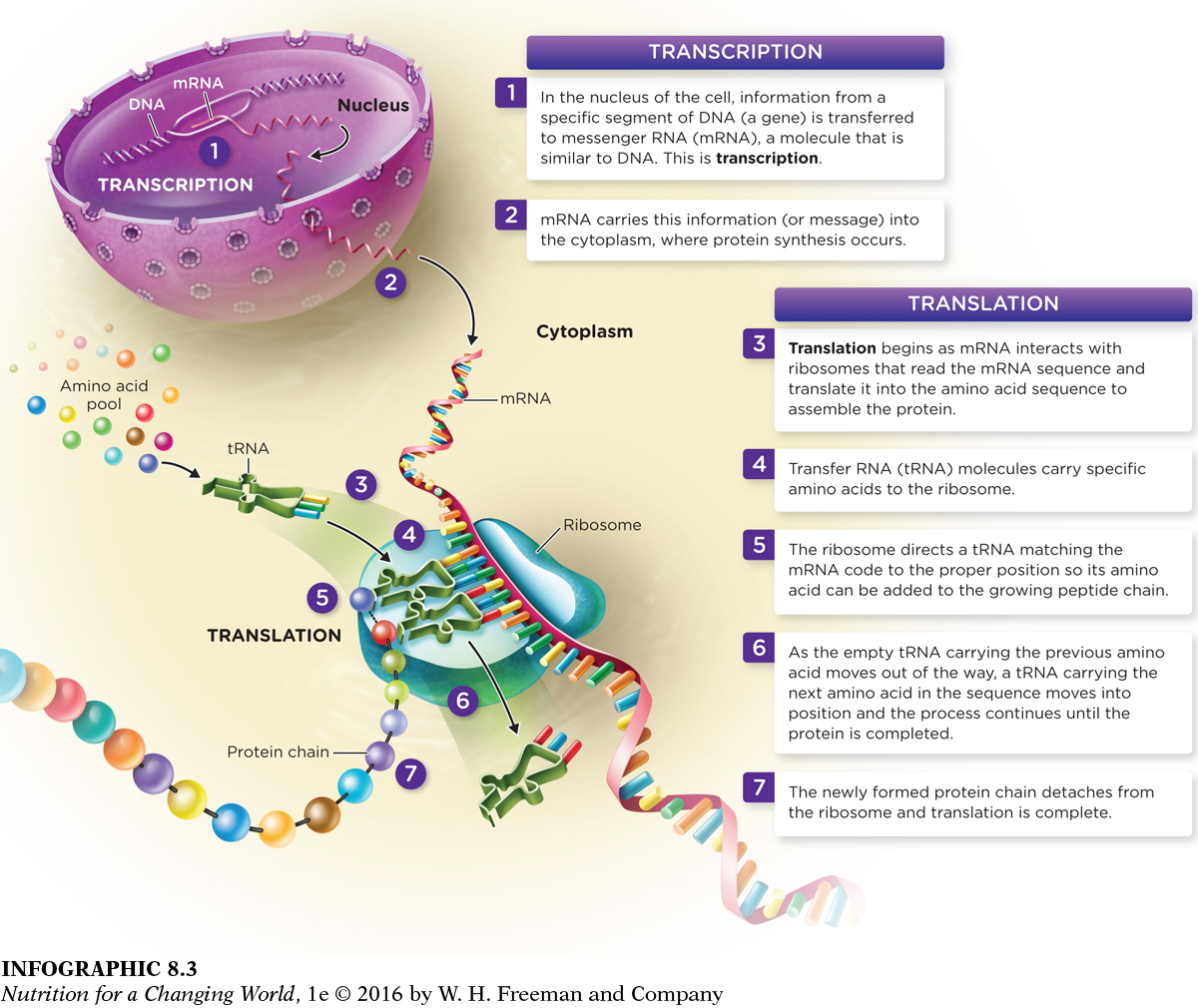
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS the process of building peptide chains and proteins from amino acids using information provided by genes in a two-
TRANSCRIPTION process by which information encoded in genes (DNA) is used to make messenger RNA
DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID (DNA) nucleic acid that stores the body’s genetic information; made of a double strand of nucleotide subunits
MESSENGER RIBONUCLEIC ACID (mRNA) the type of RNA that carries the genetic code for a specific protein from the nucleus to the cytoplasm where proteins are made
TRANSLATION process by which mRNA is decoded by ribosomes to synthesize proteins in the correct amino acid sequence
When we eat protein in foods, the body breaks them down into amino acids and then uses the amino acids to produce the particular protein needed. The nearly 22,000 proteins produced in the human body are generated through a two-
Question 8.3
 What information does mRNA provide during protein translation?
What information does mRNA provide during protein translation?
Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the instructions for building a protein—
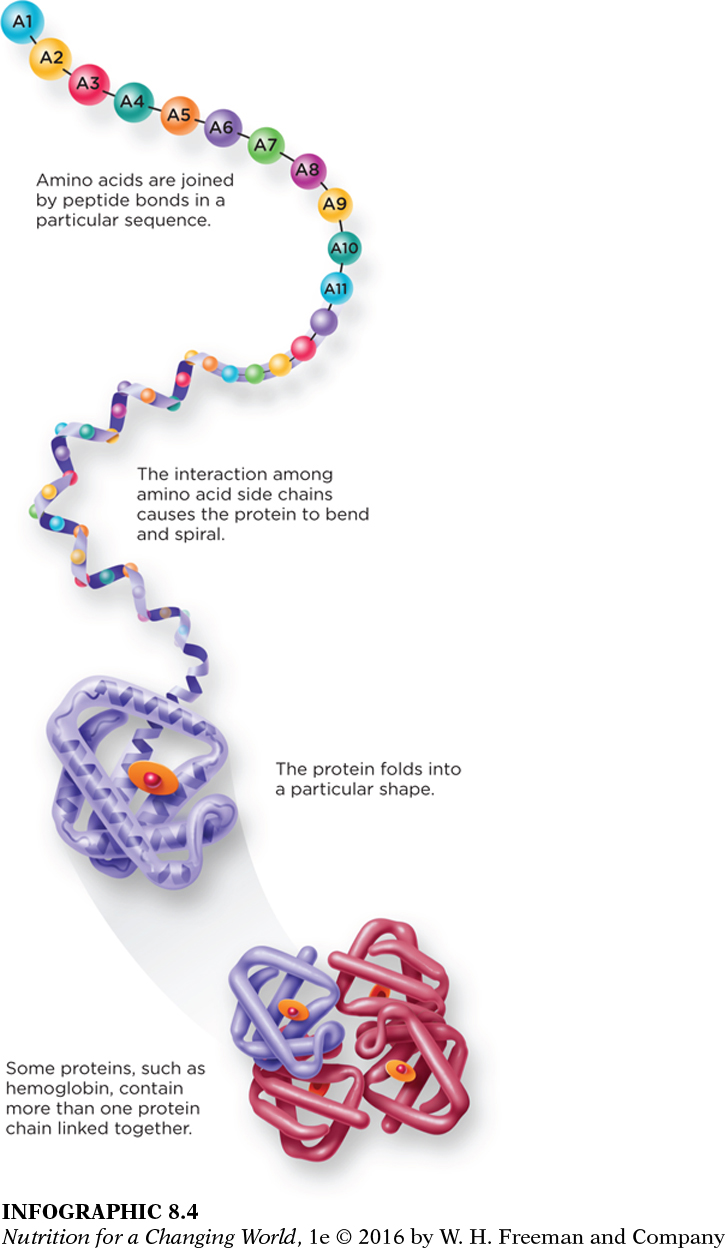
Once the synthesis of the protein is completed, it has not necessarily taken its final form. The unique nature of each amino acid in the sequence prevents the protein from remaining in a straight line. Interactions between these amino acids in the sequence cause the protein to fold into a three-
Question 8.4
 What provides the information necessary to specify the three-
What provides the information necessary to specify the three-
The sequence of the amino acids determines the three-