CHALLENGE QUESTION
Question 27
27. Transferrin is a blood protein encoded by the transferrin locus (Trf). In house mice, the two alleles at this locus (Trf a and Trf b) are codominant and encode three types of transferrin:
Transferrin is a blood protein encoded by the transferrin locus (Trf). In house mice, the two alleles at this locus (Trf a and Trf b) are codominant and encode three types of transferrin:
| Genotype | Phenotype |
|---|---|
| Trf a/Trf a | Trf- |
| Trf a/Trf b | Trf- |
| Trf b/Trf b | Trf- |
The dilution locus, found on the same chromosome, determines whether the color of a mouse is diluted or full; an allele for dilution (d) is recessive to an allele for full color (d+):
| Genotype | Phenotype |
|---|---|
| d+d+ | d+ (full color) |
| d+d | d+ (full color) |
| dd | d (dilution) |
Donald Shreffler conducted a series of crosses to determine the map distance between the transferrin locus and the dilution locus (D. C. Shreffler. 1963. Journal of Heredity 54:127–129). The following table presents a series of crosses carried out by Shreffler and the progeny resulting from these crosses.
| Progeny phenotypes | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d+ | d+ | d | d | ||||
| Cross | 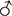 |
 |
Trf- |
Trf- |
Trf- |
Trf- |
Total |
| 1 | 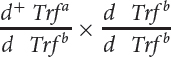 |
32 | 3 | 6 | 21 | 62 | |
| 2 | 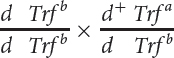 |
16 | 0 | 2 | 20 | 38 | |
| 3 | 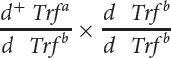 |
35 | 9 | 4 | 30 | 78 | |
| 4 | 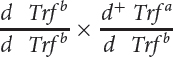 |
21 | 3 | 2 | 19 | 45 | |
| 5 | 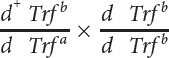 |
8 | 29 | 22 | 5 | 64 | |
| 6 | 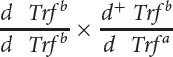 |
4 | 14 | 11 | 0 | 29 | |
Calculate the recombination frequency between the Trf and the d loci by using the pooled data from all the crosses.
Which crosses represent recombination in male gamete formation and which crosses represent recombination in female gamete formation?
On the basis of your answer to part b, calculate the frequency of recombination among male parents and female parents separately.
Are the rates of recombination in males and females the same? If not, what might produce the difference?
