ATHEROSCLEROSIS AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE
ATHEROSCLEROSIS a type of cardiovascular disease characterized by the narrowing and loss of elasticity of blood vessel walls, caused by accumulation of plaque and inflammation of tissue
Although often called “heart disease,” CVD strikes the blood vessels—
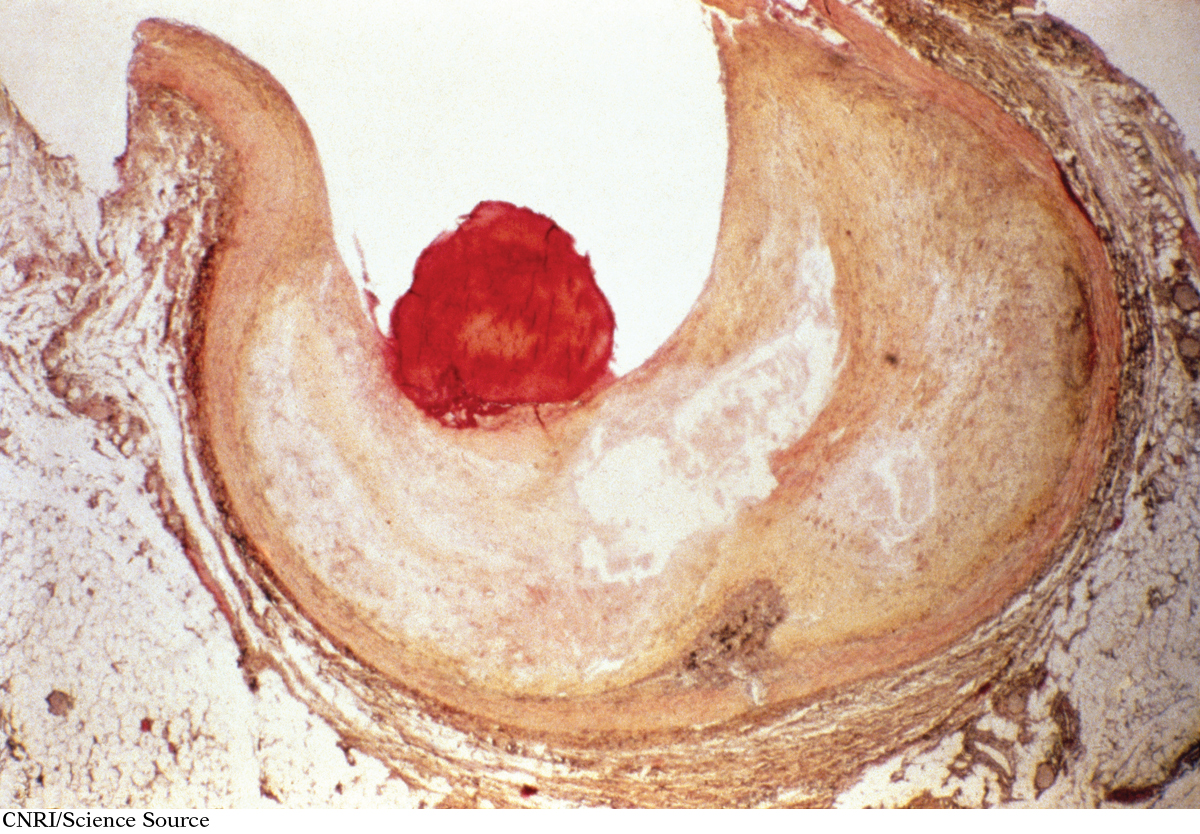
PLAQUE deposits of cholesterol, triglycerides, and cell materials that accumulate within the arterial wall
MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION (HEART ATTACK) damage to heart tissue caused by decreased blood flow to the coronary arteries
STROKE cerebral event that occurs when blood vessels supplying the brain are damaged or blocked
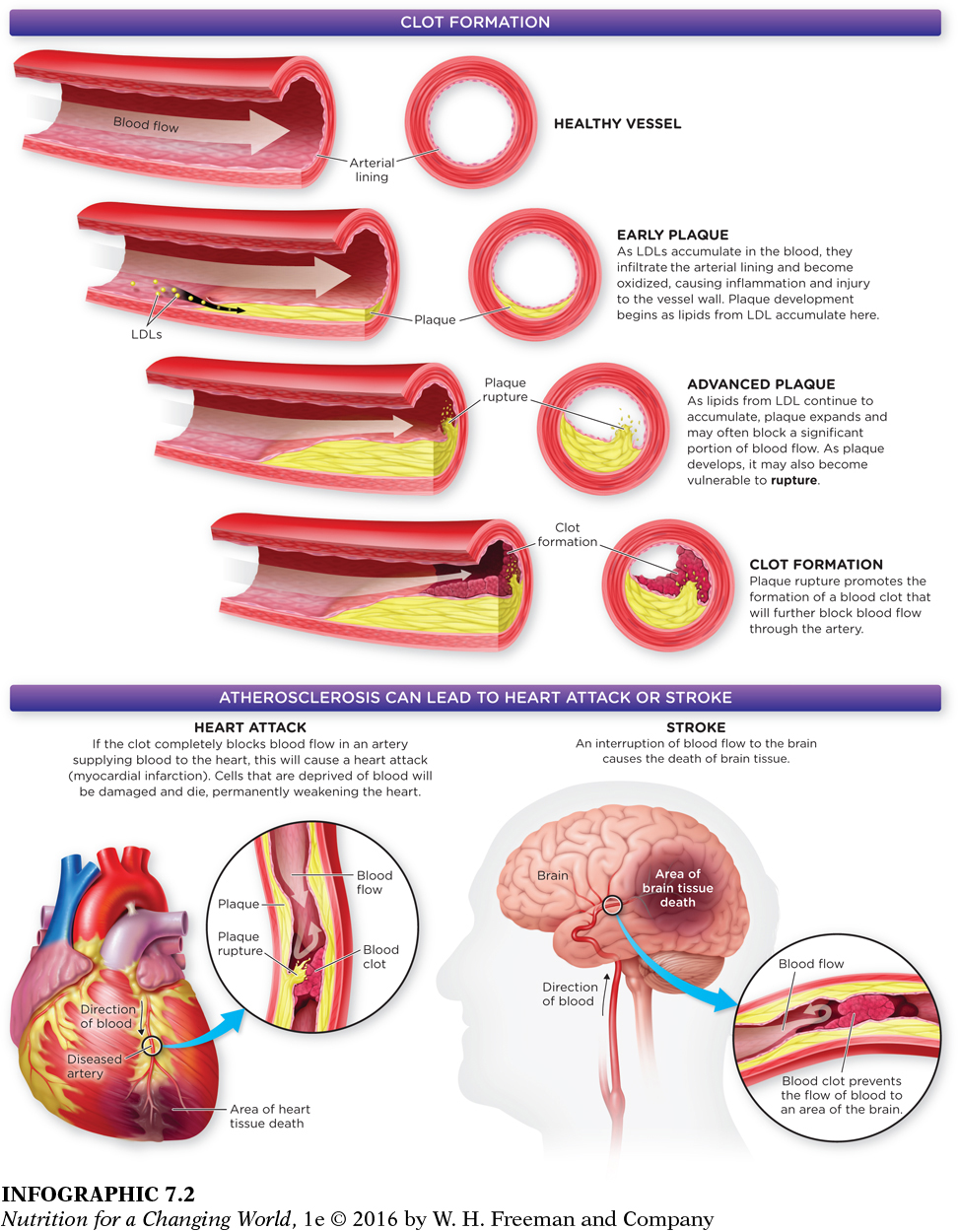
As a result, the lining of the blood vessel becomes more prone to develop a waxy accumulation of cholesterol and triglycerides, known as a plaque. Over time, plaque development, loss of elasticity, and thickening in the blood vessel walls may make it difficult for blood to flow through the vessel. This “traffic jam” increases the chances of forming blood clots that either block flow at that location or break off and travel through the bloodstream, blocking blood flow elsewhere, causing tissue damage and tissue death. When blood flow is blocked in the coronary artery, which supplies blood to the heart, people experience a heart attack, or myocardial infarction. Most cases of stroke result when a clot impairs the supply of blood to the brain. (INFOGRAPHIC 7.2)
Question 7.1
 Where in the blood vessel do LDLs have to be located to promote the development of atherosclerosis?
Where in the blood vessel do LDLs have to be located to promote the development of atherosclerosis?
LDL attaches to the lining of an artery and promotes the progression of atherosclerosis.
■ ■ ■
For the most part, young people do not have heart attacks (and those that do usually suffer from rare genetic conditions). But just because most teenagers do not die from heart disease does not mean they can ignore heart health. That’s because heart disease can be insidiously gaining a foothold long before we have any obvious symptoms.
When Gerald Berenson started his study in 1972, this was far from accepted wisdom. Cardiologists—
Question 7.2
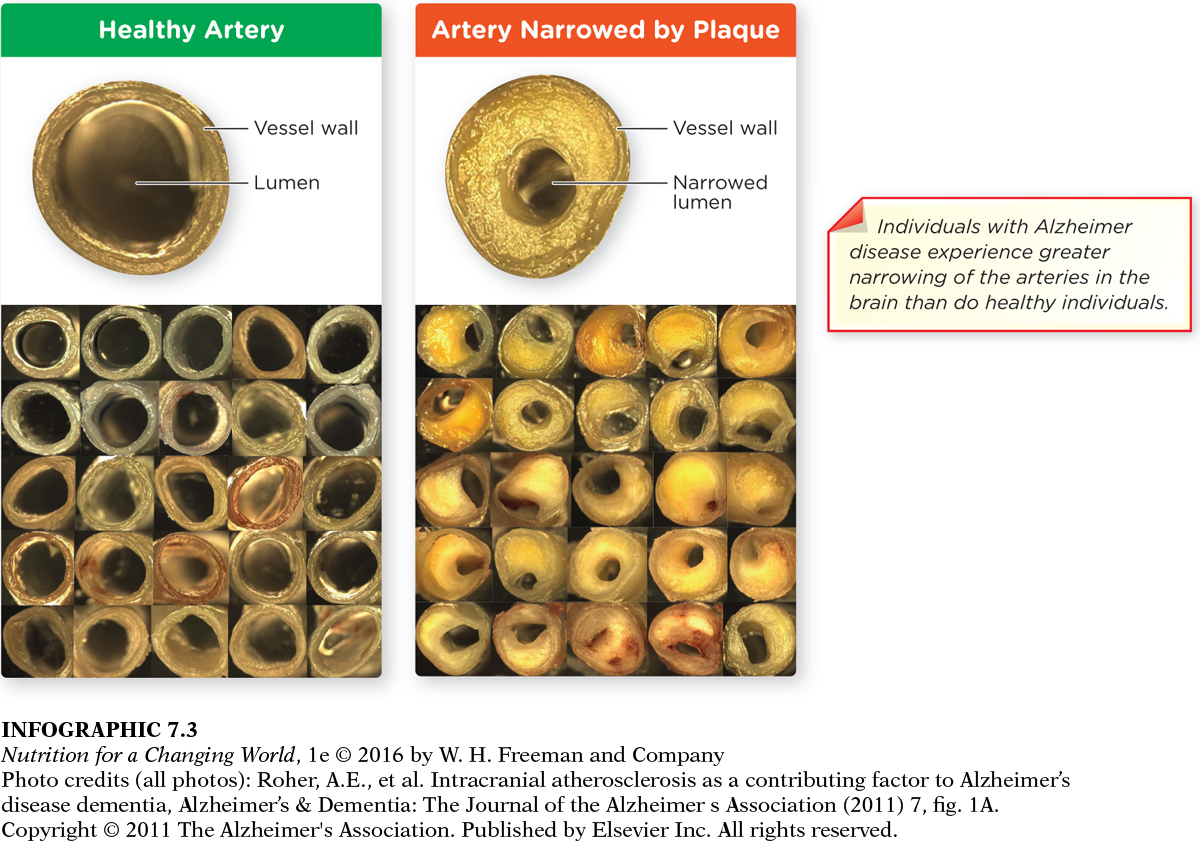
 Why might atherosclerosis in cerebral arteries contribute to dementia?
Why might atherosclerosis in cerebral arteries contribute to dementia?
Atherosclerosis in cerebral arteries causes reduced blood flow to the brain and may contribute to dementia.
He decided to follow children and young people ages 5 to 17 years in the local school system, monitoring them twice yearly. Nurses measured their height, weight, smoking history, blood pressure, and blood lipid levels, among other variables. After age 17, they returned for evaluation periodically, up to age 45. Later, it was decided that any of the study participants who died would be autopsied.
From small beginnings, the study grew to enroll some 16,000 individuals. It is now one of the longest-
RISK FACTOR any characteristic, condition, or behavior that increases the likelihood of developing a particular disease
Although the exact cause of CVD is often unknown, the Bogalusa study has shown there are certain risk factors that increase young people’s chances of developing problems—