Chapter Introduction
8
PROTEIN

LEARNING OBJECTIVES
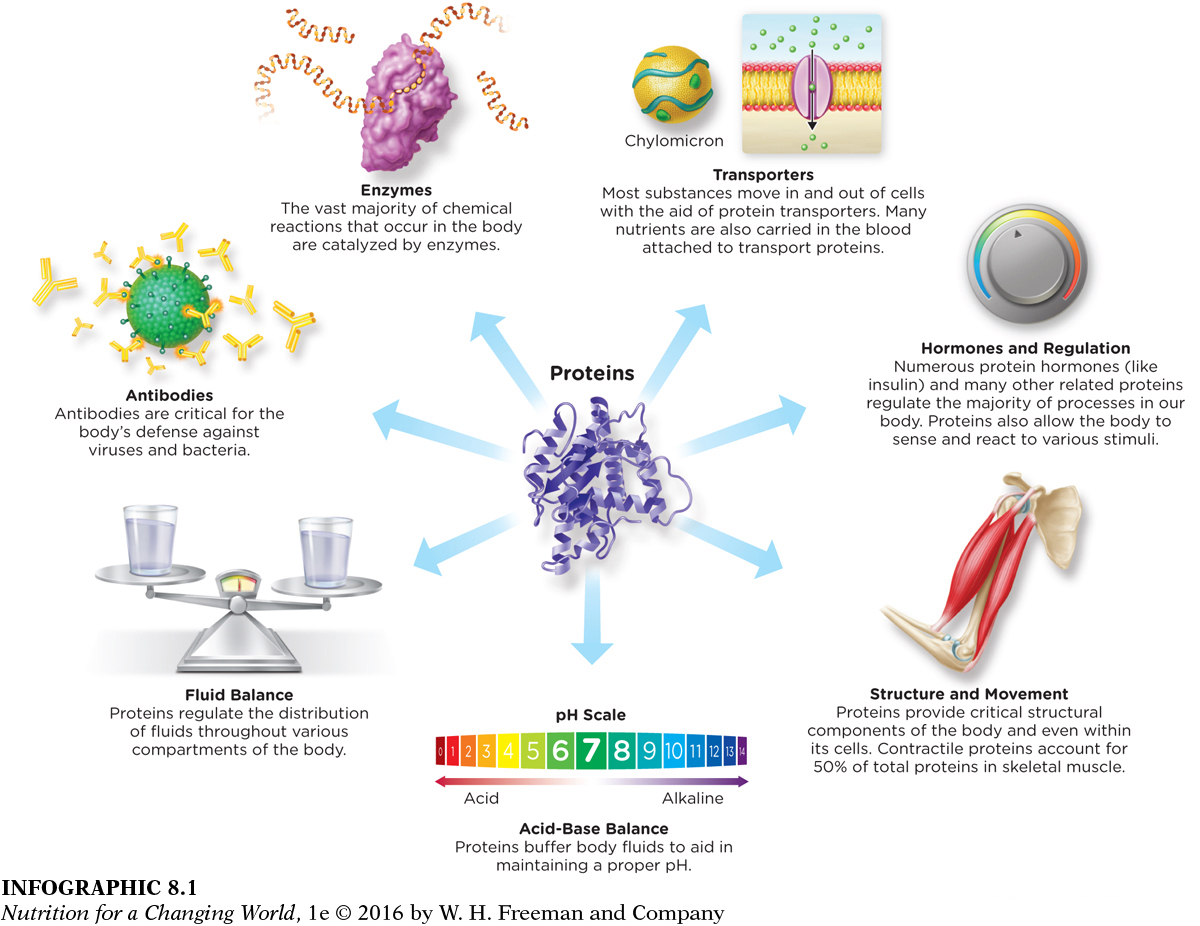
Discuss at least four functions of protein in the body (Infographic 8.1)
Distinguish between essential and nonessential amino acids (Infographic 8.2)
Describe the primary steps in protein synthesis and what determines the shape of a protein (Infographics 8.3 and 8.4)
Explain denaturation and how it may alter protein function (Infographic 8.5)
Summarize protein digestion and absorption (Infographic 8.6)
Identify the Recommended Dietary Allowances and Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Ranges for protein for adults (page 164)
Explain protein turnover and how amino acids may be used for energy (Infographics 8.7 and 8.8)
Describe protein deficiency diseases and identify regions in the world where this condition is prevalent (Infographic 8.12)
Sometimes it’s nice to start the day with a fried-
This was the regular breakfast of Michael Phelps—
Without protein, we wouldn’t be able to breathe, contract our muscles, or complete numerous basic functions. It carries out the biological instructions written in our genes. Given protein’s vital importance, it’s crucial that people get enough in their diet—
This seems particularly true for competitive athletes, like Michael Phelps. The amount of protein he ate from eggs alone, just during breakfast, nearly matches what most 150-

Many athletes who don’t have the time and Olympic staff to help them plan appropriate diets choose to boost their protein intake by mixing powders, guzzling shakes, and noshing on high-
But some experts disagree over whether that extra protein is serving any useful purpose in the body. If not, athletes—
■ ■ ■
Whether you’re an athlete, or maintain a lightly active lifestyle, adequate protein is critically important to your body for many reasons. Proteins are responsible for the majority of dynamic and adaptive processes that keep us alive and functioning. Much of the structural material in the body is provided by protein; its constituents are found in muscle, bone, hair, skin, and fingernails. They also carry out critical functions, such as facilitating chemical reactions through enzymes, regulating most body and cellular functions by hormones, maintaining fluid balance, fighting off bacteria, and blood clotting. (INFOGRAPHIC 8.1)
Question 8.1
 What do proteins do in the plasma membrane of the cell?
What do proteins do in the plasma membrane of the cell?
Protein transporters in the plasma membrane of the cell help move substances in and out of the cell.