Printed Page 152(cont.)
Types of Chromosome Mutations
Chromosome mutations can be grouped into three basic categories: chromosome rearrangements, aneuploidy, and polyploidy (Figure 6.3). Chromosome rearrangements alter the structure of chromosomes; for example, a piece of a chromosome may be duplicated, deleted, or inverted. In aneuploidy, the number of chromosomes is altered: one or more individual chromosomes are added or deleted. In polyploidy, one or more complete sets of chromosomes are added. A polyploid is any organism that has more than two sets of chromosomes (3n, 4n, 5n, or more).
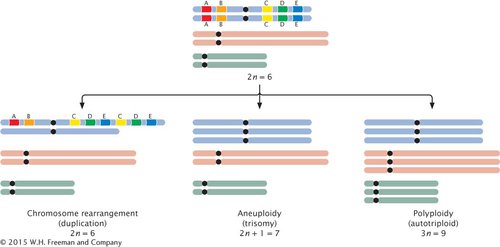
6.3 Chromosome mutations consist of chromosome rearrangements, aneuploidy, and polyploidy. An example of each category of mutation is shown here.
[Leave] [Close]