CHAPTER 1 Review Exercises
Question 1.108
1.108 Jobs for business majors.
busjobs
What types of jobs are available for students who graduate with a business degree? The website careerbuilder.com lists job opportunities classified in a variety of ways. A recent posting had 25,120 jobs. The following table gives types of jobs and the numbers of postings listed under the classification “business administration” on a recent day.31
| Type | Number |
|---|---|
| Management | 10916 |
| Sales | 5981 |
| Information technology | 4605 |
| Customer service | 4116 |
| Marketing | 3821 |
| Finance | 2339 |
| Health care | 2231 |
| Accounting | 2175 |
| Human resources | 1685 |
Describe these data using the methods you learned in this chapter, and write a short summary about jobs that are available for those who have a business degree. Include comments on the limitations that should be kept in mind when interpreting this particular set of data.
Question 1.109
1.109 Flopping in the 2014 World Cup.
flops
Soccer players are often accused of spending an excessive amount of time dramatically falling to the ground followed by other activities, suggesting that a possible injury is very serious. It has been suggested that these tactics are often designed to influence the call of a referee or to take extra time off the clock. Recordings of the first 32 games of the 2014 World Cup were analyzed, and there were 302 times when the referee interrupted the match because of a possible injury. The number of injuries and the total time, in minutes, spent flopping for each of the 32 teams who participated in these matches were recorded.32 Here are the data:
| Country | Injuries | Time | Country | Injuries | Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brazil | 17 | 3.30 | Uruguay | 9 | 4.12 |
| Chile | 16 | 6.97 | Greece | 9 | 2.65 |
| Honduras | 15 | 7.67 | Cameroon | 8 | 3.15 |
| Nigeria | 15 | 6.42 | Germany | 8 | 1.97 |
| Mexico | 15 | 3.97 | Spain | 8 | 1.82 |
| Costa Rica | 13 | 3.80 | Belgium | 7 | 3.38 |
| USA | 12 | 6.40 | Japan | 7 | 2.08 |
| Ecuador | 12 | 4.55 | Italy | 7 | 1.60 |
| France | 10 | 7.32 | Switzerland | 7 | 1.35 |
| South Korea | 10 | 4.52 | England | 7 | 3.13 |
| Algeria | 10 | 4.05 | Argentina | 6 | 2.80 |
| Iran | 9 | 5.43 | Ghana | 6 | 1.85 |
| Russia | 9 | 5.27 | Australia | 6 | 1.83 |
| Ivory Coast | 9 | 4.63 | Portugal | 4 | 1.82 |
| Croatia | 9 | 4.32 | Netherlands | 4 | 1.65 |
| Colombia | 9 | 4.32 | Bosnia and Herzegovina | 2 | 0.40 |
Describe these data using the methods you learned in this chapter, and write a short summary about flopping in the 2014 World Cup based on your analysis.
Question 1.110
1.110 Another look at T-bill rates.
tbill
Refer to Example 1.12 with the histogram in Figure 1.6 (page 13), Example 1.20 with the time plot in Figure 1.12 (page 20), and Example 1.41 with the normal quantile plot in Figure 1.29 (page 53). These examples tells us something about the distribution T-bill rates and how they vary over time. For this exercise, we will focus on very small rates.
- How do the very small rates appear in each of these plots?
- Make a histogram that improves upon Figure 1.6 in terms of focusing on these small rates.
Question 1.111
1.111 Another look at marketing products for seniors in Canada.
canadap
In Exercise 1.32 (page 23), you analyzed data on the percent of the population over 65 in the 13 Canadian provinces and territories. Those with relatively large percents might be good prospects for marketing products for seniors. In addition, you might want to examine the change in this population over time and then focus your marketing on provinces and territories where this segment of the population is increasing.
- For 2006 and for 2011, describe the total population, the population over 65, and the percent of the population over 65 for each of the 13 Canadian provinces and territories. (Note that you will need to compute some of these quantities from the information given in the data set.)
- Write a brief marketing proposal for targeting seniors based on your analysis.
1.111
(a) Population values have not changed that much from 2006 to 2011. Ontario and Quebec have the largest populations, followed by Alberta and British Columbia. For Population over 65, most regions have similar percentages of over 65 except the three territories that are most northern; similar to overall population, these numbers haven—t changed much between 2006 and 2011. For percent of population over 65, four areas dominate, namely, Ontario, Quebec, British Columbia, and Alberta. Again, the numbers have not changed drastically between 2006 and 2011. (b) Most marketing techniques for targeting seniors should mention the four areas with the most population over 65: Ontario, Quebec, British Columbia, and Alberta.
Question 1.112
1.112 Best brands variables.
brands
Refer to Exercises 1.53 and 1.54 (page 36). The data set BRANDS contains values for seven variables: (1) rank, a number between 1 and 100 with 1 being the best brand, etc.; (2) company name; (3) value of the brand, in millions of dollars; (4) change, difference between last year’s rank and current rank; (5) revenue, in US$ billions; (6) company advertising, in US$ millions; and (7) industry.
- Identify each of these variables as categorical or quantitative.
- Is there a label variable in the data set? If yes, identify it.
- What are the cases? How many are there?
Question 1.113
1.113 Best brands industry.
brands
Refer to the previous exercise.
Describe the distribution of the variable industry using the methods you have learned in this chapter.
1.113
The most popular industry among the top 100 brands is Technology, followed by Financial Services, Consumer Packaged Goods, Automotive, and Luxury.
Question 1.114
1.114 Best brands revenue.
brands
Refer to the Exercise 1.112. Describe the distribution of the variable revenue using the methods you have learned in this chapter. Your summary should include information about this characteristic of these data.
Question 1.115
1.115 Beer variables.
beer
Refer to Exercises 1.56 through 1.58 (page 36). The data set BEER contains values for five variables: (1) brand; (2) brewery; (3) percent alcohol; (4) calories per 12 ounces; and (5) carbohydrates in grams.
- Identify each of these variables as categorical or quantitative.
- Is there a label variable in the data set? If yes, identify it.
- What are the cases? How many are there?
1.115
(a) Brand—categorical, brewery—categorical, percent alcohol—quantitative, calories per 12 ounces—quantitative, carbohydrates in grams— quantitative. (b) Brand is the label. (c) A case is a domestic brand of beer; there are 175 cases.
Question 1.116
1.116 Beer carbohydrates.
beer
Refer to the previous exercise.
Describe the distribution of the variable carbohydrates using the methods you have learned in this chapter. Note that some cases have missing values for this variable. Your summary should include information about this characteristic of these data.
Question 1.117
1.117 Beer breweries.
beer
Refer to Exercise 1.115.
Describe the distribution of the variable brewery using the methods you have learned in this chapter.
1.117
Many of the brands of beer come from the Miller-Coors brewery, followed by Flying Dog Brewery, Anheuser Busch, Sierra Nevada, and Budweiser.
Question 1.118
1.118 Companies of the world.
inccom
The Word Bank collects large amounts of data related to business issues from different countries. One set of data records the number of companies that are incorporated in each country and that are listed on the country’s stock exchange at the end of the year.33
Examine the numbers of companies for 2012 using the methods that you learned in this chapter.
Question 1.119
1.119 Companies of the world.
inccom
Refer to the previous exercise. Examine the data for 2002, and compare your results with what you found in the previous exercise. Note that some cases have missing values for this variable. Your summary should include information about this characteristic of these data.
1.119
ˉX=470.9. s=1057. M=99. Q1=40. Q3=327. For 2002, the distribution is also strongly right skewed and has similar numerical summaries. The leading countries in 2002 are United States, India, Romania, Canada, Japan, and Spain. Romania did not appear in the top countries in incorporated companies for 2012. There are also 8 countries that have missing values. These missing values could change our summary somewhat if they have large or small amounts of incorporated companies.
Question 1.120
1.120 What colors sell?
vcolor
Customers’ preference for vehicle colors vary with time and place. Here are data on the most popular colors in 2012 for North America.34
| Color | (Percent) |
|---|---|
| White | 24 |
| Black | 19 |
| Silver | 16 |
| Gray | 15 |
| Red | 10 |
| Blue | 7 |
| Brown | 5 |
| Other | 4 |
Use the methods you learned in this chapter to describe these vehicle color preferences. How would you use this information for marketing vehicles in North America?
Question 1.121
1.121 Identify the histograms.
A survey of a large college class asked the following questions:
- Are you female or male? (In the data, male = 0, female = 1.)
- Are you right-handed or left-handed? (In the data, right = 0, left = 1.)
- What is your height in inches?
- How many minutes do you study on a typical week night?
Figure 1.35 shows histograms of the student responses, in scrambled order and without scale markings. Which histogram goes with each variable? Explain your reasoning.
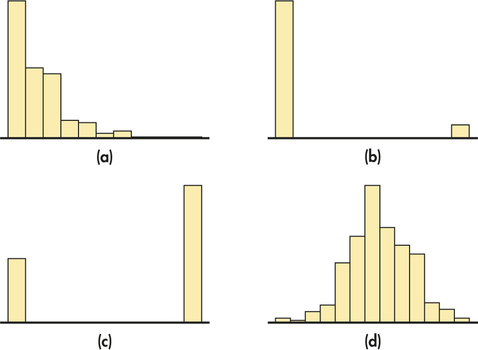
1.121
1-c—currently there are more females in college than males. 2-b—there should be more righthanded students than left-handed. 3-d—height should be Normally distributed. 4-a—should be right-skewed, because some students will study much more than others.
Question 1.122
1.122 Grading managers.
Some companies “grade on a bell curve” to compare the performance of their managers. This forces the use of some low performance ratings so that not all managers are graded “above average.” A company decides to give A’s to the managers and professional workers who score in the top 15% on their performance reviews, C’s to those who score in the bottom 15%, and B’s to the rest. Suppose that a company’s performance scores are Normally distributed. This year, managers with scores less than 25 received C’s, and those with scores above 475 received A’s. What are the mean and standard deviation of the scores?
Question 1.123
1.123 What influences buying?
Product preference depends in part on the age, income, and gender of the consumer. A market researcher selects a large sample of potential car buyers. For each consumer, she records gender, age, household income, and automobile preference. Which of these variables are categorical and which are quantitative?
1.123
Gender and automobile preference are categorical. Age and household income are quantitative.
Question 1.124
1.124 Simulated observations.
Most statistical software packages have routines for simulating values having specified distributions. Use your statistical software to generate 30 observations from the N(25, 4) distribution. Compute the mean and standard deviation ˉx and s of the 30 values you obtain. How close are ˉx and s to the μ and σ of the distribution from which the observations were drawn?
Repeat 24 more times the process of generating 25 observations from the N(25, 4) distribution and recording ˉx and s. Make a stemplot of the 25 values of ˉx and another stemplot of the 25 values of s. Make Normal quantile plots of both sets of data. Briefly describe each of these distributions. Are they symmetric or skewed? Are they roughly Normal? Where are their centers? (The distributions of measures like ˉx and s when repeated sets of observations are made from the same theoretical distribution will be very important in later chapters.)