Chapter 1. Neural Messages
Introduction
Click the Next button to start this activity
Neurons
Neurons (also called nerve cells) are the basic building blocks of the nervous system.
But isolated from one another, neurons would not enable you to see, think, react to the world, or act upon it. When psychologists study behavior or mental processes, they are really looking at the combined responses of a vast web of billions of neurons that are in constant communication.
This activity examines the way a neuron passes information (neural impulses) within its own cell and the way it relays messages to other neurons.
We'll also look at how a neuron integrates incoming signals from other neurons and how the result affects the message that neuron sends.
Types of Neurons
Neurons can be classified into three broad groups, according to the way in which they transmit messages within the body.
Sensory neurons carry information from the body's tissues and organs to the central nervous system.
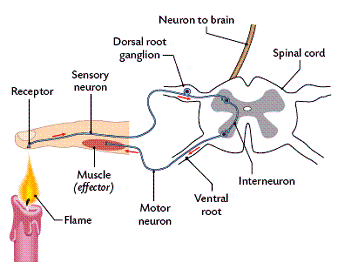
Interneurons in the brain and spinal cord link the sensory and motor neurons. They do the additional processing of the information needed to make sense of the events occurring within your body and outside in the environment.
Motor neurons carry instructions from the central nervous system to the body's organs and tissues.
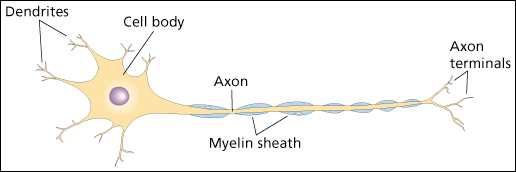
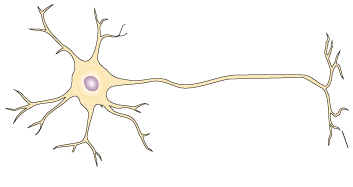
Parts of a Neuron
Neurons have three main parts. Move the cursor over the various areas of this motor neuron to see the name that we use for each of the parts.
Click on parts of the image for more information
{"title":"Cell Body","description":"The cell body contains the nucleus that controls the functioning of the entire neuron.”","type":"correct","color":"#99CCFF","code":"[{\"shape\":\"circle\",\"coords\":\"120,95,28\"}]"} {"title":"Dendrites","description":"The dendrites are small branching fibers that receive signals from other cells and pass this information to the cell body.","type":"correct","color":"#993300","code":"[{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"149,73,156,55,146,47,141,59,144,67\"},{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"120,54,119,43,122,41,135,45,135,54,125,56\"},{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"88,43,73,26,70,32,79,41,64,38,68,50,75,51,89,48\"},{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"55,74,44,64,43,53,39,54,37,62,29,56,35,65,26,68,36,67,47,75,37,80,42,80,38,86,54,73\"},{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"75,121,63,126,50,124,60,131,50,141,53,144,59,139,62,146,65,146,62,139,77,121\"},{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"106,127,92,139,92,141,101,137\"},{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"118,148,113,165,115,165,119,158,125,161,121,151,137,155,136,149,122,145\"}]"} {"title":"Choice label","description":"The axon is a single large fiber that carries signals from the neuron cell body to other cells. The end of the axon branches out into several axon terminals in order to make contact with multiple cells. Some axons are covered with a myelin sheath that speeds the transmission of the neural signal.","type":"correct","color":"#333300","code":"[{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"185,108,180,110,318,112,417,106,413,100,326,106,247,109,247,109\"},{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"379,166,418,149\"}]"}Review the Parts of the Neuron
Which part is highlighted?
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
Which part is highlighted?
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |

Which part is highlighted?
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |

Which part is highlighted?
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |

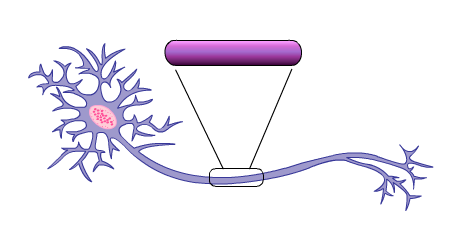
Axonal Conduction
Axons can range in length from a fraction of an inch to several feet, but they all have the same function: to carry messages to other cells.
How does the neuron send its signal down the axon?
Axonal conduction is a complicated electrical-chemical process. In simplest terms, it involves an electrical impulse that travels down the axon like a wave, as is illustrated here.

Every time an impulse travels down the axon, we say that the axon has "fired," or "responded." This impulse is also called the action potential.
A Closer Look
Let's enlarge a portion of the axon to get a closer view of this process.
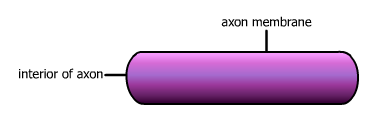
Axon Chemistry
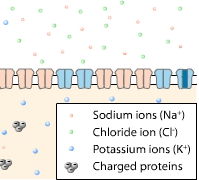
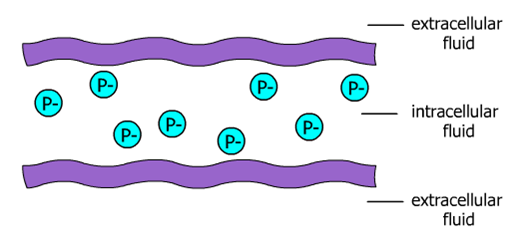
Some of the molecules in and around the axon carry an electrical charge, either positive or negative. The fluid inside the axon contains protein molecules with a negative charge. These particular protein molecules are found only in the intracellular fluid.
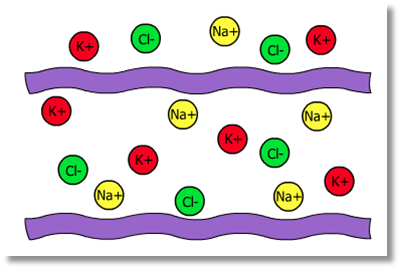
Other electrically charged ions are present in the fluid both inside and outside the axon. Sodium ions and potassium ions have a positive charge, while chloride ions have a negative charge.
Resting Potential = Polarized
New section content
Check Your Understanding: Quiz Page 2
New section content
Check Your Understanding: Quiz Page 3
1.
Match each term with its definition. Click on an item in the left column, then click the item in the right column that matches it.
ions dendrites inhibitory synapses motor neurons neurotransmitters action potential | neurons that carry instructions from the central nervous system to the body's organs and tissues synaptic connections which, when stimulated, decrease the likelihood that the receiving neuron will fire a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon positively-charged or negatively-charged particles. molecules released by the axon terminal into the synapse parts of a neuron specialized to receive messages from other neuron |
| Correct Matches: | |
1.1 Activity Completed!
Activity results are being submitted...
REFERENCES:
[Center for Disease Control] CDC Grand Rounds: Childhood Obesity in the United States. URL: http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm6002a2.htm?s_cid=mm6002a2_w Retrieved 3/31/11
Collins, A. & Peebles, R. (2011). Pediatric obesity: A pediatrician’s viewpoint. In Debasis Bagchi (Editor) Global Perspectives on Childhood Obesity: Current Status, Consequences and Prevention. Pages 257-264.