APPLICATION QUESTIONS AND PROBLEMS
Question 17
17.The introduction to this chapter, which describes the sequencing of 4000-
Question 18
18.Match the scientists with the discoveries listed.
Kossel
Watson and Crick
Levene
Miescher
Hershey and Chase
Avery, MacLeod, and McCarty
Griffith
Franklin and Wilkins
Chargaff
— Took X-
— Determined that DNA contains nitrogenous bases.
— Identified DNA as the genetic material in bacteriophage.
— Discovered regularity in the ratios of different bases in DNA.
— Determined that DNA is responsible for transformation in bacteria.
— Worked out the helical structure of DNA by building models.
— Discovered that DNA consists of repeating nucleotides.
— Determined that DNA is acidic and high in phosphorus.
— Demonstrated that heat-
Question 19
*19.A student mixes some heat-
Question 20
20.Predict what would have happened if Griffith had mixed some heat-
Question 21
*21.DNA molecules of different sizes are often separated with the use of a technique called electrophoresis (see Chapter 14). With this technique, DNA molecules are placed in a gel, an electrical current is applied to the gel, and the DNA molecules migrate toward the positive (+) pole of the current. What aspect of its structure causes a DNA molecule to migrate toward the positive pole?
Question 22
*22. Erwin Chargaff collected data on the proportions of nucleotide bases from the DNA of a variety of different organisms and tissues (E. Chargaff, in The Nucleic Acids: Chemistry and Biology, vol. 1, E. Chargaff and J. N. Davidson, Eds. New York: Academic Press, 1955). Data from the DNA of several organisms analyzed by Chargaff are shown here.
Erwin Chargaff collected data on the proportions of nucleotide bases from the DNA of a variety of different organisms and tissues (E. Chargaff, in The Nucleic Acids: Chemistry and Biology, vol. 1, E. Chargaff and J. N. Davidson, Eds. New York: Academic Press, 1955). Data from the DNA of several organisms analyzed by Chargaff are shown here.
| Percent | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organism and tissue | A | G | C | T |
| Sheep thymus | 29.3 | 21.4 | 21.0 | 28.3 |
| Pig liver | 29.4 | 20.5 | 20.5 | 29.7 |
| Human thymus | 30.9 | 19.9 | 19.8 | 29.4 |
| Rat bone marrow | 28.6 | 21.4 | 20.4 | 28.4 |
| Hen erythrocytes | 28.8 | 20.5 | 21.5 | 29.2 |
| Yeast | 31.7 | 18.3 | 17.4 | 32.6 |
| E. coli | 26.0 | 24.9 | 25.2 | 23.9 |
| Human sperm | 30.9 | 19.1 | 18.4 | 31.6 |
| Salmon sperm | 29.7 | 20.8 | 20.4 | 29.1 |
| Herring sperm | 27.8 | 22.1 | 20.7 | 27.5 |
For each organism, compute the ratio of (A + G)/(T + C) and the ratio of (A + T)/(C + G).
Are these ratios constant or do they vary among the organisms? Explain why.
Is the (A + G)/(T + C) ratio different for the sperm samples? Would you expect it to be? Why or why not?

Question 23
23. Boris Magasanik collected data on the amounts of the bases of RNA isolated from a number of sources (shown in the next column), expressed relative to a value of 10 for adenine (B. Magasanik, in The Nucleic Acids: Chemistry and Biology, vol. 1, E. Chargaff and J. N. Davidson, Eds. New York: Academic Press, 1955).
Boris Magasanik collected data on the amounts of the bases of RNA isolated from a number of sources (shown in the next column), expressed relative to a value of 10 for adenine (B. Magasanik, in The Nucleic Acids: Chemistry and Biology, vol. 1, E. Chargaff and J. N. Davidson, Eds. New York: Academic Press, 1955).
| Percent | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organism and tissue | A | G | C | U |
| Rat liver nuclei | 10 | 14.8 | 14.3 | 12.9 |
| Rabbit liver nuclei | 10 | 13.6 | 13.1 | 14.0 |
| Cat brain | 10 | 14.7 | 12.0 | 9.5 |
| Carp muscle | 10 | 21.0 | 19.0 | 11.0 |
| Yeast | 10 | 12.0 | 8.0 | 9.8 |
For each organism, compute the ratio of (A + G)/(U + C).
How do these ratios compare with the (A + G)/(T + C) ratio found in DNA (see Problem 22)? Explain.
Question 24
24.Which of the following relations or ratios would be true for a double-
A + T = G + C
A + T = T + C
A + C = G + T
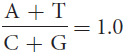
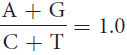
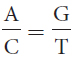
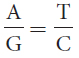
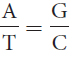
Question 25
*25.If a double-
Question 26
26. Heinz Shuster collected the following data on the base composition of the ribgrass virus (H. Shuster, in The Nucleic Acids: Chemistry and Biology, vol. 3, E. Chargaff and J. N. Davidson, Eds. New York: Academic Press, 1955). On the basis of this information, is the hereditary information of the ribgrass virus RNA or DNA? Is it likely to be single stranded or double stranded?
Heinz Shuster collected the following data on the base composition of the ribgrass virus (H. Shuster, in The Nucleic Acids: Chemistry and Biology, vol. 3, E. Chargaff and J. N. Davidson, Eds. New York: Academic Press, 1955). On the basis of this information, is the hereditary information of the ribgrass virus RNA or DNA? Is it likely to be single stranded or double stranded?
| Percent | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | G | C | T | U | |
| Ribgrass virus | 29.3 | 25.8 | 18.0 | 0.0 | 27.0 |

Question 27
*27.For entertainment on a Friday night, a genetics professor proposed that his children diagram a polynucleotide strand of DNA. Having learned about DNA in preschool, his five-
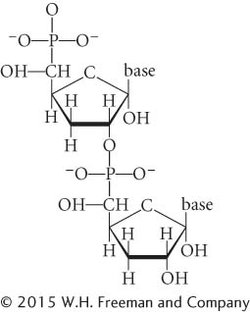
Make a list of all the mistakes in the structure of this DNA polynucleotide strand.
Draw the correct structure for the polynucleotide strand.
Question 28
28.28.One nucleotide strand of a DNA molecule has the base sequence illustrated below.
5′—ATTGCTACGG—
Give the base sequence and label the 5′ and 3′ ends of the complementary DNA nucleotide strand.
Question 29
*29.Chapter 1 considered the theory of the inheritance of acquired characteristics and noted that this theory is no longer accepted. Is the central dogma consistent with the theory of the inheritance of acquired characteristics? Why or why not?
Question 30
30.Which of the processes of information transfer illustrated in Figure 8.14 are required for the T2 phage reproduction illustrated in Figure 8.4?
Question 31
*31.Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic chromosomes. How are they alike and how do they differ?
Question 32
*32.A diploid human cell contains approximately 6.4 billion base pairs of DNA.
How many nucleosomes are present in such a cell? (Assume that the linker DNA encompasses 40 bp.)
How many histone proteins are complexed with this DNA?