TYPE 2 DIABETES

Interestingly, in the past several decades, the number of people with diabetes has doubled. Some of that increase is due to an aging population, as people with type 1 diabetes now live longer. But most of the dramatic rise in diabetes is due to an increase in a second form of the disease—
Although type 1 diabetes is typically diagnosed in children and young adults, type 2 is most frequently seen in adults. Unlike type 1, in which insulin-
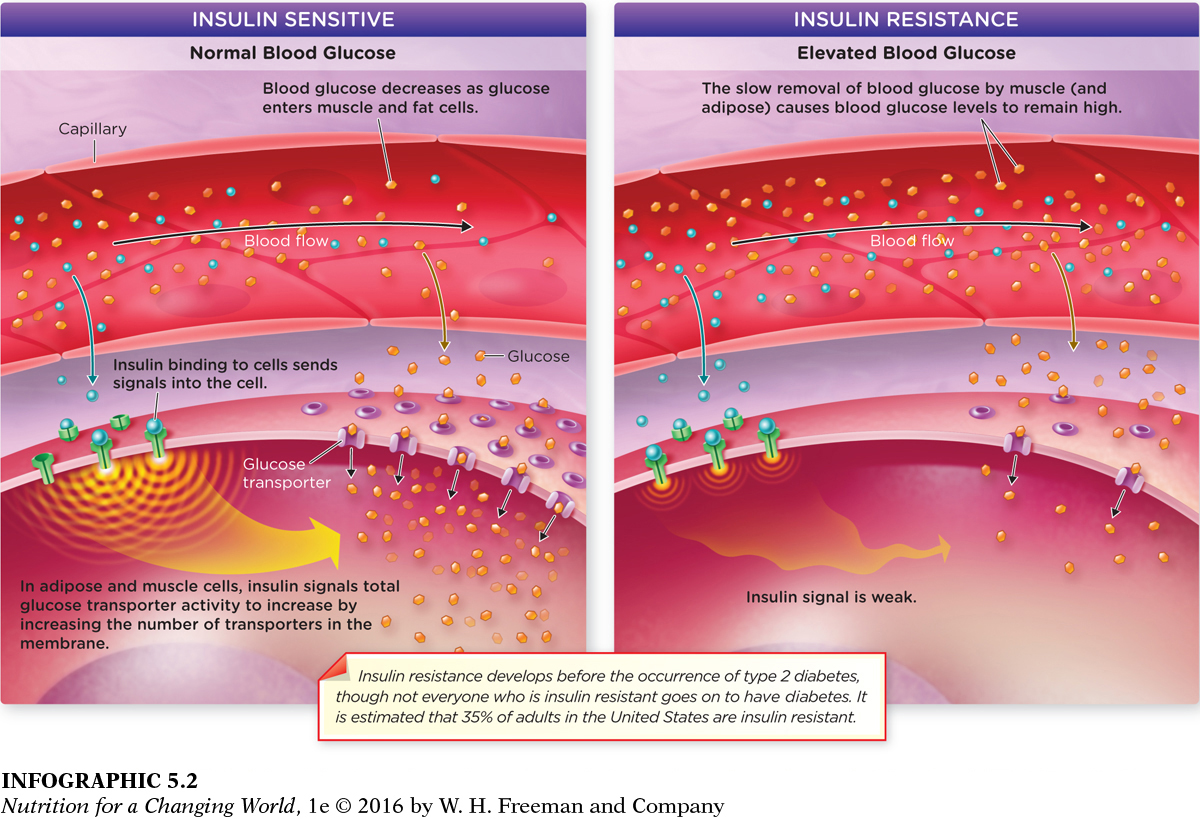
INSULIN RESISTANCE a condition in which cells have a decreased sensitivity to insulin, resulting in impaired glucose uptake from blood, increased blood glucose levels, and further insulin release from the pancreas
TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS a condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels due to insulin sensitivity (or resistance) and some impairment of insulin secretion from the pancreas
Type 2 diabetes begins with the development of insulin resistance. Most often this occurs because excess adipose tissue produces hormone-
Question 5.2
 How does insulin resistance in the liver contribute to elevated blood glucose?
How does insulin resistance in the liver contribute to elevated blood glucose?
In insulin resistance, muscle, fat, and liver cells do not respond properly to insulin, thus cannot easily absorb glucose from the bloodstream. As a result, the body needs higher levels of insulin to help glucose enter cells. Cells in the pancreas try to keep up with an increased demand for insulin by producing more insulin. Because the activity of glucose transporters is impaired, excess glucose builds up in the bloodstream, leading to diabetes, prediabetes, and other serious health disorders.
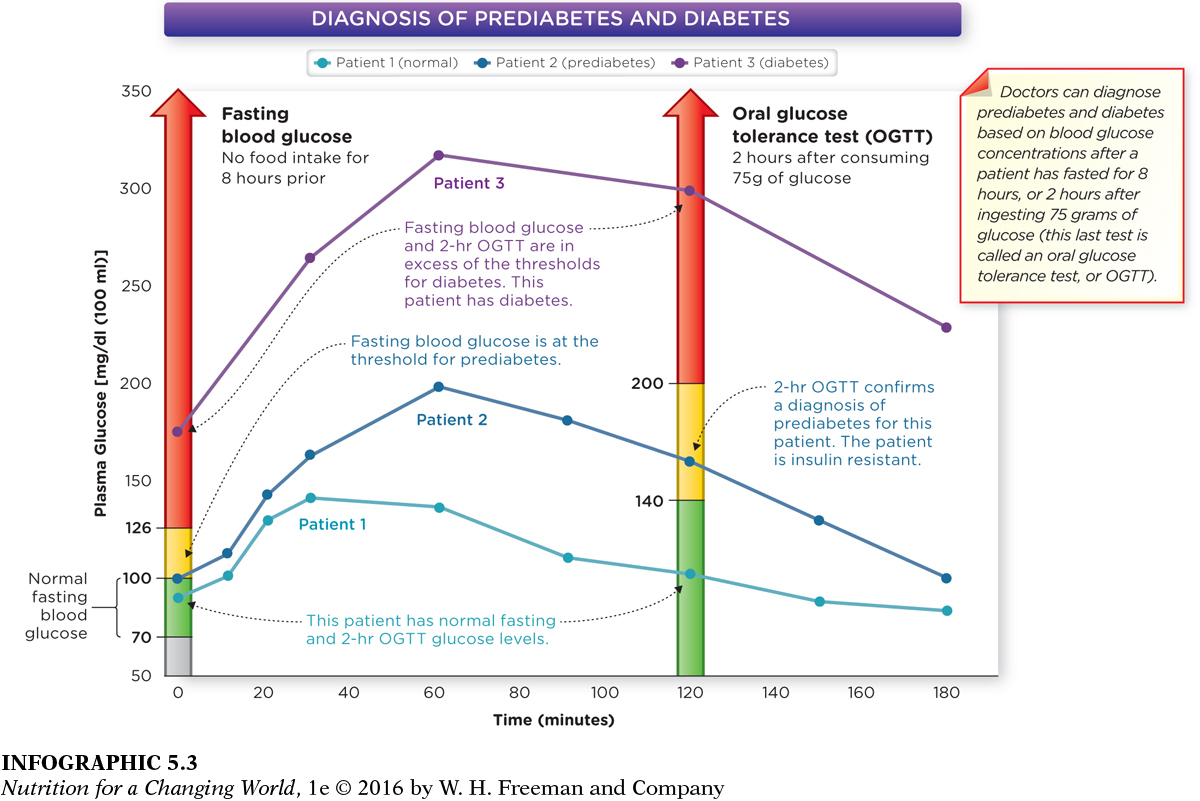
PREDIABETES a condition of higher-
ORAL GLUCOSE TOLERANCE TEST (OGTT) a test used to diagnose prediabetes and diabetes; it measures the body’s response to glucose in the bloodstream
Without intervention and lifestyle changes, many people who have insulin resistance go on to develop type 2 diabetes. However, they may first develop prediabetes, a condition in which blood glucose levels are moderately elevated above levels that are considered normal or desirable. For example, after fasting for eight hours, the blood glucose levels of someone with prediabetes would measure 100 mg to 125 mg per 100 ml blood, which is elevated but still less than the fasting level of at least 126 mg per ml that is required for a diagnosis of diabetes. After ingesting glucose as part of an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), the same person would have elevated blood glucose levels in the 140 mg to 199 mg per 100 ml range—
Question 5.3
 What condition causes blood glucose to remain at higher-
What condition causes blood glucose to remain at higher-
Insulin resistance causes higher-
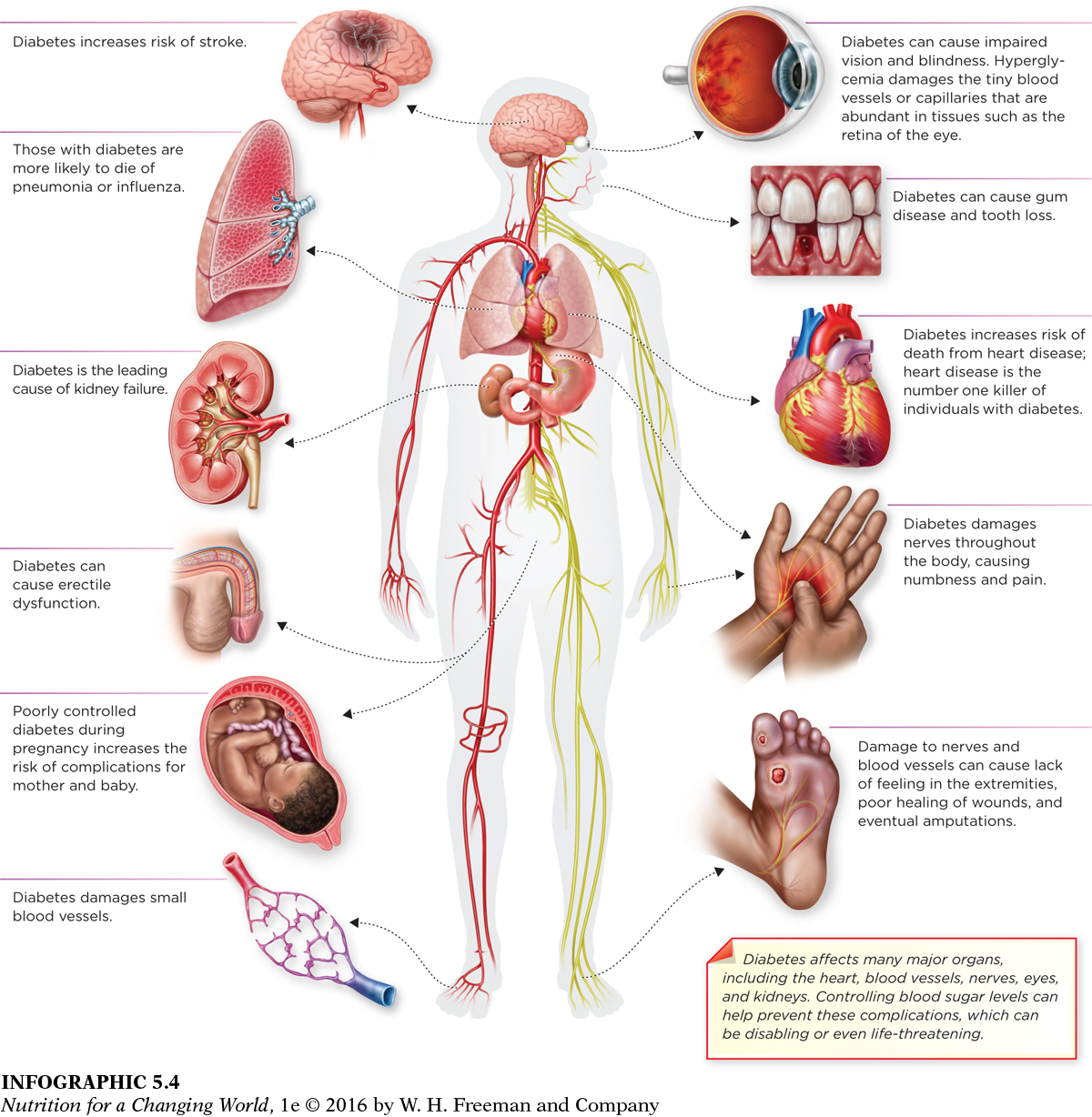
Because all forms of diabetes decrease the body’s ability to remove glucose from the blood, each can cause blood glucose concentrations to increase to dangerous levels, leading to similar symptoms—
Question 5.4
 What is the leading cause of death among those with diabetes?
What is the leading cause of death among those with diabetes?
Diabetes increases the risk of death from heart disease; heart disease is the number one killer of individuals with diabetes.
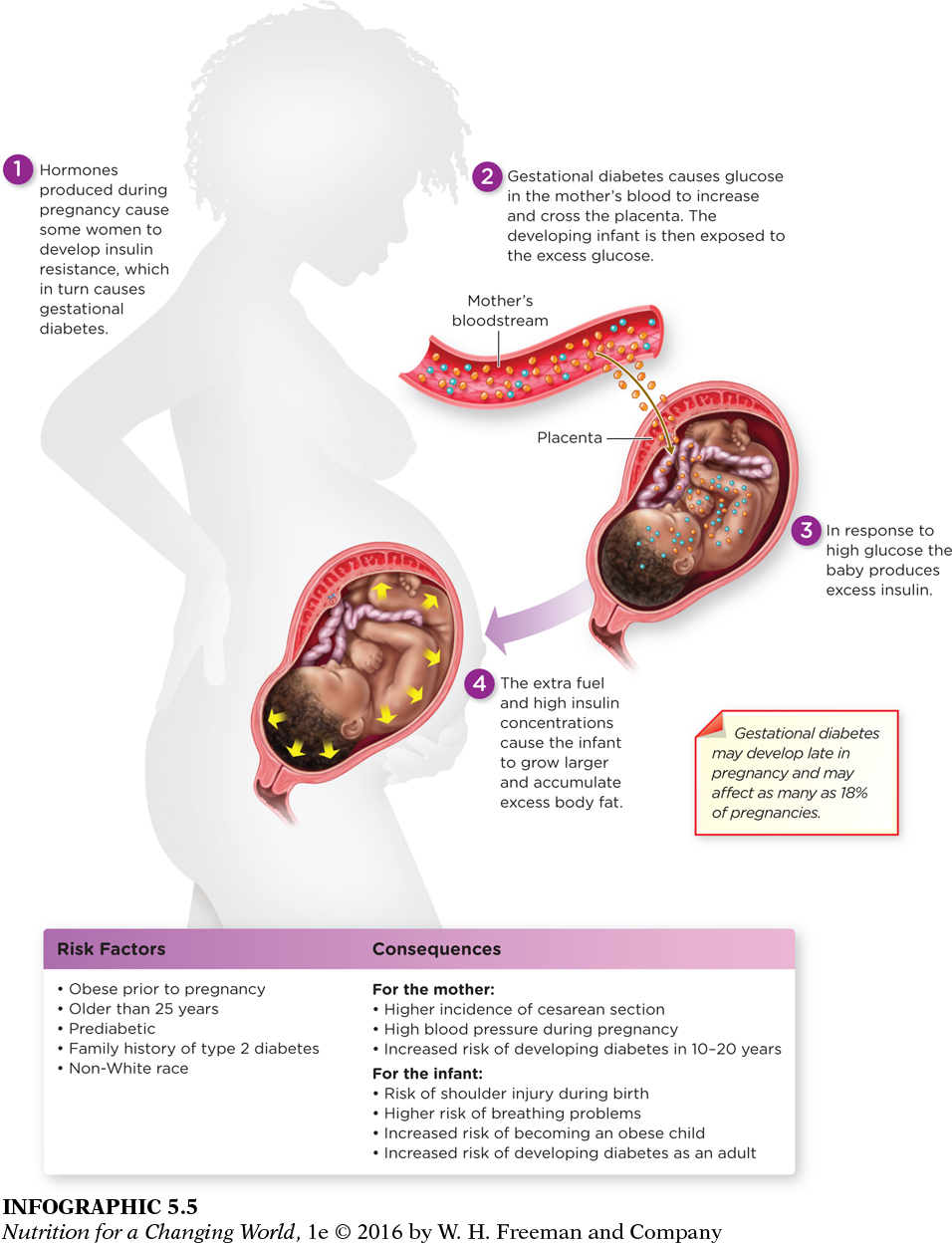
Gestational diabetes
GESTATIONAL DIABETES a condition of elevated blood glucose levels arising in approximately 18% of all pregnant women, most of whom revert to normal blood glucose levels after delivery
Pregnant women can develop a form of diabetes known as gestational diabetes. Approximately 18% of expectant mothers will experience high blood glucose levels for the first time during pregnancy, and this can affect their pregnancy—
Question 5.5
 What risk factors for gestational diabetes are similar to risk factors for type 2 diabetes?
What risk factors for gestational diabetes are similar to risk factors for type 2 diabetes?
Risk factors for both gestational diabetes and type 2 diabetes include obesity, inactivity, family history of type 2 diabetes, and non-