Deletions
A second type of chromosome rearrangement is a chromosome deletion, the loss of a chromosome segment (see Figure 6.4b). A chromosome with segments AB•CDEFG that undergoes a deletion of segment EF would generate the mutated chromosome AB•CDG.
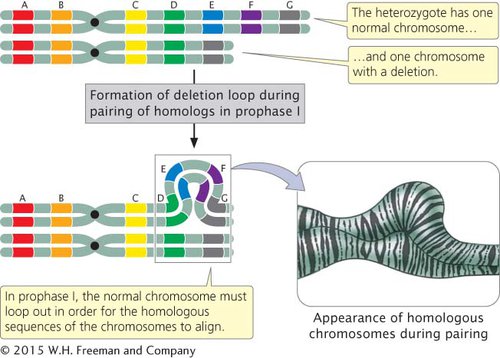
A large deletion can be easily detected because the chromosome is noticeably shortened. In individuals heterozygous for deletions, the normal chromosome must loop out during the pairing of homologs in prophase I of meiosis (Figure 6.9) to allow the homologous regions of the two chromosomes to align and undergo synapsis. This looping out generates a structure that looks very much like that seen in individuals heterozygous for duplications.
EFFECTS OF DELETIONS The phenotypic consequences of a deletion depend on which genes are located in the deleted region. If the deletion includes the centromere, the chromosome will not segregate in meiosis or mitosis and will usually be lost. Many deletions are lethal in the homozygous state because all copies of any essential genes located in the deleted region are missing.
Even individuals heterozygous for a deletion may have multiple defects, for three reasons. First, the heterozygous condition may produce imbalances in the amounts of gene products, similar to the imbalances produced by extra gene copies. Second, normally recessive mutations on the homologous chromosome lacking the deletion may be expressed when the wild-
Third, some genes must be present in two copies for normal function. When a single copy of a gene is not sufficient to produce a wild-

CONCEPTS
A chromosome deletion is a mutation in which a part of a chromosome is lost. In individuals heterozygous for a deletion, the normal chromosome loops out during prophase I of meiosis. Deletions cause recessive genes on the homologous chromosome to be expressed and may cause imbalances in gene products.
 CONCEPT CHECK 2
CONCEPT CHECK 2
What is pseudodominance and how is it produced by a chromosome deletion?
Pseudodominance is the expression of a normally recessive mutation that is produced when the dominant wild-