Subjects
For a list of pronoun types, see “The Parts of Speech.”
The subject of a sentence is the person, place, or thing that the sentence is about. The subject of the sentence can be a noun (a word that names the person, place, or thing) or a pronoun (a word that replaces the noun, such as I, you, she, or they).
To find the subject, ask yourself, “Who or what is the sentence about?”
| PERSON AS SUBJECT | Vivian works for the police department. [Who is the sentence about? Vivian] |
| THING AS SUBJECT | The tickets cost $65 apiece. [What is the sentence about? The tickets] |
A compound subject consists of two (or more) subjects joined by and, or, or nor.
| TWO SUBJECTS | Nick and Chelsea have a new baby girl. |
| SEVERAL SUBJECTS | The jacket, pants, and sweater match perfectly. |
| SEVERAL SUBJECTS | Kim, Juan, or Melba will bring dessert. |
A prepositional phrase is a word group that begins with a preposition and ends with a noun or pronoun. A preposition is a word that connects a noun, pronoun, or verb with some other information about it.
The subject of a sentence is never in a prepositional phrase.
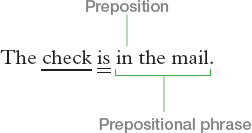
The subject of the sentence is check. The subject cannot be the word mail, which is in the prepositional phrase in the mail.

Although the word friends may seem to be the subject of the sentence, it is not. One is the subject. The word friends is not the subject because it is in the prepositional phrase of my best friends.
When you are looking for the subject of a sentence in your writing, it may help to cross out any prepositional phrases, as in the following sentences.
The rules about smoking are posted everywhere.
The sound of lightning striking a tree is like gunfire.
Many of the students work part-
Common Prepositions
| about | beneath | like | to |
| above | beside | near | toward |
| across | between | next to | under |
| after | by | of | until |
| against | down | off | up |
| along | during | on | upon |
| among | except | out | with |
| around | for | outside | within |
| at | from | over | without |
| before | in | past | |
| behind | inside | since | |
| below | into | through |