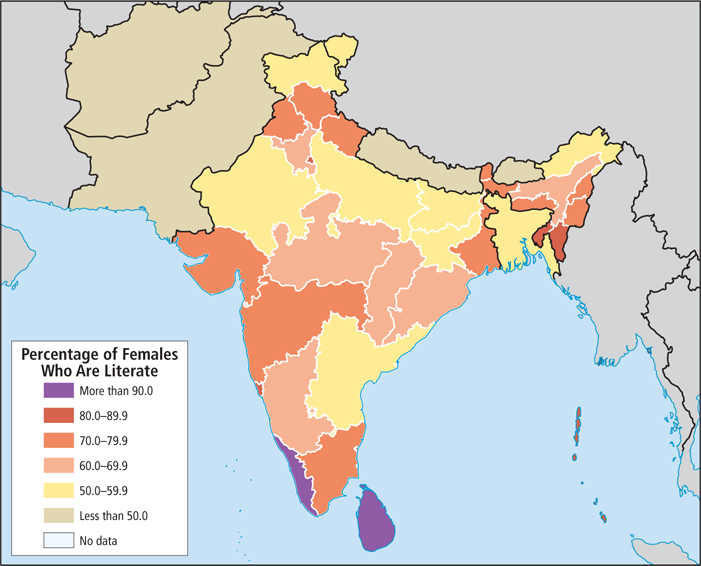
Figure 8.25: Female literacy in South Asia. Female literacy lags behind male literacy in all countries in South Asia, and is below 50 percent in four countries. Female literacy is crucial to improving the lives not only of women, but also of children: Women who can read often seize opportunities to earn an income and nearly always use this income to help their children. In India, overall literacy has risen in the past decade, and in 2011, female literacy there reached 65 percent, up from 54.5 percent in 2005.
[Sources consulted: “District Wise Female Literacy Rate of India,” Maps of India, at http://www.mapsofindia.com/census2001/femaleliteracydistrictwise.htm; United Nations Human Development Report 2009 (New York: United Nations Development Programme), Table J, “Gender- y- e- d-