THE DIGESTION OF CARBOHYDRATES
Before complex carbohydrates can be used for energy, they need to be broken down into their component sugar molecules. Only monosaccharides, such as glucose, can be absorbed by the cells of the small intestine.
Enzymes in carbohydrate digestion

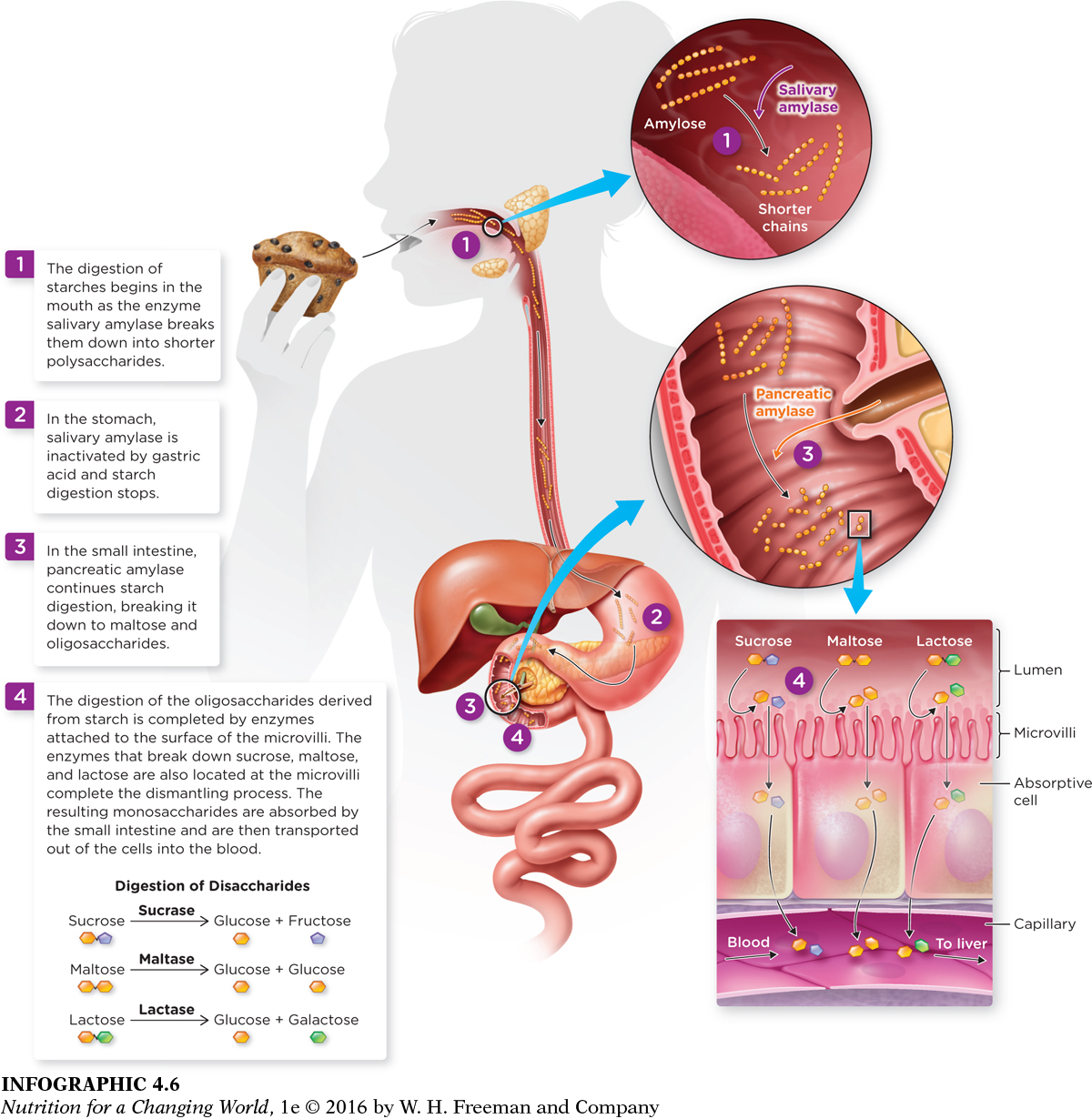
The body uses specific enzymes to break down carbohydrates. Different enzymes are specific for different carbohydrates. In the mouth, the enzyme salivary amylase breaks down starch molecules into shorter polysaccharides. In the small intestine, the enzyme pancreatic amylase digests starch into oligosaccharides and maltose; maltase is the enzyme that breaks maltose down into two glucose units; sucrase digests sucrose into fructose and glucose; and lactase breaks down lactose into glucose and galactose. These monosaccharides can be absorbed by the cells lining the small intestine, and from there travel into the blood. (INFOGRAPHIC 4.6)
Question 4.6
 To be absorbed, carbohydrates must be in what form?
To be absorbed, carbohydrates must be in what form?
Carbohydrates must be in the form of monosaccharides to be absorbed.
LACTOSE INTOLERANCE a condition characterized by diminished levels of the enzyme lactase and subsequent reduced ability to digest the disaccharide lactase
Some people experience gastrointestinal discomfort after drinking milk or consuming some dairy foods, a condition called lactose intolerance, which is the result of producing low levels of lactase in the intestines. In most people, lactase levels decline with age, but different populations of humans make differing amounts of lactase as adults, and so some people are more prone to lactose intolerance than others. Luckily, the treatment for lactose intolerance is fairly straightforward: Cut back on dairy products. There are also many lactose-
Glucose in the body
Of the several monosaccharides released from carbohydrates through the process of digestion, glucose is the one that all of our cells use as fuel. Fructose and galactose are taken up primarily by the liver where they can be converted into glucose, which then may be exported back into the blood for distribution to cells throughout the body.

Any glucose the body doesn’t use to meet its immediate energy needs is stored for later use. The liver and skeletal muscles use this excess glucose to synthesize glycogen. The liver will break down this glycogen into glucose when needed to maintain normal blood sugar levels, and skeletal muscles will use it to fuel muscle contractions during intense exercise.
Different carbohydrate-