question 14
14.Recombination frequencies between three loci in corn are shown here.
| Loci | Recombination frequency (%) |
|---|---|
| R and W2 | 17 |
| R and L2 | 35 |
| W2 and L2 | 18 |
What is the order of the genes on the chromosome?
Question 15
15.In German cockroaches, bulging eyes (bu) are recessive to normal eyes (bu+), and curved wings (cv) are recessive to straight wings (cv+). Both traits are encoded by autosomal genes that are linked. A cockroach has genotype bu+bu cv+cv and the genes are in repulsion. Which of the following sets of genes will be found in the most common gametes produced by this cockroach?
bu+ cv+
bu cv
bu+ bu
cv+ cv
bu cv+
Explain your answer.
Question 16
*16.In Drosophila melanogaster, ebony body (e) and rough eyes (ro) are encoded by autosomal recessive genes found on chromosome 3; they are separated by 20 m.u. The gene that encodes forked bristles (f) is X-
Question 17
17.Perform a chi-
Question 18
*18.A series of two-
| Loci | Recombination frequency (%) |
|---|---|
| a and b | 50 |
| a and c | 50 |
| a and d | 12 |
| a and e | 50 |
| a and f | 50 |
| a and g | 4 |
| b and c | 10 |
| b and d | 50 |
| b and e | 18 |
| b and f | 50 |
| b and g | 50 |
| c and d | 50 |
| c and e | 26 |
| c and f | 50 |
| c and g | 50 |
| d and e | 50 |
| d and f | 50 |
| d and g | 8 |
| e and f | 50 |
| e and g | 50 |
| f and g | 50 |
Question 19
19. R. W. Allard and W. M. Clement determined recombination rates for a series of genes in lima beans (R. W. Allard and W. M. Clement. 1959. Journal of Heredity 50:63–67). The following table lists paired recombination frequencies for eight of the loci (D, Wl, R, S, L1, Ms, C, and G) that they mapped. On the basis of these data, draw a series of genetic maps for the different linkage groups of the genes, indicating the distances between the genes. Keep in mind that these frequencies are estimates of the true recombination frequencies and that some error is associated with each estimate. An asterisk beside a recombination frequency indicates that the recombination frequency is significantly different from 50%.
R. W. Allard and W. M. Clement determined recombination rates for a series of genes in lima beans (R. W. Allard and W. M. Clement. 1959. Journal of Heredity 50:63–67). The following table lists paired recombination frequencies for eight of the loci (D, Wl, R, S, L1, Ms, C, and G) that they mapped. On the basis of these data, draw a series of genetic maps for the different linkage groups of the genes, indicating the distances between the genes. Keep in mind that these frequencies are estimates of the true recombination frequencies and that some error is associated with each estimate. An asterisk beside a recombination frequency indicates that the recombination frequency is significantly different from 50%.
| Recombination Frequencies (%) among Seven Loci in Lima Beans | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wl | R | S | L1 | Ms | C | G | |
| D | 2.1* | 39.3* | 52.4 | 48.1 | 53.1 | 51.4 | 49.8 |
| Wl | 38.0* | 47.3 | 47.7 | 48.8 | 50.3 | 50.4 | |
| R | 51.9 | 52.7 | 54.6 | 49.3 | 52.6 | ||
| S | 26.9* | 54.9 | 52.0 | 48.0 | |||
| L1 | 48.2 | 45.3 | 50.4 | ||||
| Ms | 14.7* | 43.1 | |||||
| C | 52.0 | ||||||
* Significantly different from 50%
Question 20
*20.Waxy endosperm (wx), shrunken endosperm (sh), and yellow seedlings (v) are encoded by three recessive genes in corn that are linked on chromosome 5. A corn plant homozygous for all three recessive alleles is crossed with a plant homozygous for all the dominant alleles. The resulting F1 are then crossed with a plant homozygous for the recessive alleles in a three-
| wx | sh | V | 87 |
| Wx | Sh | v | 94 |
| Wx | Sh | V | 3,479 |
| wx | sh | v | 3,478 |
| Wx | sh | V | 1,515 |
| wx | Sh | v | 1,531 |
| wx | Sh | V | 292 |
| Wx | sh | v | 280 |
| Total | 10,756 |
Determine the order of these genes on the chromosome.
Calculate the map distances between the genes.
Determine the coefficient of coincidence and the interference among these genes.
Question 21
21. Priscilla Lane and Margaret Green studied the linkage relations of three genes affecting coat color in mice: mahogany (mg), agouti (a), and ragged (Rg). They carried out a series of three-
Priscilla Lane and Margaret Green studied the linkage relations of three genes affecting coat color in mice: mahogany (mg), agouti (a), and ragged (Rg). They carried out a series of three-
| Phenotype | Number | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| a | Rg | + | 1 |
| + | + | mg | 1 |
| a | + | + | 15 |
| + | Rg | mg | 9 |
| + | + | + | 16 |
| a | Rg | mg | 36 |
| a | + | mg | 76 |
| + | Rg | + | 69 |
| Total | 213 | ||
Note: + represents a wild-
Determine the order of the loci that encode mahogany, agouti, and ragged on the chromosome, the map distances between them, and the interference and coefficient of coincidence for these genes.
Draw a picture of the two chromosomes in the triply heterozygous mice used in the testcrosses, indicating which of the alleles are present on each chromosome.
Question 22
22. Fine spines (s), smooth fruit (tu), and uniform fruit color (u) are three recessive traits in cucumbers, the genes for which are linked on the same chromosome. A cucumber plant heterozygous for all three traits is used in a testcross, and the following progeny are produced by this testcross:
| S | U | Tu | 2 |
| s | u | Tu | 70 |
| S | u | Tu | 21 |
| s | u | tu | 4 |
| S | U | tu | 82 |
| s | U | tu | 21 |
| s | U | Tu | 13 |
| S | u | tu | 17 |
| Total | 230 |
Determine the order of these genes on the chromosome.
Calculate the map distances between the genes.
Determine the coefficient of coincidence and the interference among these genes.
List the genes found on each chromosome in the parents used in the testcross.
Question 23
*23. Raymond Popp studied linkage among genes for pink eye (p), shaker-
Raymond Popp studied linkage among genes for pink eye (p), shaker-
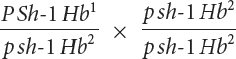
The following progeny were produced:
| Progeny genotype | Number |
|---|---|
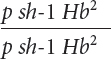 |
274 |
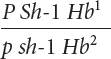 |
320 |
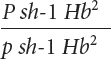 |
57 |
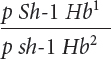 |
45 |
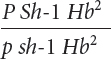 |
6 |
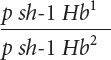 |
5 |
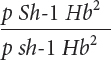 |
0 |
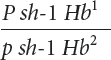 |
1 |
| Total | 708 |
Determine the order of these genes on the chromosome.
Calculate the map distances between the genes.
Determine the coefficient of coincidence and the interference among these genes.
Question 24
*24.In Drosophila melanogaster, black body (b) is recessive to gray body (b+), purple eyes (pr) are recessive to red eyes (pr+), and vestigial wings (vg) are recessive to normal wings (vg+). The loci encoding these traits are linked, with the following map distances:

The interference among these genes is 0.5. A fly with a black body, purple eyes, and vestigial wings is crossed with a fly homozygous for a gray body, red eyes, and normal wings. The female progeny are then crossed with males that have a black body, purple eyes, and vestigial wings. If 1000 progeny are produced by this testcross, what will be the phenotypes and proportions of the progeny?
Question 25
25.Sepia eyes, spineless bristles, and striped thorax are three recessive mutations in Drosophila found on chromosome 3. A genetics student crosses a fly homozygous for sepia eyes, spineless bristles, and striped thorax with a fly homozygous for the wild-
Question 26
26.Eight DNA sequences from different individuals are given in the diagram below.
| Nucleotide position | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 5 10 15 | ||||
| Sequence 1 | ....T C T G G A T C A T C A C A T... | |||
| Sequence 2 | ....A C A G C A T C A T T A C G T... | |||
| Sequence 3 | ....T C A G G A T C A T T A C T A... | |||
| Sequence 4 | ....T C A G G A T C A T T A C A T... | |||
| Sequence 5 | ....A C A G C A T C A T T A C G T... | |||
| Sequence 6 | ....T C T G G A T C A T C A C A T... | |||
| Sequence 7 | ....T C A G G A T C A T T A C A T... | |||
| Sequence 8 | ....A C A G C A T C A T T A C G T... | |||
Give the nucleotide positions of all single-
nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs; nucleotide positions where individuals vary in which base is present) in these sequences. How many different haplotypes (sets of linked variants) are found in these eight sequences?
Give the haplotype of each sequence by listing the specific bases at each variable position in that particular haplotype. (Hint: See Figure 15.6.)