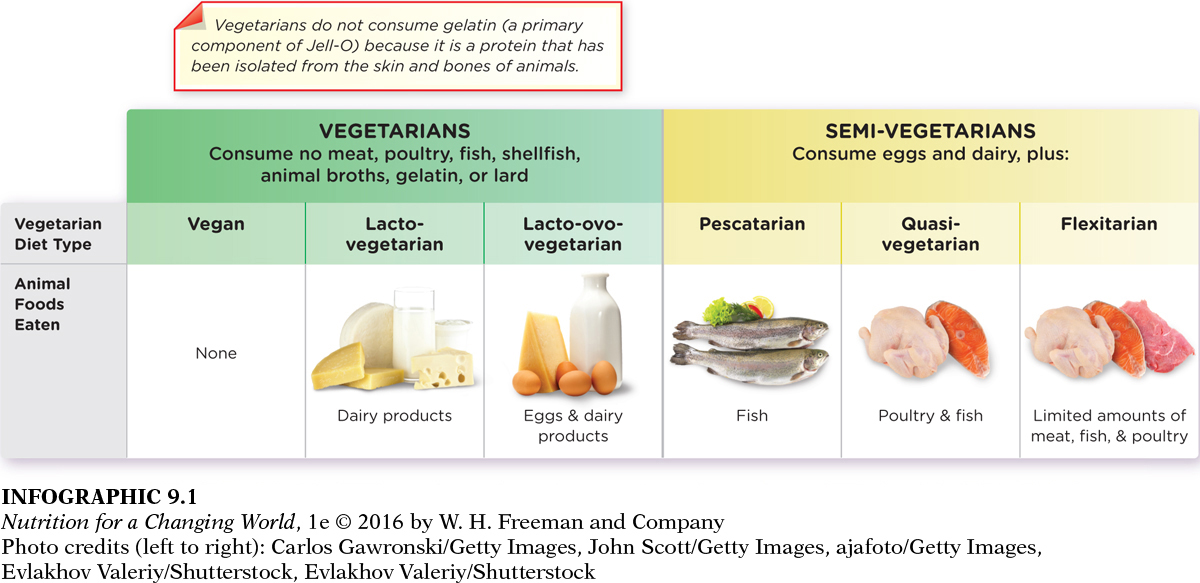
VEGETARIAN AND SEMI-VEGETARIAN DIETS
VEGETARIAN a diet consisting of plant-
LACTO-
VEGAN a vegetarian diet that eliminates all foods of animal origin
PESCATARIAN a semi-
All true vegetarian diets completely eliminate meat, poultry, fish, and shellfish. The lacto-
Question 9.1
 What do you think may be the most common difference in the reasons given for why people chose to be vegetarians versus semi-
What do you think may be the most common difference in the reasons given for why people chose to be vegetarians versus semi-
For some people, consuming animals may be against their moral or religious beliefs. These people will choose to be vegetarian over being semi-
Not only can vegetarians meet the recommended intakes for various nutrients with a bit of dietary planning, but they can also benefit from a reduced incidence of chronic disease and lower mortality rates compared with people eating a typical Western diet of high meat intake, and refined grains. However, the decision to “go vegetarian” does not necessarily guarantee better health. Some vegetarians eat primarily grain-
